Abstract
Purpose
Internal phosphorus (P) input has been proven to be an important cause of eutrophication. The purpose of this study is to explore the process and mechanism of P release from sediments in seasonal hypoxic reservoirs.
Material and methods
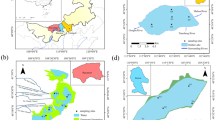
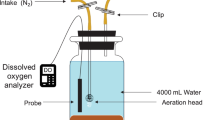
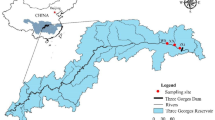
Six sediment cores were collected from Hongfeng Reservoir, one of the largest reservoirs in southwestern China. Incubation experiments were conducted using the sediment cores under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The diffusion gradients in thin films (DGT) technique was employed to determine the concentration profiles and release characteristics of labile-P and labile-Fe at the sediment–water interface. The microbial community structure in surface sediments was determined by 16S rRNA sequencing.
Results and discussion
Compared with the aerobic condition, the P release flux was ~3.75 times under anaerobic condition, which mainly came from BD-P and NaOH-P. In addition, DGT-P and DGT-Fe were significantly positively correlated (R2 > 0.66, p < 0.001). From 16S rRNA sequencing, SRB and PSB were shown to promote P release through sulfate reduction and P dissolution in sediments. Moreover, the control measures of internal P release are discussed due to the potential risk of it in deep-water reservoirs.
Conclusion
Dissolved oxygen is the key control factor of P release; thus, anaerobic conditions promoted the release of P from sediments. Fe-P reduction and dissolution are the main processes. SRB and PSB played an important role in the P cycle of sediments. It is necessary to increase oxygen in seasonal hypoxic reservoirs to reduce the risk of internal P release.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlgren J, Reitzel K, Brabandere HD, Goqow A, Rydin E (2011) Release of organic P forms from lake sediments. Water Res 45:565–572
Bai YN, Wang XN, Wu J, Lu YZ, Fu L, Zhang F, Lau TC, Zeng RJ (2019) Humic substances as electron acceptors for anaerobic oxidation of methane driven by ANME-2d. Water Res 164:114935
Carpenter SR (2005) Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems: bistability and soil phosphorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10002–10005
Chen YP, Rekha PD, Arun AB, Shen FT, Lai WA, Young CC (2006) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl Soil Ecol 34:33–41
Chen M, Li XH, He YH, Song N, Cai HY, Wang C, Li YT, Chu HY, Krumholz LR, Jiang HL (2016) Increasing sulfate concentrations result in higher sulfide production and phosphorous mobilization in a shallow eutrophic freshwater lake. Water Res 96:94–104
Chen JA, Wang JF, Guo JY, Yu J, Zeng Y, Yang HQ, Zhang RX (2018) Eco-environment of reservoirs in China: characteristics and research prospects. Prog Phys Geogr 42:185–201
Chen MS, Ding SM, Wu YX, Fan XF, Jin ZF, Tsang DCW, Wang Y, Zhang CS (2019a) Phosphorus mobilization in lake sediments: experimental evidence of strong control by iron and negligible influences of manganese redox reactions. Environ Pollut 246:472–481
Chen Q, Chen JA, Wang JF, Guo JY, Jin ZX, Yu PP, Ma ZZ (2019b) In situ , high-resolution evidence of phosphorus release from sediments controlled by the reductive dissolution of iron-bound phosphorus in a deep reservoir, southwestern China. Sci Total Environ 666:39–45
Conley DJ, Bj̈Orck S, Bonsdorff E, Carstensen J, Destouni G, Gustafsson BG, Hietanen S, Kortekaas M, Kuosa H, Markus Meier H (2009) Hypoxia-related processes in the Baltic Sea. Environ Sci Technol 43:3412–3420
Cummings DE, Caccavo F, Spring S, Rosenzweig RF (1999) Ferribacterium limneticum, gen. nov., sp. nov., an Fe(III)-reducing microorganism isolated from mining-impacted freshwater lake sediments. Arch Microbiol 171:183–188
Ding S, Han C, Wang Y, Yao L, Wang Y, Xu D, Sun Q, Williams PN, Zhang C (2015) In situ, high-resolution imaging of labile phosphorus in sediments of a large eutrophic lake. Water Res 74:100–109
