Abstract
Purpose
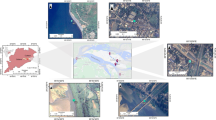
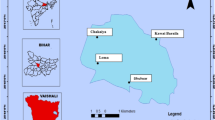
Texcoco saline lake in Mexico is an important habitat for over 300 species and recharges the Mexico City aquifer. Presently, it is on the verge of disappearance due to increasing anthropogenic pressure and comprises only a few wetland remnants. The impacts of human activities on these wetlands are unknown and uninvestigated. In this regard, this study investigates the degree of metal contamination in this ecosystem during the period of 2015–2018.
Materials and methods
Twenty-six sediment samples were collected from nine different wetlands of Texcoco Lake and examined for 17 metals (Al, Fe, Ca, Mg, Na, K, As, Ba, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn, and Hg) using atomic absorption spectroscopy. The degree of metal accumulation and its ecological risks were evaluated on the basis of several indicators (geoaccumulation index, enrichment factor, sediment quality guidelines, ecotoxicological values, and potential ecological risk index). Furthermore, co-occurrence via multivariate statistical techniques was employed using the measured metal concentrations to identify their possible sources.
Results and discussion
The Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, and Hg sediment concentrations were higher in magnitude than the background North American shale composite values, suggesting their external origin in all studied sediments. According to the calculated enrichment factors and geoaccumulation index, the sediments were mostly contaminated with Cd and Hg. The sediment quality guidelines and ecotoxicological values together with the ecological risk index suggested probable adverse biological effects due to the presence of Cr, Cu, Ni, and Hg. Cadmium and Hg accounted for nearly 51 and 45% of the ecological threat in the sediments. Based on the knowledge about metal levels and co-occurrence in different matrices and the multivariate data analyses of the detected metal concentrations, we infer that the main sources of metals are as follows: (1) Solonchaks and Vertisol soil types (Ca, Mg, Na, and K); (2) urban-industrial effluents from surrounding municipalities and Mexico City (Cu, Pb, and Zn); and (3) industrial discharges of Xalostoc zone (Cd and Hg) near Texcoco.
Conclusions
Our results emphasize the impacts of unregulated discharges from municipal, industrial, and metropolitan zones of Mexico City and construction activities for the elevated metal concentrations in the wetland sediments of Texcoco Lake.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuduwaili J, Zhang ZY, Jiang FQ (2015) Assessment of the distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the dry surface sediment of Aibi Lake in Northwest China. PLoS One 10(3):e0120001. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120001
Akpor OB, Ohiobor GO, Olaolu TD (2014) Heavy metal pollutants in wastewater effluents: sources, effects and remediation. Adv Biol Bioeng 2(4):37–43
Alcántara C, Escalante-Pliego P (2005) Current threats to the Lake Texcoco globally important bird area. In: CJ Ralph y TD Rich (eds) Bird conservation implementation and integration in the Americas. Proceedings of the third international partners in flight conference, 2002 March 20-24; Asilomar, California, volume 2. General technical report PSW-GTR-191. Department of Agriculture, Forest service, Pacific Southwest Research Station. Albany, California, pp 1143-1150.
Alcocer J, Escobar E (1990) The drying up of the Mexican plateau axalapazcos. Salinet 4:44–46
Alcocer J, Williams WD (1996) Historical and recent changes in Lake Texcoco, a saline lake in Mexico. Int J Salt Lake Res 5:45–61
Alharbi T, El-Sorogy A (2017) Assessment of metal contamination in coastal sediments of Al-Khobar area, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. J Afr Earth Sci 129:458–468
Aydinalp C, Cresser MS (2009) Distribution of heavy metals in irrigated vertisol profiles in semiarid region of Turkey. Pol J Environ Stud 18(4):539–545
Bastami KD, Neyestani MR, Molamohyedin N, Shafeian E, Haghparast S, Shirzadi IA, Baniamam M (2018) Bioavailability, mobility, and origination of metals in sediments from Anzali Wetland, Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 136:22–32
Belmont MA, Cantellano E, Thompson S, Williamson M, Sánchez A, Metcalfe CD (2004) Treatment of domestic wastewater in a pilot-scale natural treatment system in Central Mexico. Ecol Eng 23:299–311
