Abstract
Purpose
Nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) has been widely proposed to reduce nitrogen (N) loss and improve N availability in paddy soil. However, little knowledge exists regarding the optimum dose of DMPP required for inhibiting nitrification in different soil types.
Materials and methods
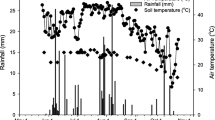
In undisturbed soil columns under greenhouse conditions, dynamics of ammonium (NH4+–N) and nitrate (NO3−–N) in floodwater and leachate, and ammonia (NH3) volatilization were studied in two paddy soils (hydragic and gleyed), amended with urea-N at 180 N kg/ha with DMPP applied at 0, 0.45, 0.675, and 0.90 kg/ha (0.25%, 0.375%, and 0.5% of urea-N, respectively). The source of DMPP was Entec® 46 (46% urea-N and DMPP at 0.5% of urea-N) that was mixed with pure urea (fertilizer mixture).
Results and discussion
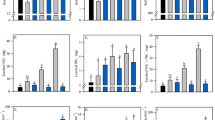
DMPP application rates and soil types significantly influenced NH4+–N and NO3−–N concentrations in floodwater and leachate; however, DMPP application rates did not significantly impact NH4+–N concentrations in floodwater. Results indicate that concentrations of both NH4+– N and NO3−–N in leachate and floodwater were peaked between 10 and 20 days after fertilizer application. Increased DMPP application rates increased floodwater and leachate NH4+–N concentrations, while significantly decreasing NO3−–N concentrations in floodwater and leachate, with largest decrease seen in the 0.90-kg/ha DMPP treatment. NH3 emissions were observed after fertilizer was applied and decreased gradually, with no significant differences in response to the DMPP amount. The total N losses via leaching and NH3 emission were significantly decreased at treatments of 0.675 kg/ha and 0.90 kg/ha DMPP, and positively correlated with sand fraction in soil. Compared with the gleyed paddy soil, higher total N loss was observed in the hydragic paddy soil, which was related to the higher sand fraction of the hydragic paddy soil and the better behavior of DMPP in this soil type.
Conclusions
Considering economic factors, mineral N concentrations in floodwater and leachate, together with N losses via leaching and volatilization, application of 0.675 kg/ha DMPP could significantly inhibit nitrification in the hydragic paddy soil while application of 0.90 kg/ha DMPP was shown to be the best choice to inhibit nitrification in the gleyed paddy soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalos D, Jeffery S, Sanz-Cobena A, Guardia G, Vallejo A (2014) Meta-analysis of the effect of urease and nitrification inhibitors on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Agric Ecosyst Environ 189:136–144
Anderson CR, Hamonts K, Clough TJ, Condron LM (2014) Biochar does not affect soil N-transformations or microbial community structure under ruminant urine patches but does alter relative proportions of nitrogen cycling bacteria. Agric Ecosyst Environ 191:63–72
Barth G, Von Tucher S, Schmidhalter U (2001) Influence of soil parameters on the effect of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole-phosphate as a nitrification inhibitor. Biol Fertil Soils 34:98–102
Barth G, Von Tucher S, Schmidhalter U (2008) Effectiveness of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate as nitriflcation inhibitor in soil as influenced by inhibitor concentration, application form, and soil matric potential. Pedosphere 18:378–385
Barth G, Tucher S, Schmidhalter U, Otto R, Motavalli P, Ferraz-Almeida R, Meinl Schmiedt Sattolo T, Cantarella H, Vitti GC (2019) Performance of nitrification inhibitors with different nitrogen fertilizers and soil textures. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 182:694–700
Chaves B, Opoku A, De Neve S, Boeckx P, Van Cleemput O, Hofman G (2005) Influence of DCD and DMPP on soil N dynamics after incorporation of vegetable crop residues. Biol Fertil Soils 43:62–68
Chen D, Suter HC, Islam A, Edis R (2010) Influence of nitrification inhibitors on nitrification and nitrous oxide (N2O) emission from a clay loam soil fertilized with urea. Soil Biol Biochem 42:660–664
Di HJ, Cameron KC (2005) Reducing environmental impacts of agriculture by using a fine particle suspension nitrification inhibitor to decrease nitrate leaching from grazed pastures. Agric Ecosyst Environ 109:202–212
Di HJ, Cameron KC (2012) How does the application of different nitrification inhibitors affect nitrous oxide emissions and nitrate leaching from cow urine in grazed pastures? Soil Use Manag 28:54–61
