Abstract
Purpose
Different amendments have diverse adsorption capacity for heavy metals. The objectives of this study were to evaluate adsorption efficiency of different kinds of amendments for heavy metals and to provide theoretical guidance for alleviation of heavy metals.
Materials and methods
The indoor oscillating experiments were carried out to investigate the adsorption efficiency of five amendments (i.e., lime, illite ilerite, ground phosphate rock, chitin, and corn straw charcoal) for adsorption capacity of heavy metals (i.e., Zn, Pb, and Cd).
Results and discussion
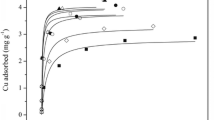
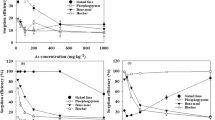
The adsorption efficiency of lime for Zn and Cd was 99.64% and 99.99% followed by chitin with adsorption efficiency of 74.94% and 81.63% respectively. The adsorption efficiency of amendments for Pb, Zn, and Cd was increased gradually with adsorption time. The adsorption efficiency has gradually reached a stable stage after certain time. In addition to adsorption of Pb by corn straw charcoal, the other four materials (i.e., lime, illite ilerite, ground phosphate rock, and chitin) have reached equilibrium when pH value was 3. The adsorption efficiency of lime (1%) for Zn was highest (99.98%). The adsorption efficiency of other materials for Pb was enhanced with increase in dosage except for chitin; however, the unit adsorption capacity was not decreased.
Conclusions
It is concluded that adsorption efficiency of lime and chitin for heavy metals such as Zn, Pb, and Cd was more than illite ilerite, ground phosphate rock, and corn straw charcoal, which can be considered as an active sorption materials.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barriada JL, Herrero R, Prada-Rodríguez D et al (2010) Waste spider crab shell and derived chitin as low-cost materials for cadmium and lead removal. J Chem Technol Biot 82:39–46
Chao X, Qian X, Han-hua Z, Shuai W, Qi-hong Z, Dao-you H, Yang-zhu Z (2018) Effect of biochar from peanut shell on speciation and availability of lead and zinc in an acidic paddy soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 164:554–561
Chen G, Shah KJ, Shi L, Chiang PC (2017) Removal of cd (II) and Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions by synthetic mineral adsorbent: performance and mechanisms. Appl Surf Sci 409:296–305
Chen J, Peng D, Shafi M et al (2015) Phytoremediation potential of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) for zinc and ultrastructure changes under zinc toxicity. Russ J Ecol 46:444–449
Chiu AC, Akesseh R, Moumouni IM et al (2019) Laboratory assessment of rice husk ash (RHA) in the solidification/stabilization of heavy metal contaminated slurry. J Hazard Mater 371:62–71
El Kadib A (2015) Chitosan as a sustainable Organocatalyst: a concise overview. Chemsuschem 8:217–244
Fang Y, Cao X, Zhao L (2012) Effects of phosphorus amendments and plant growth on the mobility of Pb, Cu, and Zn in a multi-metal-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut R 19:1659–1667
Houben D, Pircar J, Sonnet P (2012) Heavy metal immobilization by cost-effective amendments in a contaminated soil: effects on metal leaching and phytoavailability. J Geochem Explor 123:87–94
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013) Mobility, bioavailability and pH-dependent leaching of cadmium, zinc and lead in a contaminated soil amended with biochar. Chemosphere 92:1450–1457
Irani M, Ismail H, Ahmad Z, Fan M (2015) Synthesis of linear low-density polyethylene-g-poly (acrylic acid)-co-starch/organo-montmorillonite hydrogel composite as an adsorbent for removal of Pb (ΙΙ) from aqueous solutions. J Environ Sci (China) 27:9–20
Kong L-L, Liu W-T, Zhou Q-X (2014) Biochar: an effective amendment for remediating contaminated soil. Rev Environ Contam T228:83–99
Lei M, Peng L, Tie B et al (2017) Effect of mineral-based amendments on rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth and cadmium content in plant and polluted soil. Environ Eng Sci 34:854–860
Li S, Islam E, Peng D et al (2015) Accumulation and localization of cadmium in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) grown hydroponically. Acta Physiol Plant 37:56
Li YC, Li YF, Chang SX, Yang Y, Fu S, Jiang P, Luo Y, Yang M, Chen Z, Hu S, Zhao M, Liang X, Xu Q, Zhou G, Zhou J (2018a) Biochar reduces soil heterotrophic respiration in a subtropical plantation through increasing soil organic carbon recalcitrancy and decreasing carbon-degrading microbial activity. Soil Biol Biochem 122:173–185
Li YF, Hu SD, Chen JH, Müller K, Li Y, Fu W, Lin Z, Wang H (2018b) Effects of biochar application in forest ecosystems on soil properties and greenhouse gas emissions: a review. J Soils Sediments 18:546–563
Liu D, Chen J, Mahmood Q, Li S, Wu J, Ye Z, Peng D, Yan W, Lu K (2014a) Effect of Zn toxicity on root morphology, ultrastructure, and the ability to accumulate Zn in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Environ Sci Pollut R 21:13615–13624
Liu D, Li S, Islam E, Chen JR, Wu JS, Ye ZQ, Peng DL, Yan WB, Lu KP (2015) Lead accumulation and tolerance of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) seedlings: applications of phytoremediation. J Zhejiang Univ-Sc B 16:123–130
Liu H, Xu F, Xie Y, Wang C, Zhang A, Li L, Xu H (2018) Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 645:702–709
Liu T, Liu B, Zhang W (2014b) Nutrients and heavy metals in biochar produced by sewage sludge pyrolysis: its application in soil amendment. Pol J Environ Stud 23:271–275
