Abstract
Purpose
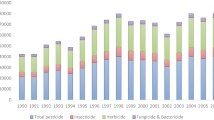
Phthalate esters (PAEs) have been and remain the most widely used plasticizers worldwide, and they are also the most frequently detected environmental pollutants. It is known that the management style and agricultural inputs should play a critical role in the PAE contamination. However, the status of six priority controlled PAEs remains unclear in soils used for tobacco on farms that are under the compulsorily management of national tobacco company.
Materials and methods
The samples included soils, water, and fertilizers were collected from tobacco cultivation sites in the Shandong province. The six priority controlled PAEs were extracted from the samples according to the reported methods, and they were analyzed using a GC-TQ-MS/MS under MRM mode. The hazard quotients and carcinogenic risks for people by gender and age were assessed first time by the recommended method of US Environmental Protection Agency.
Results and discussion
Soils were contaminated by PAEs from 218.4 to 1168.9 μg kg−1, with the average value of 611.1 μg kg−1. More than 80% Σ6PAEs consisted of DBP and DEHP, and regional characteristics of Shandong province showed the highest content of DBP. Besides plastic film, agricultural inputs such as irrigation water and fertilizers were also the PAE sources. At present, the non-cancer risk has not exceeded the threshold of 1, and carcinogenic risk was still low in the range of 10−6–10−4 with the highest risk of DEHP exposure through dietary consumption.
Conclusions
Pollution status of PAEs in tobacco cultivation soils and its health risk to Chinese people were already present at low levels. Thus, we should pay more attention to PAE contamination in order to prevent further deterioration, particularly for the DEHP exposure to middle-aged people.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chai C, Cheng H, Ge W, Ma D, Shi Y (2014) Phthalic acid esters in soils from vegetable greenhouses in Shandong Peninsula, East China. PLoS One 9:e95701
Chen Z, Tian T, Gao L, Tian Y (2016) Nutrients, heavy metals and phthalate acid esters in solar greenhouse soils in Round-Bohai Bay-Region, China: impacts of cultivation year and biogeography. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:13076–13087
Chen N, Shuai W, Hao X, Zhang H, Zhou D, Gao J (2017) Contamination of phthalate esters in vegetable agriculture and human cumulative risk assessment. Pedosphere 27:439–451
Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2002) Nutrition data yearbook. http://www.chinanutri.cn/sjnj/. Accessed Dec 2019.
Du L, Li G, Liu M, Li Y, Yin S, Zhao J, Zhang X (2015) Evaluation of DNA damage and antioxidant system induced by di-n-butyl phthalates exposure in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotox Environ Safe 115:75–82
Gao D, Li Z, Wen Z, Ren N (2014) Occurrence and fate of phthalate esters in full-scale domestic wastewater treatment plants and their impact on receiving waters along the Songhua River in China. Chemosphere 95:24–32
Gao D, Li Z, Wang H, Liang H (2018) An overview of phthalate acid ester pollution in China over the last decade: environmental occurrence and human exposure. Sci Total Environ 645:1400–1409
Gao X, Li J, Wang X, Zhou J, Fan B, Li W, Liu Z (2019) Exposure and ecological risk of phthalate esters in the Taihu Lake basin, China. Ecotox Environ Safe 171:564–570
Gejlsbjerg B, Andersen TT, Madsen T (2004) Mineralization of organic contaminants under aerobic and anaerobic conditions in sludge-soil mixtures. J Soil Sediment 4:30–36
Giulivo M, de Alda ML, Capri E, Barceló D (2016) Human exposure to endocrine disrupting compounds: their role in reproductive systems, metabolic syndrome and breast cancer. A review. Environ Res 151:251–264
Gomez-Hens A, Aguilar-Caballos MP (2003) Social and economic interest in the control of phthalic acid esters. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 22:847–857
He W, Qin N, Kong X, Liu W, He Q, Ouyang H, Yang C, Jiang Y, Wang Q, Yang B, Xu F (2013) Spatio-temporal distributions and the ecological and health risks of phthalate esters (PAEs) in the surface water of a large, shallow Chinese lake. Sci Total Environ 461:672–680
