Abstract
Purpose
For the limitation of techniques on the saline soil improvement, the effect of a new method with some effective materials on saline soil improvement was studied by soil column experiment. Biochar and wood fibre were used as a buried layer to identify their effects on the saline soil reclamation.
Materials and methods
Soil samples were packed in each column (height, 130 cm; diameter, 20 cm). A tape measure (length, 100 cm) was fixed vertically to the outer wall of each soil column; it was used to record the location of the wetting front during infiltration. Biochar and wood fibre were inserted at depths of either 30 cm or 50 cm (thickness in each treatment, 2 cm). Soil columns were irrigated once with 15 L of brackish water (2 g/L). Soil water content and salt content were measured with a TRIME-PICO sensor at the 25, 60 and 100 cm layers, and Mariotte’s bottle was used at the 100-cm layer to measure the underground water level.
Results and discussion
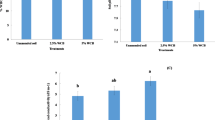
Wood fibre and biochar used as the buried layer was found that they caused a breakdown in the continuity of capillary movement and salt reduction. Wood fibre and biochar were able to retard the rate of water infiltration at 0–30-cm depth, for high water potential created when the buried layer contained sufficient water; it improved the more water infiltration than evaporation. Thus, it could serve to increase the salt leaching efficiency during the longer time scales of soil water infiltration; results showed that the buried layer was at 30-cm depth; the desalting rates were 3.69% (biochar) and 29.38% (wood fibre); the desalting rates were 4.76% (biochar) and 17.07% (wood fibre) when buried layer at 50 cm. And, the better performance in soil water infiltration and salt reduction was caused by a higher pore width, abundant fibrous tissue and saturation moisture content (Ɵs).
Conclusions
The buried layer can improve the soil water infiltration process, especially when the wood fibre layer was at 30 cm. Both biochar and wood fibre layers could limit salt accumulation in surface soil, indicating that the continuity of capillary movement was broken after embedding the interlayer; wood fibre was superior to biochar in this regard. This study provides a new method on the saline soil improvement that could improve the mulching development, and the effect of the evaporation could be further considered by the buried layer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Hur M, Shainberg I, Bakker D, Keren R (1985) Effect of soil texture and CaCO3 content on infiltration in crusted soils as related to water salinity. Irrig Sci 6:281–294
Cao JS, Liu CM, Zhang WJ, Guo YL (2012) Effect of integrating straw into agricultural soils on soil infiltration and evaporation. Water Sci Technol 65:2213–2218
Cui BS, Yang QC, Zhang KJ, Zhao XS, You ZY (2010) Responses of saltcedar (tamarix chinensis) to water table depth and soil salinity in the yellow river delta, china. Plant Ecol 209(2):279–290
Cui S, Zhang J, Sun M, Chen H, Feng Z (2018) Leaching effectiveness of desalinization by rainfall combined with wheat straw mulching on heavy saline soil. Arch Adron Soil Sci 64(7):891–902
Fan XM, Liu GH, Tang ZP, Shu LC (2010) Analysis on main contributors influencing soil salinization of Yellow River Delta. J Soil Water Conserv 24(1):139–144 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Fan F, Xu SJ, Song GY, Zhang QG, Hou MH, Song XF (2012a) Studies on improvement of saline and alkali soil with the interlayer of maize straw in West Liaohe region. Chin. J Soil Sci 43:696–701 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Fan X, Pedroli B, Liu G, Liu Q, Liu H, Shu L (2012b) Soil salinity development in the yellow river delta in relation to groundwater dynamics. Land Degrad Dev 23:175–189
Fanning CD, Carter DL (1963) The effectiveness of a cotton bur mulch and a ridge-furrow system in reclaiming saline soils by rainfall1. Soil Sci Soc Am J 27(6):703–706
Gao HF, Bai JH, Wang QG, Huang LB, Xiao R (2010) Profile distribution of soil nutrients in unrestored and restored wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China. Procedia Environ Sci 2:1652–1661
Gruda N, Schnitzler WH (2004) Suitability of wood fiber substrate for production of vegetable transplants: i. physical properties of wood fiber substrates. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 100(1-4):309–322