Dutton CL, Subalusky AL, Hamilton SK, Rosi EJ, Post DM (2018) Organic matter loading by hippopotami causes subsidy overload resulting in downstream hypoxia and fish kills. Nat Commun 9:1951
Einsele W (1936) Über die Beziehungen des Eisenkreislaufs zum Phosphatkreislauf im eutrophen See. Arch Hydrobiol 29:664–686
El-Tarabily AK, Youssef T (2010) Enhancement of morphological, anatomical and physiological characteristics of seedlings of the mangrove Avicennia marina inoculated with a native phosphate-solubilizing isolate of Oceanobacillus picturae under greenhouse conditions. Plant Soil 332:147–162
Fisher MM, Reddy KR (2001) Phosphorus flux from wetland soils affected by long-term nutrient loading. J Environ Qual 30:261–271
Frankowski L, Bolaek J, Szostek A (2002) Phosphorus in bottom sediments of Pomeranian Bay (Southern Baltic—Poland). Estuar Coast Shelf S 54:1027–1038
Gao Y, Liang T, Tian S, Wang L, Holm PE, Hansen HCB (2016) High-resolution imaging of labile phosphorus and its relationship with iron redox state in lake sediments. Environ Pollut 219:466–474
Gibbons KJ, Bridgeman TB (2020) Effect of temperature on phosphorus flux from anoxic western Lake Erie sediments. Water Res 182:116022
Grangeasse C, Doublet P, Vincent C, Vaganay E, Riberty M, Duclos B, Cozzone AJ (1998) Functional characterization of the low-molecular-mass phosphotyrosine-protein phosphatase of Acinetobacter johnsonii. J Mol Biol 278:339–347
Gu J, Zhang W, Li Y, Niu L, Zhang H (2020) Source identification of phosphorus in the river-lake interconnected system using microbial community fingerprints. Environ Res 186:109498
Guo W, Zhao Y, Li Y, Guo J (2020) Trophic level and its historical evolution in Lake Hongfeng, Southwest China (In Chinese). Chinese J Ecol 39:3371–3378
Henry (1999) Heat budgets, thermal structure and dissolved oxygen in Brazilian reservoirs, Theoretical reservoir ecology and its Applications. International Institute of Ecology, São Paulo, pp 125–151
Hupfer M, Gächter R, Giovanoli R (1995) Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquat Sci 57:305–324
Ingall ED, Jahnke RA (1997) Influence of water-column anoxia on the elemental fractionation of carbon and phosphorus during sediment diagenesis. Mar Geol 139:219–229
Jin X, Wang S, Pang Y, Wu FC (2006) Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Pollut 139:288–295
Kang M, Peng S, Tian Y, Zhang H (2018) Effects of dissolved oxygen and nutrient loading on phosphorus fluxes at the sediment–water interface in the Hai River Estuary. China Mar Pollut Bull 130:132–139
Kannapiran E, Ramkumar VS (2011) Isolation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from the sediments of Thondi coast, Palk Strait, Southeast coast of India. Annals of Biological Research 2:157–163
Kim YH, Bae B, Choung YK (2005) Optimization of biological phosphorus removal from contaminated sediments with phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. J Biosci Bioeng 99:23–29
Kwak DH, Jeon YT, Hur YD (2018) Phosphorus fractionation and release characteristics of sediment in the Saemangeum Reservoir for seasonal change. Int J Sediment Res 3:250–261
Lee KS, Song SB, Kim KE, Kim YH, Kim SK, Kho BH, Ko DK, Choi YK, Lee YK, Kim CK (2000) Cloning and characterization of the UDP-sugar hydrolase gene (ushA) of Enterobacter aerogenes IFO 12010. Biochem Bioph Res Co 269:526–531
Lehner B, Liermann CR, Revenga C, Vörösmarty C, Fekete B, Crouzet P, Döll P, Endejan M, Frenken K, Magome J (2011) High-resolution mapping of the world's reservoirs and dams for sustainable river-flow management. Front Ecol Environ 9:494–502
Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang J, Xu W, Mou Z (2019) Characteristics of inorganic phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from the sediments of a eutrophic lake. Int J Env Res Pub He 16:2141