Birch GF (2018) A review of chemical-based sediment quality assessment methodologies for the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 133:218–232
Bocquier G (1972) Genèse et évolution de deux toposéquences de sols tropicaux du Tchad, interprétation biogéodynamique. Mém. ORSTM 67, Paris, France, 350 pp
Boros E, V-Balogh K, Voros L, Horvath ZS (2017) Multiple extreme environmental conditions of intermittent soda pans in the Carpathian Basin (Central Europe). Limnology 62:38–46
Boulet R (1978) Toposéquences de sols tropicaux en Haute-Volta: équilibres dynamiques et bioclimats. Mém. ORSTOM 85, Paris, France, 272 pp
Buat-Ménard P, Chesselet R (1979) Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet Sci Lett 42:398–411
Buccolieri A, Buccolieri G, Cardellicchio N, Atti AD, Leo AD, Maci A (2006) Heavy metals in marine sediments of Taranto Gulf (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Mar Chem 99:227–235
Bühmann C, Schoeman JL (1995) A mineralogical characterization of vertisols from the northern regions of the republic of South Africa. Geoderma 66:239–257
Chai L, Li H, Yang Z, Min X, Liao Q, Liu Y, Men S, Yan Y, Xu J (2017) Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:874–885
Cheng WH, Yap CK (2015) Potential human health risks from toxic metals via mangrove snail consumption and their ecological risk assessments in the habitat sediment from Peninsular Malaysia. Chemosphere 135:156–165
Cheung K, Poon B, Lan C, Wong M (2003) Assessment of metal and nutrient concentrations in river water and sediment collected from the cities in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Chemosphere 52:1431–1440
CONAGUA (2015) Actualización de la disponibilidad media anual de agua en la acuífero Texcoco (1507), Estado de México. https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/103138/DR_1507.pdf
Cortés Martínez F, Treviño Cansino A, Luévanos Rojas A, Luévanos Rojas R, Uranga Sifuentes AC (2014) Objective function in the design of the facultative lagoon (case study). Rev Mex Cienc Agríc 5(3)
Dabrin A, Durand CL, Garric J, Geffard O, Ferrari BJD, Coquery M (2012) Coupling geochemical and biological approaches to assess the availability of cadmium in freshwater sediment. Sci Total Environ 424:308–315
DDF (Departamento del Distrito Federal) (1975) Memoria de las obras del sistema de drenaje profundo. Talleres gráficos de la nación, México. Volumes: I, II and IV
Delgado J, Nieto JM, Boski T (2010) Analysis of the spatial variation of heavy metals in the Guadiana estuary sediments (SW Iberian Peninsula) based on GIS mapping techniques. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 88:71–83
Delshab H, Farshchi P, Keshavarzi B (2017) Geochemical distribution, fractionation and contamination assessment of heavy metals in marine sediments of the Asaluyeh port, Persian Gulf. Mar Pollut Bull 115:401–411
Deocampo DM, Jones BF (2014) Geochemistry of saline lakes. Treatise on geochemistry, 2nd edn, pp 437–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-095975-7.00515-5
Domagalski JL, Eugster HP (1990) Trace metal geochemistry of Walker, Mono, and Great Salt Lakes. Fluid-mineral interactions: a tribute to H. P. Eugster. The Geochemical Society, Special Publication No 2:315–353
Dou Y, Li J, Zhao J, Hu B (2013) Distribution, enrichment and source of heavy metals in surface sediments of the eastern Beibu Bay, South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 67:137–145
Duncan AE, Vries N, Nyarko KB (2018) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediments of the river Pra and its tributaries. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:272
ElNemr AH, El Sikaily A, Khaled A (2007) Total and leachable heavy metals in muddy and sandy sediments of Egyptian coast along Mediterranean Sea. J Coast Shelf Sci 129:151–168
EPA Method 3051A (2007) Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, solids and oils. Revision 1, Feb, 2007, Washington, DC, USA, pp 1–30
Esteller MV, Diaz-Delgado C (2002) Environmental effects of aquifer overexploitation: a case study in the highlands of Mexico. Environ Manag 29(2):266–278
FAO (2010) La clasificación FAO-WRB y los suelos del Estado de México. 1–158
Fernández-Bucesa N, Siebea C, Cramb S, Palacio JL (2006) Mapping soil salinity using a combined spectral response index for bare soil and vegetation: a case study in the former lake Texcoco, Mexico. J Arid Environ 65:644–667
