Abstract
Purpose
Microplastics are considered emerging pollutants and already currently present in measurable quantities in aquatic ecosystems. However, information on the current status of microplastic pollution in the upper Yangtze River, the most important water body in China, is insufficient. In the present study, the abundance and distribution of microplastics in the surface water and sediments were investigated to obtain the characteristics of microplastic pollution in Yangtze River along Chongqing City.
Materials and methods
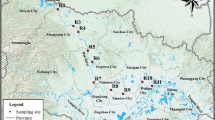
Ten sampling sites along Yangtze River in the Chongqing urban area were selected to collect surface water and sediment samples. Abundance and morphological characteristics of microplastics were determined by counting using a digital stereo microscope. Micro-Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (μ-FTIR) analysis was used to identify polymer type of the microplastics.
Results and discussion
The abundance of microplastics ranged within 46.7–204 n L−1 and 100–583 n kg−1 dw (dry weight) in the surface water and sediment samples, respectively. Fibers and films were dominant in most of samples, and the average proportion of fibers reached 74.3% in surface water. Whether in surface water or sediments, most of the microplastics were less than 0.7 mm in size, and the average proportion of microplastics with a size of less than 0.3 mm reached 62.6% in the sediment samples. Moreover, fibrous and small were the primary characteristics of the microplastics. Polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, high-density polyethylene, polyester, and wool fibers were identified in the surface water samples.
Conclusion
The Yangtze River along Chongqing City is contaminated by microplastic, like many urban rivers. Anthropogenic activities, including sewage treatment effluents, might be the main sources of microplastic pollution in Yangtze River (Chongqing urban section). This study reveals the contamination and characteristics of microplastics in the Yangtze River along Chongqing and supplies important data for further research on microplastics in Yangtze River’s basin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrady AL (2011) Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1596–1605
Boots B, Russell CW, Green DS (2019) Effects of microplastics in soil ecosystems: above and below ground. Environ Sci Technol 53:11496–11506
Browne MA, Crump P, Niven SJ, Teuten E, Tonkin A, Galloway T, Thompson R (2011) Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines worldwide: sources and sinks. Environ Sci Technol 45:9175–9179
Browne MA, Galloway TS, Thompson RC (2010) Spatial patterns of plastic debris along estuarine shorelines. Environ Sci Technol 44:3404–3409
Cai M, He H, Liu M, Li S, Tang G, Wang W, Huang P, Wei G, Lin Y, Chen B, Hu J, Cen Z (2018) Lost but can’t be neglected: huge quantities of small microplastics hide in the South China Sea. Sci Total Environ 633:1206–1216
Cole M, Lindeque P, Halsband C, Galloway TS (2011) Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 62:2588–2597
Cózar A, Echevarría F, González-Gordillo JI, Irigoien X, Úbeda B, Hernández-León S, Palma ÁT, Navarro S, García-de-Lomas J, Ruiz A, Fernández-de-Puelles ML, Duarte CM (2014) Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:10239–10244
Di M, Liu X, Wang W, Wang J (2019) Manuscript prepared for submission to environmental toxicology and pharmacology pollution in drinking water source areas: microplastics in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 65:82–89
Di M, Wang J (2018) Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 616-617:1620–1627
Ding L, Mao RF, Guo X, Yang X, Zhang Q, Yang C (2019) Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Wei River, in the northwest of China. Sci Total Environ 667:427–434
Driedger AGJ, Dürr HH, Mitchell K, Van Cappellen P (2015) Plastic debris in the Laurentian Great Lakes: a review. J Great Lakes Res 41:9–19
Duis K, Coors A (2016) Microplastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment: sources (with a specific focus on personal care products), fate and effects. Environ Sci Eur 28:2–2
Eriksen M, Lebreton LCM, Carson HS, Thiel M, Moore CJ, Borerro JC, Galgani F, Ryan PG, Reisser J (2014) Plastic pollution in the world’s oceans: more than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PLoS One 9:e111913–e111913
Eriksen M, Mason S, Wilson S, Box C, Zellers A, Edwards W, Farley H, Amato S (2013) Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar Pollut Bull 77:177–182
Fan Y, Zheng K, Zhu Z, Chen G, Peng X (2019) Distribution, sedimentary record, and persistence of microplastics in the Pearl River catchment, China. Environ Pollut 251:862–870
Faure F, Saini C, Potter G, Galgani F, de Alencastro LF, Hagmann P (2015) An evaluation of surface micro- and mesoplastic pollution in pelagic ecosystems of the Western Mediterranean Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:12190–12197
Fendall LS, Sewell MA (2009) Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1225–1228
Ferreira GVB, Barletta M, Lima ARA, Morley SA, Justino AKS, Costa MF (2018) High intake rates of microplastics in a Western Atlantic predatory fish, and insights of a direct fishery effect. Environ Pollut 236:706–717
Henry B, Laitala K, Klepp IG (2019) Microfibres from apparel and home textiles: prospects for including microplastics in environmental sustainability assessment. Sci Total Environ 652:483–494
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Gutow L, Thompson RC, Thiel M (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46:3060–3075
Horton AA, Walton A, Spurgeon DJ, Lahive E, Svendsen C (2017) Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci Total Environ 586:127–141