Li Y, Kuang S, Wang Z, Shen Q, Kang D (2020a) Characteristics and significance of nitrogen, phosphorus and oxygen transportation at the sediment-water interface in east Lake Chaohu (In Chinese). J Lake Sci 32:688–700
Li Y, Wang L, Yan Z, Chao C, Liu C (2020b) Effectiveness of dredging on internal phosphorus loading in a typical aquacultural lake. Sci Total Environ 744:140883
Li H, Song C, Yang L, Qin H, Cao X, Zhou Y (2021) Phosphorus supply pathways and mechanisms in shallow lakes with different regime. Water Res 193:116886
Lin TF, Huang HI, Shen FT, Young CC (2006) The protons of gluconic acid are the major factor responsible for the dissolution of tricalcium phosphate by Burkholderia cepacia CC-Al74[J]. Bioresour Technol 97(7):957–960
Liu YQ, Cao X, Li H, Zhou Z, Wang S, Wang Z, Song C, Zhou Y (2017) Distribution of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria in relation to fractionation and sorption behaviors of phosphorus in sediment of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ Sci Pol 24:17679–17687
Liu Z, Zhang Y, Yan P, Luo J, Wu Z (2020) Synergistic control of internal phosphorus loading from eutrophic lake sediment using MMF coupled with submerged macrophytes. Sci Total Environ 731:138697
Lovley D, Fraga J, Blunt-Harris E, Hayes L, Phillips E, Coates J (1998) Humic substances as a mediator for microbially catalyzed metal reduction. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 26:152–157
Ma WW, Zhu MX, Yang GP, Li T (2017) In situ, high-resolution DGT measurements of dissolved sulfide, iron and phosphorus in sediments of the East China Sea: insights into phosphorus mobilization and microbial iron reduction. Mar Pollut Bull 124:400–410
Maavara T, Lauerwald R, Regnier P, Van Cappellen P (2017) Global perturbation of organic carbon cycling by river damming. Nat Commun 8:15347
Maitra N, Manna SK, Samanta S, Sarkar K, Debnath D, Bandopadhyay C, Sahu SK, Sharma AP (2015) Ecological significance and phosphorus release potential of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in freshwater ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 745:69–83
Markovic S, Liang A, Watson SB, Guo J, Mugalingam S, Arhonditsis G, Morley A, Dittrich M (2019) Biogeochemical mechanisms controlling phosphorus diagenesis and internal loading in a remediated hard water eutrophic embayment. Chem Geol 514:122–137
Mcginnis DF, Lorke A, Wuest A, Stoeckli A, Little JC (2004) Interaction between a bubble plume and the near field in a stratified lake. Water Resour Res 40:187–203
Midwood AJ, Boutton TW (1998) Soil carbonate decomposition by acid has little effect on δ13C of organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1301–1307
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:678–681
Mwr (2013) Bulletin of first national census for water. China WaterPower Press
Nilsson C, Reidy CA, Dynesius M, Revenga C (2005) Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 308:405–408
Nóbrega GN, Otero XL, Macías F, Ferreira TO (2014) Phosphorus geochemistry in a Brazilian semiarid mangrove soil affected by shrimp farm effluents. Environ Monit Assess 186:5749–5762
Och LM, Müller B, Voegelin A, Ulrich A, Göttlicher J, Steiniger R (2012) New insights into the formation and burial of Fe/Mn accumulations in Lake Baikal sediments. Chem Geol:330–331
Oldenborg KA, Steinman AD (2019) Impact of sediment dredging on sediment phosphorus flux in a restored riparian wetland. Sci Total Environ 650:1969–1979
Panda B, Rahman H, Panda J (2016) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from the acidic soils of Eastern Himalayan region and their antagonistic effect on fungal pathogens. Rhizosphere 2:62–71
Paul D, Sinha NS (2013) Bacteria showing phosphate solubilizing efficiency in river sediment. Electron J Biosciences 1:1–5
Paytan A, Roberts K, Watson S, Peek S, Chuang P-C, Defforey D, Kendall C (2017) Internal loading of phosphate in Lake Erie Central Basin. Sci Total Environ 579:1356–1365