GACM (2018) Acciones de monitoreo y conservación de aves para el proyecto nuevo aeropuerto internacional de la Ciudad de México en la etapa de preparación del sitio y construcción. https://lopezobrador.org.mx/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/1.-Informe-de-Acciones-de-Monitoreo-y-Conservaci%C3%B3n-de-Aves_GACM_NAIM-1.pdf
González-Morán T, Rodríguez R, Cortes SA (1999) The basin of Mexico and its metropolitan area: water abstraction and related environmental problems. S Am Earth Sci 12(6):607–613
Grant WD (2004) Half a lifetime in Soda Lakes. In: Ventosa A (ed) Halophilic microorganisms. Springer, Berlin, pp 17–31
Grant WD (2006) Alkaline environments and biodiversity, in extremophilies. In: Charles G, Nicolas G (eds) Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS) Developed under the Auspices of the UNESCO. Eolss Publishers, Oxford http://www.eolss.net
Gromet LP, Haskin LA, Korotev RL, Dymek RF (1984) The “North American shale composite”: its compilation, major and trace element characteristics. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48(12):2469–2482
Gross M (2017) The world’s vanishing lakes. Curr Biol 27:43–46
Gutiérrez-Yurrita PJ, López MA (2011) Reflexiones ambientalistas sobre los criterios para proponer espacios naturales protegidos: hacia una nueva categoría de conservación, el paisaje místico. Rev Aranzadi Der Amb 20(2):19–42
Habes G, Nugem Y (2006) Assessing Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, and Cd pollution in bottom sediments of Wadi Al-Arab Dam, Jordan. Chemosphere 65:2114–2121
Haglund A-L, Lantz P, Törnblom E, Tranvik L (2003) Depth distribution of active bacteria and bacterial activity in lake sediment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 46:31–38
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk assessment index for aquatic contamination control, a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Int Toxicol 7(2):60–72
Jellison R, Williams WD, Timms B, Alocer J, Aladin NV (2008) In: Polunin NVC (ed) Aquatic ecosystems: trends and global prospects. Cambridge Univ. Press, pp 94–112
Khodami S, Surif M, Wan MWO, Daryanabard R (2017) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Bayan Lepas area, Penang, Malaysia. Mar Pollut Bull 114(1):615–622
Li X, Wai O, Li Y, Coles B, Ramsey M, Thornton I (2000) Heavy metal distribution in sediment profiles of the Pearl River estuary, South China. Appl Geochem 15:567–581
Li H, Shi A, Li M, Zhang X (2013) Effect of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and flow rate of overlying water on heavy metals release from storm sewer sediments. J Chem Article ID 434012
Lira BP, Polo AO, Sánchez EMO, Ruiz ER, Sandoval OAA, García FP, Ramírez CAG (2013) Physical characterization of an extensive volcanic rock in México: “red tezontle” from Cerro de la Cruz, in Tlahuelilpan, Hidalgo. Acta Univ 23(4):9–16
Liu J, Wu H, Feng J, Li Z, Lin G (2014) Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessments in the sediments and zoobenthos of selected mangrove ecosystems, South China. Catena 119:136–142
Long ER, MacDonanld DD, Smith S, Calder F (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manag 19:81–97
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Krishnakumar S, Peter TS (2017) Trace element contamination in the nearshore sediments of the Tamiraparani estuary, southeast coast of India. Mar Pollut Bull 116:508–516
Mahu E, Nyarko E, Hulme S, Coale KH (2015) Distribution and enrichment of trace metals in marine sediments from the Eastern Equatorial Atlantic, off the Coast of Ghana in the Gulf of Guinea. Mar Pollut Bull 98:301–307
Mancini F, Stecchi F, Zanni M, Gabbianelli G (2009) Monitoring ground subsidence induced by salt mining in the city of Tuzla (Bosnia and Herzegovina). Environ Geol 58:381–389
Marín-Guirao L, Atucha AM, Barba JL, López EM, García Fernández AJ (2005) Effects of mining wastes on a seagrass ecosystem: metal accumulation and bioavailability, seagrass dynamics and associated community structure. Mar Environ Res 60:317–337
Miloud SH, Djili K, Benidir M (2018) Fuzzy logic expert system for classifying solonchaks of Algeria. Appl Environ Soil Sci Article ID 8741567
Mugai EN (2004) Salinity characterization of the Kenyan saline soils. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 50(2):181–188
Muller G (1979) Heavy metals in the sediment of the Rhine—changes seity. 1971.4j 79:778–783
Mustafa G, Singh B, Kookana RS (2004) Cadmium adsorption and desorption behavior on goethite at low equilibrium concentrations: effects of pH and index cations. Chemosphere 57:1325–1333