Imhof HK, Laforsch C, Wiesheu AC, Schmid J, Anger PM, Niessner R, Ivleva NP (2016) Pigments and plastic in limnetic ecosystems: a qualitative and quantitative study on microparticles of different size classes. Water Res 98:64–74
Jiang C, Yin L, Li Z, Wen X, Luo X, Hu S, Yang H, Long Y, Deng B, Huang L, Liu Y (2019) Microplastic pollution in the rivers of the Tibet Plateau. Environ Pollut 249:91–98
Jiang C, Yin L, Wen X, Du C, Wu L, Long Y, Liu Y, Ma Y, Yin Q, Zhou Z, Pan H (2018) Microplastics in sediment and surface water of West Dongting Lake and South Dongting Lake: abundance, source and composition. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(10):2164–2175
Kumar M, Xiong X, He M, Tsang DCW, Gupta J, Khan E, Harrad S, Hou D, Ok Y, Bolan NS (2020) Microplastics as pollutants in agricultural soils. Environ Pollut 265:114980
Lebreton LC, Greer SD, Borrero JC (2012) Numerical modelling of floating debris in the world’s oceans. Mar Pollut Bull 64:653–661
Li Y, Lu Z, Zheng H, Wang J, Chen C (2020) Microplastics in surface water and sediments of Chongming Island in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ Sci Eur 32:15
Li HX, Ma LS, Lin L, Ni ZX, Xu XR, Shi HH, Yan Y, Zheng GM, Rittschof D (2018) Microplastics in oysters Saccostrea cucullata along the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ Pollut 236:619–625
Lin L, Zuo LZ, Peng JP, Cai LQ, Fok L, Yan Y, Li HX, Xu XR (2018) Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in an urban river: a case study in the Pearl River along Guangzhou City, China. Sci Total Environ 644:375–381
Maximenko N, Hafner J, Niiler P (2012) Pathways of marine debris derived from trajectories of Lagrangian drifters. Mar Pollut Bull 65:51–62
Moore CJ (2008) Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: a rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ Res 108:131–139
Nuelle MT, Dekiff JH, Remy D, Fries E (2014) A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ Pollut 184:161–169
Peng G, Xu P, Zhu B, Bai M, Li D (2018) Microplastics in freshwater river sediments in Shanghai, China: a case study of risk assessment in mega-cities. Environ Pollut 234:448–456
Phuong NN, Zalouk-Vergnoux A, Poirier L, Kamari A, Châtel A, Mouneyrac C, Lagarde F (2016) Is there any consistency between the microplastics found in the field and those used in laboratory experiments? Environ Pollut 211:111–123
PlasticsEurope (2019) Plastics - the Facts 2018 An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. www.plasticseurope.org
Ryan PG (2015) A brief history of marine litter research, in Marine anthropogenic litter. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 1–25
Schwarz AE, Ligthart TN, Boukris E, van Harmelen T (2019) Sources, transport, and accumulation of different types of plastic litter in aquatic environments: a review study. Mar Pollut Bull 143:92–100
Su L, Xue Y, Li L, Yang D, Kolandhasamy P, Li D, Shi H (2016) Microplastics in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Pollut 216:711–719
Thompson RC, Olsen Y, Mitchell RP, Davis A, Rowland SJ, John AWG, McGonigle D, Russell AE (2004) Lost at sea: where is all the plastic? Science 304:838–838
Vaughan R, Turner SD, Rose NL (2017) Microplastics in the sediments of a UK urban lake. Environ Pollut 229:10–18
Wang W, Ndungu AW, Li Z, Wang J (2017) Microplastics pollution in inland freshwaters of China: a case study in urban surface waters of Wuhan, China. Sci Total Environ 575:1369–1374
Wang W, Yuan W, Chen Y, Wang J (2018) Microplastics in surface waters of Dongting Lake and Hong Lake, China. Sci Total Enviro 633:539–545
Wen X, Du C, Xu P, Zeng G, Huang D, Yin L, Yin Q, Hu L, Wan J, Zhang J, Tan S, Deng R (2018) Microplastic pollution in surface sediments of urban water areas in Changsha, China: abundance, composition, surface textures. Mar Pollut Bull 136:414–423
Xiong X, Wu C, Elser JJ, Mei Z, Hao Y (2019) Occurrence and fate of microplastic debris in middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River - from inland to the sea. Sci Total Environ. 659:66–73
Xiong X, Zhang K, Chen X, Shi H, Luo Z, Wu C (2018) Sources and distribution of microplastics in China’s largest inland lake – Qinghai Lake. Environ Pollut 235:899–906
Yan M, Nie H, Xu K, He Y, Hu Y, Huang Y, Wang J (2019) Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in the Pearl River along Guangzhou city and Pearl River estuary, China. Chemosphere 217:879–886
Yonkos LT, Friedel EA, Perez-Reyes AC, Ghosal S, Arthur CD (2014) Microplastics in four estuarine rivers in the Chesapeake Bay, U.S.A. Environ Sci Technol 48:14195–14202
Zhang K, Chen X, Xiong X, Ruan Y, Zhou H, Wu C, Lam PKS (2019) The hydro-fluctuation belt of the Three Gorges Reservoir: source or sink of microplastics in the water? Environ Pollut 248:279–285
Zhang K, Gong W, Lv J, Xiong X, Wu C (2015) Accumulation of floating microplastics behind the Three Gorges Dam. Environ Pollut 204:117–123
Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Du F, Cai H, Wang G, Shi H (2020) Microplastic fallout in different indoor environments. Environ Sci Technol. 54:6530–6539
Zhao S, Zhu L, Li D (2015) Microplastic in three urban estuaries, China. Environ Pollut 206:597–604
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977337), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing of China (cstc2018jcyjAX0054), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M650821), and the Scientific and Technological Research Program of the Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (KJQN201800702).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Patrick Byrne
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, J., Zou, L. & Zhao, G. Microplastic abundance, distribution, and composition in the surface water and sediments of the Yangtze River along Chongqing City, China. J Soils Sediments 21, 1840–1851 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02902-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02902-5