He L, Gielen G, Bolan NS, Zhang X, Qin H, Huang H, Wang H (2015) Contamination and remediation of phthalic acid esters in agricultural soils in China: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 35:519–534
Jiang XH, Song DA, Wang DB, Zhang RM, Fang QN, Sun HQ, Kong FY (2020) Eliminating imidacloprid and its toxicity by permanganate via highly selective partial oxidation. Ecotox Environ Safe 191:110234
Kong S, Ji Y, Liu L, Chen L, Zhao X, Wang J, Bai Z, Sun Z (2012) Diversities of phthalate esters in suburban agricultural soils and wasteland soil appeared with urbanization in China. Environ Pollut 170:161–168
Kong X, Jin D, Jin S, Wang Z, Yin H, Xu M, Deng Y (2018) Responses of bacterial community to dibutyl phthalate pollution in a soil-vegetable ecosystem. J Hazard Mater 353:142–150
Li C, Chen J, Wang J, Han P, Luan Y, Ma X, Lu A (2016a) Phthalate esters in soil, plastic film, and vegetable from greenhouse vegetable production bases in Beijing, China: concentrations, sources, and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 568:1037–1043
Li K, Ma D, Wu J, Chai C, Shi Y (2016b) Distribution of phthalate esters in agricultural soil with plastic film mulching in Shandong Peninsula, East China. Chemosphere 164:314–321
Lin YC, Wei KS, Gao WC, Chen Y, Lin YC, Chen W, Li HX, Pan WJ (2018) Effects of plastic mulching film-induced leaf burning on seedling growth in tobacco cultivation: different findings beyond conservation view. J Integr Agr 17:1327–1337
Lü HX, Mo CH, Zhao HM, Xiang L, Katsoyiannis A, Li YW, Cai QY, Wong MH (2018) Soil contamination and sources of phthalates and its health risk in china: a review. Environ Res 164:417–429
Ma TT, Wu LH, Chen L, Zhang HB, Teng Y, Luo YM (2015) Phthalate esters contamination in soils and vegetables of plastic film greenhouses of suburb Nanjing, China and the potential human health risk. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:12018–12028
Mo CH, Cai QY, Li YH, Zeng QY (2008) Occurrence of priority organic pollutants in the fertilizers, China. J Hazard Mater 152:1208–1213
National Bureau of Statistics of China, China statistical yearbook (2003) http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/yearbook2003_c.pdf. Accessed Dec 2019.
National Bureau of Statistics of China, China statistical yearbook (2017) http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2017/indexch.htm. Accessed Dec 2019.
Net S, Sempere R, Delmont A, Paluselli A, Ouddane B (2015) Occurrence, fate, behavior and ecotoxicological state of phthalates in different environmental matrices. Environ Sci Technol 49:4019–4035
Niu L, Xu Y, Xu C, Yun L, Liu W (2014) Status of phthalate esters contamination in agricultural soils across China and associated health risks. Environ Pollut 195:16–23
Paluselli A, Fauvelle V, Galgani F, Sempéré R (2018) Phthalate release from plastic fragments and degradation in seawater. Environ Sci Technol 53:166–175
Rahman M, Brazel CS (2004) The plasticizer market: an assessment of traditional plasticizers and research trends to meet new challenges. Prog Polym Sci 29:1223–1248
Sifakis S, Androutsopoulos VP, Tsatsakis AM, Spandidos D (2017) Human exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals: effects on the male and female reproductive systems. Environ Toxicol Phar 51:56–70
Song DA, Liang RN, Zhang RM, Ding JW, Zhang J, Qin W (2010) Potentiometric detection of polyions based on functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Chinese Chem Lett 21:1378–1381
Song DA, Cheng HY, Liu RP, Qiang ZM, He H, Liu HJ, Qu JH (2017) Enhanced oxidation of tetracycline by permanganate via the alkali-induced alteration of the highest occupied molecular orbital and the electrostatic potential. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:4703–4708
Song DA, Liang RN, Jiang XH, Sun HQ, Kong FY, Lv B, Fang QN, Qin W (2018) Modeling the response of a control-released ion-selective electrode and employing it for the study of permanganate oxidation kinetics. Anal Methods 10:467–473
Staples CA, Peterson DR, Parkerton TF, Adams WJ (1997) The environmental fate of phthalate esters: a literature review. Chemosphere 35:667–749