Guo G, Araya K, Jia H, Zhang Z, Ohomiyaand K, Matsuda J (2006) Improvement of salt-affected soils, Part 1: Interception of capillarity. Biosyst Eng 94:139–150
Guo G, Zhang H, Araya K, Jia H, Ohomiya K, Matsuda J (2007) Improvement of salt-affected soils, Part 3: Specific heat of saltaffected soils. Biosyst Eng 96:413–418
Han GX, Sun BY, Chu XJ, Xing QH, Song WM, Xia JY (2018) Precipitation events reduce soil respiration in a coastal wetland based on four-year continuous field measurements. Agric For Meteorol 256:292–303
Haque MA, Jahiruddin M, Clarke D (2018) Effect of plastic mulch on crop yield and land degradation in south coastal saline soils of bangladesh. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 6(4):317–324
He FH, Pan YH, Tan LL, Zhang ZH, Li P, Liu J, Ji SX, Qin ZH, Shao HB, Song XY (2017) Study of the water transportation characteristics of marsh saline soil in the yellow river delta. Sci Total Environ 574:716–723
Jia H, Zhang H, Araya K, Guo G, Zhang Z, Ohomiya K, Matsuda J (2006) Improvement of salt-affected soils, Part 2: Interception of capillarity by soil sintering. Biosyst Eng 94:263–273
Jiang R, Li X, Zhu W, Wang K, Guo S, Misselbrook T, Hatano R (2018) Effects of the ridge mulched system on soil water and inorganic nitrogen distribution in the loess plateau of china. Agr Water Manage 203:277–288
Li HQ, Wang SL, Guo MM, Gao HY, Pang HC, Li YY (2012) Effect of different straw interlayer on soil water-salt movement and maize yield in Hetao Irrigation District in Inner Mongolia. J Irrig Drain 31:91–94 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Li YY, Pang HC, Han XF, Yan SW, Zhao YG, Wang J, Zhai Z, Zhang JL (2016) Buried straw layer and plastic mulching increase microlfora diversity in salinized soil. J Integr Agric 15(7):1602–1611
Li XB, Kang YH, Wan SQ, Chen XL, Liu SP, Xu JC (2017) Effect of ridge planting on reclamation of coastal saline soil using drip-irrigation with saline water. CATENA 150:24–31
Lin XW, Xie ZB, Zheng JY, Liu Q, Bei QC, Zhu JG (2015) Effects of biochar application on greenhouse gas emissions, carbon sequestration and crop growth in coastal saline soil. Eur J Soil Sci 66(2):329–338
Liu PP, Bai JH, Ding QY, Shao HB, Gao HF, Xiao R (2012) Effects of water level and salinity on tn and tp contents in marsh soils of the yellow river delta, china. CLEAN - Soil Air Water 40(10):1118–1124
Long H, Pang H, Zhao Y, Jing W, Lu C, Li Y (2017) Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching improves soil organic carbon fractions in an arid saline soil from northwest china. Soil Tillage Res 165:286–293
Matuana LM, Park CB, Balatinecz JJ (2010) Cell morphology and property relationships of microcellular foamed pvc/wood fiber composites. Polym Eng Sci 38(11):1862–1872
Mazaheri MR, Mahmoodabadi M (2012) Study on infiltration rate based on primary particle size distribution data in arid and semi arid region soils. Arab J Geosci 5:1039–1046
Porro I, Wierenga PJ, Hills RG (1993) Solute transport through large uniform and layered soil columns. Water Resour Res 29:1321–1330
Qiao YH, Yu ZR (2002) Simulation study on the effects of irrigation on soil salt and saline water exploration. Acta Ecol Sin 23(10):2050–2056 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Qiao HL, Liu XJ, Li WQ, Huang W (2006) Effects of straw deep mulching on soil moisture infiltration and evaporation. Sci Soil Water Conserv 4:34–38 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Rong LS, Li GH, Shu LC, Song CY, Huang C (2010) Study on ecologic water level cover depth in yellow river delta. Water Resour Power 6:98–101+148 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Rooney DJ, Brown KW, Thomas JC (1998) The effectiveness of capillary barriers to hydraulically isolate salt contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 104:403–411
Shi WJ, Wang ZR, Shen B, Wang WY (2007) Characteristics of saline ions movement in sand-layered soil profiles under evaporation. J Northwest Agric Forest Uni 35(1):133–137 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Singh K (2015) Microbial and enzyme activities of saline and sodic soils. Land Degrad Dev 27(3):706–718