Pomeroy LR, Smith EE, Grant CM (1965) The exchange of phosphate between estuarine water and sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 10:167–172
Qian Y, Shi J, Chen Y, Lou L, Cui X, Cao R, Li P, Tang J (2010) Characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in sediments from a shallow eutrophic lake and a wetland: isolation, molecular identification and phosphorus release ability determination. Molecules 15:8518–8533
Qu JH, Li HF, Chen N, Yuan HL (2013) Biogeochemical function of phosphorus-solubilising bacteria on cycling of phosphorus at the water-sediment interface under laboratorial simulated conditions. Int J Environ Pollut 52:104–116
Roden EE, Zachara JM (1996) Microbial reduction of crystalline iron(III) oxides: influence of oxide surface area and potential for cell growth. Environ Sci Technol 30:1618–1628
Ruttenberg KC (2019) Phosphorus cycle ☆. Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences (Third Edition) 1:447–460
Rydin E (2000) Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Res 34:2037–2042
Schindler DW, Carpenter SR, Chapra SC, Hecky RE, Orihel DM (2016) Reducing phosphorus to curb lake eutrophication is a success. Environ Sci Technol 50:8923–8929
Serra T, Vidal J, Casamitjana X, Soler M, Colomer J (2007) The role of surface vertical mixing in phytoplankton distribution in a stratified reservoir. Limnol Oceanogr 52:620–634
Shi WQ, Pan G, Chen QW, Song LR, Zhu L (2018) Hypoxia remediation and methane emission manipulation using surface oxygen nanobubbles. Environ Sci Technol 25:8712–8717
Sinkko H, Lukkari K, Sihvonen LM, Sivonen K, Leivuori M, Rantanen M, Paulin L, Lyra C (2013) Bacteria contribute to sediment nutrient release and reflect progressed eutrophication-driven hypoxia in an organic-rich continental sea. PLoS One 8:e67061–e67061
Smith L, Watzin MC, Druschel G (2011) Relating sediment phosphorus mobility to seasonal and diel redox fluctuations at the sediment-water interface in a eutrophic freshwater lake. Limnol Oceanogr 56:2251–2264
Speece RE (1971) Hypolimnion aeration. Journal 63:6–9
Su M, Han FY, Wu YL, Yan ZP, Lv ZS, Tian D, Wang SM, Hu SJ, Shen ZT, Li Z (2019) Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on phosphorous release and sorption on montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci 181:105227
Sun QQ, Chen JA, Wang JF, Yang HQ (2017) High-resolution distribution characteristics of phosphorous, iron and sulfur across the sediment-water interface of Aha Reservoir (In Chinese). Environ Sci 38:2810–2818
Tammeorg O, Nürnberg G, Horppila J, Haldna M, Niemistö J (2020) Redox-related release of phosphorus from sediments in large and shallow Lake Peipsi: evidence from sediment studies and long-term monitoring data. J Great Lakes Res 46:1595–1603
Tamura H, Goto K, Yotsuyanagi T, Nagayama M (1974) Spectrophotometric determination of iron(II) with 1,10-phenanthroline in the presence of large amounts of iron(III). Talanta 21:314–318
Tang W, Zhang H, Zhang W, Wang C, Shan B (2013) Biological invasions induced phosphorus release from sediments in freshwater ecosystems. Colloid Surface A 436:873–880
Venkateswaran K, Natarajan R (1983) Seasonal distribution of inorganic phosphate solubilising bacteria and phosphatase producing bacteria in Porto Novo waters. Indian J Geo-Mar Sci 12:213–217
Voordeckers JW, Kim BC, Izallalen M, Lovley DR (2010) Role of Geobacter sulfurreducens outer surface c-type cytochromes in reduction of soil humic acid and anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:2371–2375
Wang S, Jin X, Bu Q, Jiao L, Wu F (2008) Effects of dissolved oxygen supply level on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 316:245–252
Wang JF, Chen JA, Dallimore C, Yang HQ, Dai ZH (2015) Spatial distribution, fractions, and potential release of sediment phosphorus in the Hongfeng Reservoir, southwest China. Lake Reserv Manage 31:214–224