Sun J, Pan L, Zhan Y, Lu H, Tsang DCW, Liu W, Wang X, Li X, Zhu L (2016) Contamination of phthalate esters, organochlorine pesticides and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in agricultural soils from the Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci Total Environ 544:670–676
Sun J, Pan L, Li Z, Zeng Q, Wang L, Zhu L (2018) Comparison of greenhouse and open field cultivations across China: soil characteristics, contamination and microbial diversity. Environ Pollut 243:1509–1516
US Environmental Protection Agency (2013) Mid Atlantic risk assessment. Regional Screening Level (RSL) Summary Table, Washington
Wang J, Luo Y, Teng Y, Ma W, Christie P, Li Z (2013) Soil contamination by phthalate esters in Chinese intensive vegetable production systems with different modes of use of plastic film. Environ Pollut 180:265–273
Wang J, Chen G, Christie P, Zhang M, Luo Y, Teng Y (2015) Occurrence and risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in vegetables and soils of suburban plastic film greenhouses. Sci Total Environ 523:129–137
Wang H, Liang H, Gao DW (2017a) Occurrence and risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in agricultural soils of the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:19723–19732
Wang L, Zhang W, Tao W, Wang L, Shi X, Lu X (2017b) Investigating into composition, distribution, sources and health risk of phthalic acid esters in street dust of Xi’an City, Northwest China. Environ Geochem Hlth 39:865–877
Wang L, Liu M, Tao W, Zhang W, Wang L, Shi X, Lu X, Li X (2018a) Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of phthalate esters in urban soil in the typical semi-arid city of Xi’an, Northwest China. Chemosphere 191:467–476
Wang W, Leung AOW, Chu LH, Wong MH (2018b) Phthalates contamination in China: status, trends and human exposure-with an emphasis on oral intake. Environ Pollut 238:771–782
Wen Z, Huang X, Gao D, Liu G, Fang C, Shang Y, Du J, Zhao Y, Lv L, Song K (2018) Phthalate esters in surface water of Songhua River watershed associated with land use types, Northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:7688–7698
Yang GCC, Wang CL, Chiu YH (2015) Occurrence and distribution of phthalate esters and pharmaceuticals in Taiwan river sediments. J Soil Sediment 15:198–210
Zeng F, Cui K, Xie Z, Wu L, Liu M, Sun G, Lin Y, Luo D, Zeng Z (2008) Phthalate esters (PAEs): emerging organic contaminants in agricultural soils in peri-urban areas around Guangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 156:425–434
Zhang Z, He G, Peng X, Lu L (2014) Distribution and sources of phthalate esters in the topsoils of Beijing, China. Environ Geochem Hlth 36:505–515
Zhang Y, Liang Q, Gao R, Hou H, Tan W, He X, Zhang H, Yu M, Ma L, Xi B, Wang X (2015a) Contamination of phthalate esters (PAEs) in typical wastewater-irrigated agricultural soils in Hebei, North China. PLoS One 10:e0137998
Zhang Y, Wang P, Wang L, Sun G, Zhao J, Zhang H, Du N (2015b) The influence of facility agriculture production on phthalate esters distribution in black soils of northeast China. Sci Total Environ 506:118–125
Zhao HM, Du H, Xiang L, Chen YL, Lu LA, Li YW, Li H, Cai QY, Mo CH (2015) Variations in phthalate ester (PAE) accumulation and their formation mechanism in Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica parachinensis L.) cultivars grown on PAE-contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 206:95–103
Funding
This project was financially supported by the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (1610232019005), the National Agricultural Product Quality and Safety Risk Assessment Project (GJFP2019034), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIPTRIC06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhaohui Wang
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1950 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, D., Sun, H., Yang, Y. et al. Status of phthalate esters in tobacco cultivation soils and its health risk to Chinese people. J Soils Sediments 21, 307–318 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02773-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02773-2