Abstract
Purpose
Increasing the migration of arsenic in contaminated soil is an important topic in the field of soil remediation. The purpose of this study was to investigate the enhancement of arsenic migration in soil by low molecular weight organic acids.
Materials and methods
Four different low molecular weight organic acids were used to wash the soil to increase arsenic mobility under different experimental conditions, including the type of LMWOA, reaction time, and pH. The arsenic fractions in the soil were further quantitated and analyzed.
Results and discussion
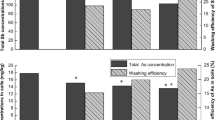
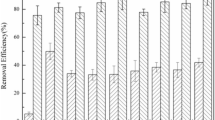
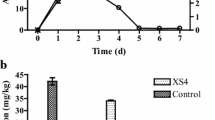
In the batch experiment, the LMWOA enhancement of arsenic migration was in the order of 3-mercaptopropionic acid > aspartic acid > succinic acid > propionic acid. At pH 11, 247.29 mg/kg arsenic was leached from the soil with 3-mercaptopropionic acid over 48 h. This was confirmed in column experiments where 3-mercaptopropionic acid was also the most effective, releasing 21.02% of the arsenic after 75 h. This suggests that the sulfhydryl group of 3-mercaptopropionic acid was superior to other groups in accelerating arsenic migration.
Conclusions
These results enhance our understanding of the interaction between arsenic migration and organic acid functional groups and have applications for the development of soil remediation technology.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M, Sarzanini C, Mentasti E (2003) Adsorption of heavy metals on Na-montmorillonite. Effect of pH and organic substances. Water Res 37:1619–1627
Bhattacharya P, Welch AH, Stollenwerk KG, McLaughlin MJ, Bundschuh J, Panaullah G (2007) Arsenic in the environment: biology and chemistry. Sci Total Environ 379:109–120
Busto Y, Cabrera X, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2011) Potential of thermal treatment for decontamination of mercury containing wastes from chlor-alkali industry. J Hazard Mater 186:114–118
Catrouillet C, Davranche M, Dia A, Bouhnik-Le Coz M, Pedrot M, Marsac R, Gruau G (2015) Thiol groups controls on arsenite binding by organic matter: new experimental and modeling evidence. J Colloid Interface Sci 460:310–320
Debela F, Arocena JM, Thring RW, Whitcombe T (2013) Organic acids inhibit the formation of pyromorphite and Zn-phosphate in phosphorous amended Pb- and Zn-contaminated soil. J Environ Manage 116:156–162
Debiec-Andrzejewska K, Krucon T, Piatkowska K, Drewniak L (2020) Enhancing the plants growth and arsenic uptake from soil using arsenite-oxidizing bacteria. Environ Pollut 264:114692
Dixit S, Hering JG (2003) Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility. Environ Sci Technol 37:4182–4189
do Nascimento CWA, Amarasiriwardena D, Xing BS, (2006) Comparison of natural organic acids and synthetic chelates at enhancing phytoextraction of metals from a multi-metal contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 140:114–123
Douay F, Roussel H, Pruvot C, Loriette A, Fourrier H (2008) Assessment of a remediation technique using the replacement of contaminated soils in kitchen gardens nearby a former lead smelter in Northern France. Sci Total Environ 401:29–38
Eze VC, Harvey AP (2018) Extractive recovery and valorisation of arsenic from contaminated soil through phytoremediation using Pteris cretica. Chemosphere 208:484–492
Gao YZ, He JZ, Ling WT, Hu HQ, Liu F (2003) Effects of organic acids on copper and cadmium desorption from contaminated soils. Environ Int 29:613–618
Hoffmann M, Mikutta C, Kretzschmar R (2012) Bisulfide reaction with natural organic matter enhances arsenite sorption: insights from X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 46:11788–11797
Jones DL (1998) Organic acids in the rhizosphere-a critical review. Plant Soil 205:25–44
Kertulis-Tartar GM, Ma LQ, Tu C, Chirenje T (2006) Phytoremediation of an arsenic-contaminated site using Pteris vitrata L.: a two-year study. Int J Phytoremediation 8:311–322
Krishnamurti GSR, Cieslinski G, Huang PM, VanRees KCJ (1997) Kinetics of cadmium release from soils as influenced by organic acids: implication in cadmium availability. J Environ Qual 26:271–277
Li J, Kosugi T, Riya S, Hashimoto Y, Hou H, Terada A, Hosomi M (2016) Potential for leaching of arsenic from excavated rock after different drying treatments. Chemosphere 154:276–282
Liang C, Peng X (2017) Mobilization of arsenic from contaminated sediment by anionic and nonionic surfactants. J Environ Sci 56:281–289