Wang JF, Chen JA, Ding SM, Guo JY, Christopher D (2016) Effects of seasonal hypoxia on the release of phosphorus from sediments in deep-water ecosystem: a case study in Hongfeng Reservoir, Southwest China. Environ Pollut 219:858–865
Wang Y, Li K, Liang R, Han S, Li Y (2019) Distribution and release characteristics of phosphorus in a reservoir in southwest China. Int J Env Res Pub He 16
Wu GF, Zhou XP (2005) Characterization of phosphorus-releasing bacteria in a small eutrophic shallow lake, Eastern China. Water Res 39:4623–4632
Wu Q, Zhang R, Huang S, Zhang H (2008) Effects of bacteria on nitrogen and phosphorus release from river sediment. J Environ Sci 20:404–412
Wu Y, Wen Y, Zhou J, Wu Y (2014) Phosphorus release from lake sediments: effects of pH, temperature and dissolved oxygen. KSCE J Civ Eng 18:323–329
Wu S, Zhao Y, Chen Y, Dong X, Wang M, Wang G (2018) Sulfur cycling in freshwater sediments: a cryptic driving force of iron deposition and phosphorus mobilization. Sci Total Environ 657:1294–1303
Wu S, Zhao Y, Chen Y, Dong X, Wang M, Wang G (2019) Sulfur cycling in freshwater sediments: a cryptic driving force of iron deposition and phosphorus mobilization. Sci Total Environ 657:1294–1303
Xu D, Chen YF, Ding SM, Sun Q, Wang Y, Zhang CS (2013) Diffusive gradients in thin films technique equipped with a mixed binding gel for simultaneous measurements of dissolved reactive phosphorus and dissolved iron. Environ Sci Technol 47:10477–10484
Yang X, Lu X (2014) Drastic change in China’s lakes and reservoirs over the past decades. Sci Rep 4:6041
Yang CH, Yang P, Geng J, Yin HB, Chen KN (2020) Sediment internal nutrient loading in the most polluted area of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and its contribution to lake eutrophication. Environ Pollut 262:114292
Yin H, Yang P, Kong M, Li W (2020) Preparation of the lanthanum–aluminum-amended attapulgite composite as a novel inactivation material to immobilize phosphorus in lake sediment. Environ Sci Technol 54:11602–11610
Yu J, Ding S, Zhong J, Fan C, Chen Q, Yin H, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2017) Evaluation of simulated dredging to control internal phosphorus release from sediments: focused on phosphorus transfer and resupply across the sediment-water interface. Sci Total Environ 592:662–673
Zhang HG, Lyu T, Bi L, Hamilton GT, Pan G (2018) Combating hypoxia/anoxia at sediment-water interfaces: a preliminary study of oxygen nanobubble modified clay materials. Sci Total Environ 637–638:550–560
Zhao Y, Yang Z, Xia X, Wang F (2012) A shallow lake remediation regime with Phragmites australis: incorporating nutrient removal and water evapotranspiration. Water Res 46:5635–5644
Funding
This study was sponsored jointly by the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS (No. XDB40020400), the Chinese NSF Joint Fund Project (No. U1612441), the Chinese NSF project (No. 41773145, 41977296), the Guizhou Science and Technology Project of China (No. [2019]2-9), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2019389), and the CAS Interdisciplinary Innovation Team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaohong Yang: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Ruixue Zhang: investigation, writing—review and editing. Jingfu Wang: conceptualization, methodology, resources, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. Kangkang He: investigation, formal analysis. Jingan Chen: investigation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Haihan Zhang
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 544 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhang, R., Wang, J. et al. Fluxes and mechanisms of phosphorus release from sediments in seasonal hypoxic reservoirs: a simulation-based experimental study. J Soils Sediments 21, 3246–3258 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02946-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02946-7