Di HJ, Cameron KC (2016) Inhibition of nitrification to mitigate nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions in grazed grassland: a review. J Soils Sediments 16:1401–1420
Dougherty WJ, Collins D, Van Zwieten L, Rowlings DW (2016) Nitrification (DMPP) and urease (NBPT) inhibitors had no effect on pasture yield, nitrous oxide emissions, or nitrate leaching under irrigation in a hot-dry climate. Soil Res 54:675–683
Florio A, Clark IM, Hirsch PR, Jhurreea D, Benedetti A (2014) Effects of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on abundance and activity of ammonia oxidizers in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 50:795–807
Florio A, Maienza A, Dell’Abate MT, Stazi SR, Benedetti A (2016) Changes in the activity and abundance of the soil microbial community in response to the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP). J Soils Sediments 16:2687–2697
Guardia G, Marsden KA, Vallejo A, Jones DL, Chadwick DR (2018) Determining the influence of environmental and edaphic factors on the fate of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP in soil. Sci Total Environ 624:1202–1212
Harris RH, Armstrong RD, Wallace AJ, Belyaeva ON (2016) Delaying nitrogen fertiliser application improves wheat 15N recovery from high rainfall cropping soils in south eastern Australia. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 106:113–128
Huérfano X, Fuertes-Mendizábal T, Duñabeitia MK, González-Murua C, Estavillo JM, Menéndez S (2015) Splitting the application of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP): influence on greenhouse gases emissions and wheat yield and quality under humid Mediterranean conditions. Eur J Agron 64:47–57
Hu Y, Schraml M, Tucher S, Li F, Schmidhalter U (2013) Influence of nitrification inhibitors on yields of arable crops: a meta-analysis of recent studies in Germany. Int J Plant Prod 8:33–50
Koci J, Nelson PN (2016) Tropical dairy pasture yield and nitrogen cycling: effect of urea application rate and a nitrification inhibitor, DMPP. Crop Pasture Sci 67:766–779
Lam SK, Suter H, Bai M, Walker C, Davies R, Mosier AR, Chen D (2018) Using urease and nitrification inhibitors to decrease ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions and improve productivity in a subtropical pasture. Sci Total Environ 644:1531–1535
Li H, Liang X, Chen Y, Lian Y, Tian G, Ni W (2008a) Effect of nitrification inhibitor DMPP on nitrogen leaching, nitrifying organisms, and enzyme activities in a rice-oilseed rape cropping system. J Environ Sci 20:149–155
Li H, Liang X, Chen Y, Tian G, Zhang Z (2008b) Ammonia volatilization from urea in rice fields with zero-drainage water management. Agr Water Manag 95:887–894
Li J, Shi Y, Luo J, Li Y, Wang L, Lindsey S (2019) Effects of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on the abundance of ammonia oxidizers and denitrifiers in two different intensive vegetable cultivation soils. J Soils Sediments 19:1250–1259
Liu J, Ouyang X, Shen J, Li Y, Sun W, Jiang W, Wu J (2020) Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses were influenced by chemical fertilization but not by pesticide application in a double rice-cropping system in the subtropical hilly region of China. Sci Total Environ 715:136852
Macadam XMB, Ad P, Merino P, Estavillo JM, Pinto M, González-Murua C (2003) Dicyandiamide and 3,4-dimethyl pyrazole phosphate decrease N2O emissions from grassland but dicyandiamide produces deleterious effects in clover. J Plant Physiol 160:1517–1523
Marsden KA, Marín-Martínez AJ, Vallejo A, Hill PW, Jones DL, Chadwick DR (2016) The mobility of nitrification inhibitors under simulated ruminant urine deposition and rainfall: a comparison between DCD and DMPP. Biol Fertil Soils 52:491–503
Merino P, Merino P, Menéndez S, Pinto M, González-Murua C, Estavillo JM (2005) 3, 4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate reduces nitrous oxide emissions from grassland after slurry application. Soil Use Manag 21:53–57
Nair D, Baral KR, Abalos D, Strobel BW, Petersen SO (2020) Nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions from maize after grass-clover on a coarse sandy soil: Mitigation potentials of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP). J Environ Manag 260:110165
Qiao C, Liu L, Hu S, Compton JE, Greaver TL, Li Q (2015) How inhibiting nitrification affects nitrogen cycle and reduces environmental impacts of anthropogenic nitrogen input. Glob Chang Biol 21:1249–1257