Moghal AAB, Reddy KR, Mohammed SAS, al-Shamrani MA, Zahid WM (2016) Lime-amended semi-arid soils in retaining copper, lead, and zinc from aqueous solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:372
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth T (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Naidu R, Bolan NS, Kookana RS et al (2010) Ionic-strength and pH effects on the sorption of cadmium and the surface charge of soils. Eur J Soil Sc 45:419–429
Park J-H, Ok YS, Kim S-H, Cho JS, Heo JS, Delaune RD, Seo DC (2016) Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 142:77–83
Ping L, Man L, Wang XX et al (2016) Sorption and desorption of copper and cadmium in a contaminated soil affected by soil amendments. Clean Soil, Air, Water 44:1547–1556
Puga AP, Melo LCA, Abreu CAD et al (2016) Leaching and fractionation of heavy metals in mining soils amended with biochar. Soil Till Res 164:S0167198716300083
Ravandi SAH, Kalantari S, Izadan H et al (2014) Optimization of the parameters involved in the removal of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) ions from aqueous solutions using nanofibrous membrane of Sulfonated poly (ethylene terephthalate). Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 4:103
Salameh Y, Albadarin AB, Allen S et al (2015) Arsenic (III, V) adsorption onto charred dolomite: charring optimization and batch studies. Chem Eng J 259:663–671
Sofiane B, Sofia K (2015) Biosorption of heavy metals by chitin and the chitosan. Dev Pharma Chemica 7:54–63
Song L, Han Z, Zhang W et al (2018) Remediation of Cd-contaminated cropland soil in northern China via the amendment of modified biofuel ash. J Agro Environ Sci 37:1484–1494
Sulyman M, Namiesnik J, Gierak A (2017) Low-cost adsorbents derived from agricultural by-products/wastes for enhancing contaminant uptakes from wastewater: a review. Pol J Environ Stud 26:479
Van Poucke R, Egene CE, Allaert S, et al (2018): Application of cow manure biochar to stabilize Cd and Zn in smelter contaminated soil, Internation Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environ, July 22–25, 2018 Athens, GA USA, pp 1
Wang R, Shafi M, Ma J, Zhong B, Guo J, Hu X, Xu W, Yang Y, Ruan Z, Wang Y, Ye Z, Liu D (2018) Effect of amendments on contaminated soil of multiple heavy metals and accumulation of heavy metals in plants. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:28695–28704
Xi Y, Wang H, Guo L et al (2018) Utilization of cement and other additives for solidification/stabilization of soil contaminated simultaneously with Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions. Environ Prot Eng 44:61
Xu W, Shafi M, Penttinen P et al (2019) Bioavailability of heavy metals in contaminated soil as affected by different mass ratios of biochars. Environ Technol 13:1–9
Yan W, Liu D, Peng D, Mahmood Q, Chen T, Wang Y, Li S, Chen J (2016) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in the farmland along mineral product transportation routes in Zhejiang, China. Soil Use Manag 32:338–349
Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H et al (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. EnvironPollut 159:84–91
Zhang H, Wang Z, Gao J et al (2016) Adsorption characteristics of norfloxacin by biochars derived from reed straw and municipal sludge. Environ Sci 37:689–696
Zhang R, Zhang Y, Song L, Song X, Hänninen H, Wu J (2017) Biochar enhances nut quality of Torreyagrandis and soil fertility under simulated nitrogen deposition. Forest Ecol Manag 391:321–329
Zhang R, Zhao Y, Lin J et al (2019) Biochar application alleviates unbalanced nutrient uptake caused by N deposition in Torreyagrandis trees and seedlings. Forest Ecol Manag 432:319–326
Zhang X, Wang H, He L, Lu K, Sarmah A, Li J, Bolan NS, Pei J, Huang H (2013) Using biochar for remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals and organic pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:8472–8483
Zhao K, Fu W, Qiu Q, Ye Z, Li Y, Tunney H, Dou C, Zhou K, Qian X (2019) Spatial patterns of potentially hazardous metals in paddy soils in a typical electrical waste dismantling area and their pollution characteristics. Geoderma 337:453–462
Zhong B, Chen J, Shafi M et al (2017) Effect of lead (Pb) on antioxidation system and accumulation ability of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Ecotox Environ Safe 138:71–77
Zhu Z, Pan X, Peng Z (2018) Cadmium passivation by four Passivators: isotherm adsorption, desorption and mechanisms. Mater Sci Eng R 394:052062
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from key research and development project of Science Technology Department of Zhejiang province (grant number 2018C03028), Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 31670617), and key research and development project of Science Technology Department of Zhejiang province (grant number 2015C03020-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This research does not involve studies with human participants and/or animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Yong Sik Ok
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 394 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Ma, J., Shafi, M. et al. Effects of adsorption characteristics of different amendments on heavy metals (Pb, Zn, and Cd). J Soils Sediments 20, 2868–2876 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02620-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02620-4