Maguffin SC, Abu-Ali L, Tappero RV, Pena J, Rohila JS, McClung AM, Reid MC (2020) Influence of manganese abundances on iron and arsenic solubility in rice paddy soils. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 276:50–69
Mandal J, Golui D, Datta SP (2019) Assessing equilibria of organo-arsenic complexes and predicting uptake of arsenic by wheat grain from organic matter amended soils. Chemosphere 234:419–426
Mei K, Liu J, Shi R, Guo X, Lu H, Yan C (2020) The migrated behavior and bioavailability of arsenic in mangrove sediments affected by pH and organic acids. Mar Pollut Bull 159:111480
Onireti OO, Lin C, Qin J (2017) Combined effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids on mobilization of arsenic and lead from multi-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 170:161–168
Qiao J, Li X, Li F, Liu T, Young LY, Huang W, Sun K, Tong H, Hu M (2019) Humic substances facilitate arsenic reduction and release in flooded paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 53:5034–5042
Qin F, Shan XQ, Wei B (2004) Effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids and residence time on desorption of Cu, Cd, and Pb from soils. Chemosphere 57:253–263
Renella G, Landi L, Nannipieni P (2004) Degradation of low molecular weight organic acids complexed with heavy metals in soil. Geoderma 122:311–315
Salgado P, Visnevschi-Necrasov T, Kiene RP, Azevedo I, Rocha ACS, Almeida CMR, Magalhaes C (2015) Determination of 3-mercaptopropionic acid by HPLC: a sensitive method for environmental applications. J Chromatogr B: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 992:103–108
Strobel BW (2001) Influence of vegetation on low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids in soil solution - a review. Geoderma 99:169–198
Tessema DA, Kosmus W (2001) Influence of humic and low molecular weight polycarboxylic acids on the release of arsenic from soils. J Trace Microprobe Tech 19:267–278
Tripathi P, Khare P, Barnawal D, Shanker K, Srivastava PK, Tripathi RD, Kalra A (2020) Bioremediation of arsenic by soil methylating fungi: role of Humicola sp. strain 2WS1 in amelioration of arsenic phytotoxicity in Bacopa monnieri L. Sci Total Environ 716:136758
Vitkova M, Komarek M, Tejnecky V, Sillerova H (2015) Interactions of nano-oxides with low-molecular-weight organic acids in a contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 293:7–14
Wang S, Mulligan CN (2009) Enhanced mobilization of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings by humic acid. Chemosphere 74:274–279
Wang S, Mulligan CN (2013) Effects of three low-molecular-weight organic acids (LMWOAs) and pH on the mobilization of arsenic and heavy metals (Cu, Pb, and Zn) from mine tailings. Environ Geochem Health 35:111–118
Williams PN, Price AH, Raab A, Hossain SA, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2005) Variation in arsenic speciation and concentration in paddy rice related to dietary exposure. Environ Sci Technol 39:5531–5540
Xu RK, Zhao AZ, Ji GL (2003) Effect of low-molecular-weight organic anions on surface charge of variable charge soils. J Colloid Interface Sci 264:322–326
Xu Y, Wang K, Zhou Q, Zhang L, Qian G (2020) Effects of humus on the mobility of arsenic in tailing soil and the thiol-modification of humus. Chemosphere 259: 127403
Yang C, Ho Y-N, Makita R, Inoue C, Chien M-F (2020) A multifunctional rhizobacterial strain with wide application in different ferns facilitates arsenic phytoremediation. Sci Total Environ 712:134504
Yang F, Xie S, Wei C, Liu J, Zhang H, Chen T, Zhang J (2018) Arsenic characteristics in the terrestrial environment in the vicinity of the Shimen realgar mine, China. Sci Total Environ 626:77–86
Yang X, Chen X, Guo E, Yang X (2019) Path analysis of phosphorus activation capacity as induced by low-molecular-weight organic acids in a black soil of Northeast China. J Soils Sed 19:840–847
Yu Z, Qiu W, Wang F, Lei M, Wang D, Song Z (2017) Effects of manganese oxide-modified biochar composites on arsenic speciation and accumulation in an indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivar. Chemosphere 168:341–349
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 21878183) and National Key Research and Development Project of China (2020YFC1807802).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Wan, L., Wang, K. et al. Enhanced mobilization of arsenic from tailing soil by four types of low molecular weight organic acids with different functional groups. J Soils Sediments 21, 3834–3844 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03057-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03057-z