Rodríguez VA, Luaces PA, Píccoli AB, Mazza SM, Martínez GC (2011) 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) efficiency in sweet orange in Argentina northeast. Rev Bras Frutic 33:1344–1349
Rowlings DW, Scheer C, Liu S, Grace PR (2016) Annual nitrogen dynamics and urea fertilizer recoveries from a dairy pasture using 15N; effect of nitrification inhibitor DMPP and reduced application rates. Agric Ecosyst Environ 216:216–225
Selbie DR, Buckthought LE, Shepherd MA (2015) The challenge of the urine patch for managing nitrogen in grazed pasture systems. Adv Agron 129:229–292
Shi X, Hu HW, Müller C, He JZ, Chen D, Suter HC (2016) effects of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate on nitrification and nitrifiers in two contrasting agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:5236–5248
Suter HC, Sultana H, Davies R, Walker C, Chen D (2016) Influence of enhanced efficiency fertilisation techniques on nitrous oxide emissions and productivity response from urea in a temperate Australian ryegrass pasture. Soil Res 54:523–532
Tian G, Cai Z, Cao J, Li X (2001) Factors affecting ammonia volatilisation from a rice-wheat rotation system. Chemosphere 42:123–129
Vilas MP, Verburg K, Thorburn PJ, Probert ME, Bonnett GD (2019) A framework for analysing nitrification inhibition: a case study on 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP). Sci Total Environ 672:846–854
Vitale L, Ottaiano L, Polimeno F, Maglione G, Amato U, Arena C, di Tommasi P, Mori M, Magliulo V (2013) Effects of 3,4-dimethylphyrazole phosphate-added nitrogen fertilizers on crop growth and N2O emissions in Southern Italy. Plant Soil Environ 59:517–523
Weiske A, Benckiser G, Herbert T, Ottow J (2001) Influence of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) in comparison to dicyandiamide (DCD) on nitrous oxide emissions, carbon dioxide fluxes and methane oxidation during 3 years of repeated application in field experiments. Biol Fertil Soils 34:109–117
Wu SF, Wu LH, Shi QW, Wang ZQ, Chen XY, Li YS (2007) Effects of a new nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on nitrate and potassium leaching in two soils. J Environ Sci 19:841–847
Xu C, Wu LH, Ju XT, Zhang FS (2005) Role of nitrification inhibitor DMPP (3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate) in NO3---N accumulation in greengrocery (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis) and vegetable soil. J Environ Sci 17:81–83
Xu J, Zhu T, Xue W, Ni D, Sun Y, Yang J, Xu L, Chen X, Li H, Liu M (2019) Influences of nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) and application method on nitrogen dynamics at the centimeter-scale. Eur J Agron 90:44–50
Xue Y, Wu ZJ, Zhang LL, Gong P, Dong XX, Nie YX (2012) Inhibitory effect of DMPP on soil nitrification as affected by soil moisture content, pH and organic matter. Chin J Appl Ecol 23:2663–2669
Yang J, Li X, Xu L, Hu F, Li H, Liu M (2012) Influence of the nitrification inhibitor DMPP on the community composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria at microsites with increasing distance from the fertilizer zone. Biol Fertil Soils 49:23–30
Yang M, Fang Y, Sun D, Shi Y (2016) Efficiency of two nitrification inhibitors (dicyandiamide and 3, 4-dimethypyrazole phosphate) on soil nitrogen transformations and plant productivity: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 6:22075
Yu Q, Chen Y, Ye X, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Tian P (2007) Evaluation of nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethyl pyrazole phosphate on nitrogen leaching in undisturbed soil columns. Chemosphere 67:872–878
Funding
This work was financed by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41671300), National Key Research and Development Plan of China (2016YFD0200804), and Science and technology cooperation project of agricultural and rural Department of Zhejiang Province (2018SNLF027). Shaoxian Wang is grateful for funding from Open Fund from Key Laboratory for Water Pollution Control and Environmental Safety.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants and/or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Weixin Ding
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 245 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Chen, X., Liu, C. et al. Effect of various doses of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate on mineral nitrogen losses in two paddy soils. J Soils Sediments 20, 3825–3834 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02711-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02711-2