Sun B, Xie JC, Wang N (2012) Effect of straw mulching on change of evaporation and water-salt in the saline soil. J Soil Water Conserv 26(1):246–250 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Sun JN, He FH, Shao HB, Zhang ZH, Xu G (2016a) Temperature and moisture responses to carbon mineralization in the biochar-amended saline soil. Sci Total Environ 569-570:390–394
Sun JN, He FH, Shao HB, Zhang ZH, Xu G (2016b) Effects of biochar application on suaeda salsa growth and saline soil properties. Environ Earth Sci 75(8):630
Taufiq A, Wijanarko A, Kristiono A (2017) Effect of mulching and amelioration on growth and yied of groundnut on saline soil. J Degrade Min Land Manage 4(4):945–954
Tejedor M, Jiménez CC, Díaz F (2003) Use of volcanic mulch to rehabilitate saline-sodic soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67(6):1856–1861
Wang ZQ, Zhu SQ, Yu RP (1993) Saline soil in China. China, Beijing
Wang H, Gong P, Liu GH (2004) The review and prospect on land use and land cover change research in Yellow River Delta. J Nat Res 19(1):110–118 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Wang RL, Huang Y, Wei FL, Bai XW, Li E, Zhang YL (2011) Design and testing of plough for deep furrowing and riding of straw amendment fields. J Shenyang Agric Univ 42:231–234 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Wang J, Pang HC, Ren TZ, Li YY, Zhao YG (2012) Effect of plastic film mulching and straw buried on soil water-salt dynamic in Hetao plain. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 28:52–59 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Wang TT, Stewart CE, Sun CC, Wang Y, Zheng JY (2018) Effects of biochar addition on evaporation in the five typical loess plateau soils. CATENA 162:29–39
Woodhams RT, Thomas G, Rodgers DK (1984) Wood fibres as reinforcing fillers for polyolifin. Polym Eng Sci 24(15):1166–1171
Wu Y, Xu G, Shao HB (2014) Furfural and its biochar improve the general properties of a saline soil. Solid Earth 5(2):665–671
Yang JS (2008) Development and prospect of the research on salt-affected soils in china. Acta Pedol Sin 45(5):837–845 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Yang F, Li XQ, Xing Y, Cheng HG, Zhang LK, He YY, Wang B (2014) Effect of biochar amendment on nitrogen leaching in saline soil. J Agro-Env Sci 33(5):972–977 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Yao RJ, Yang JS, Jiang L (2006) Study on spatial variability and appropriate sampling quantity of soil salinity in Yellow River Delta. J Soil Water Conserv 6:89–94 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Yu RP, Chen DM (1999) Resources and exploitation of saline soil in China. Chin J Soil Sci 30(4):158–159 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Zhang K, Miao CC, Xu YY, Hua XF, Han HL, Yang JM et al (2009) Process fundamentals and field demonstration of wheat straw enhanced salt leaching of petroleum contaminated farmland. Environ Sci 30:233–238 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Zhang S, Kong DG, Chang XH, Zhai LM (2010) Effect of straw deep application on soil water storage capacity. J Northeast Agric Univ 41:127–129 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Zhao YG, Wang J, Li YY, Pang HC (2013) Reducing evaporation from phreatic water and soil resalinization by using straw interlayer and plastic mulch. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 29(23):109–117 (In Chinese with english abstract)
Zhao YG, Pang HC, Wang J, Huo L, Li Y (2014) Effects of straw mulch and buried straw on soil moisture and salinity in relation to sunflower growth and yield. Field Crop Res 161:16–25
Zhao YG, Li YY, Wang J, Pang HC, Li Y (2016) Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching reduces soil salinity and increases sunflower yield in saline soils. Soil Tillage Res 155:363–370
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China-Shandong Joint Fund (No. U1806215), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977015), National Key Research and Development Programme of China (NO. 2019YFD1002702), National Natural Science Foundation of China-Shandong Joint Fund (No. U1906221).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, W., Yang, J., Yao, R. et al. Buried layers change soil water flow and solute transport from the Yellow River Delta, China. J Soils Sediments 21, 1598–1608 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02848-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02848-0