Navarrete-López M, Jonathan MP, Rodríguez-Espinosa PF, Salgado-Galeana JA (2012) Autoclave decomposition method for metals in soils and sediments. Environ Monit Assess 184:2285–2293
Ochieng EZ, Lalah JO, Wandiga SO (2007) Analysis of heavy metals in water and surface sediment in five Rift Valley lakes in Kenya for assessment of recent increase in anthropogenic activities. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:570–576
Ortiz-Polo A, Richards-Uribe RM, Otazo-Sánchez EM, Prieto-García F, Hernández-Ávila J, Acevedo-Sandoval O (2007) New organic-inorganic materials for water contaminants remediation. Mater Res Soc 1007:8
Padilla RJ, Sanchez (1989) Geology and tectonics of the basin of Mexico and their relationship with the damage caused by the earthquakes of September 1985. Int J Min Geol Eng 7:17–28
Paul VG, Mormile MR (2017) A case for the protection of saline and hypersaline environments: a microbiological perspective. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93
Pejman A, Bidhendi GN, Ardestani M, Saeedi M, Baghvand A (2015) A new index for assessing heavy metals contamination in sediments: a case study. Ecol Indic 58:365–373
Philip JYN, Mosha DMS (2012) Salt Lakes of the African Rift system: a valuable research opportunity for insight into nature’s concentrated multi-electrolyte science. Tanz J Sci 38(3):1–13
Reghunath R, Murthy TRS, Raghavan BR (2002) The utility of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies: an example from Karnataka, India. Water Res 36:2437–2442
RETC-SEMERNAT (2017) https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/acciones-y-programas/registro-de-emisiones-y-transferencia-de-contaminantes-retc
RETC-SEMERNAT (2018) https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/acciones-y-programas/registro-de-emisiones-y-transferencia-de-contaminantes-retc
Rivera-Vázquez R, Palacios-Vélez OL, Chávez Morales J, Belmont MA, Nikolski-Gavrilov I, De La Isla De Bauer ML, Guzmán-Quintero A, Terrazas-Onofre L, Carrillo-Gonzalez R (2007) Contaminación por coliformes y helmintos en los ríos Texcoco, Chapingo y San Bernardino tributarios de la parte oriental de la cuenca del valle de México. Rev Int Contam Ambient 23(2):69–77
Rodriguez-Hernandez CM, Fernandez-Caldas E, Fedoroff N, Quantin P (1979) Les vertisols des Iles Canaries Occidentales. Etude physico-chimique, mineralogique et micro-mor-phologique. Pédologie 24:71–107
Ruiz-Romero E, Alacántara-Hernández R, Cruz-Mondragon C, Marsch R, Luna-Guido ML, Dendooven L (2009) Denitrification in extreme alkaline saline soils of the former lake Texcoco. Plant Soil 319(1–2):247–257
Salas PM, Sujatha CH, Ratheesh Kumar CS, Cheriyan E (2017) Heavy metal distribution and contamination status in the sedimentary environment of Cochin estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 119:191–203
San Román J, Muñoz-Sevilla NP, Marín-García L, López-Flores M, Gutiérrez-Yurrita PJ (2013) Integrated environmental studies to propose large-scale zoning for managing the Texcoco Lake ecological park, Mexico. Int J Ecol Environ Sci 39(1):23–36
Schagerl M, Burian A (2016) The ecology of African soda lakes: driven by variable and extreme conditions, chapter14. In: Schagerl M (ed) Soda lakes of East Africa. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, pp 295–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28622-8_12
Sedeño-Díaz JE, Rodríguez-Romero AJ, Mendoza-Martínez E, López-López E (2016) Chemometric analysis of wetlands remnants of the former Texcoco Lake: a multivariate approach. Lake Sci Clim Chang:135–153
SEMARNAT (United States Fish and Wildlife Service, Canadian Wildlife Service and Secretaria de Medio Ambiente Y Recursos Naturales, Mexico) (2012) Guide of North American waterfowl management plan: landscape approach. 230 pages
Sorokin Kravchenko IK, Doroshenko EV, Boulygina ES, Zadorina EV, Tourova TP, Sorokin DY (2008) Haloalkaliphilic diazotrophs in soda solonchak soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65:425–433
Sotelo Ruíz ED, Hernández AG, Bello GC, Sánchez FM, Cárdenas GC (2011) The soils of Mexico State and their update to the world reference base for soil resources 2006. Rev Mex Cienc Farm 2:8
Srinivas R, Shynu R, Sreeraj SK, Ramachandran KK (2017) Trace metal pollution assessment in the surface sediments of nearshore area, off Calicut, southwest coast of India. Mar Pollut Bull 120:370–375
Srinivasarao C, Gayatri SR, Venkateswarlu B, Jakkula VS, Wani SP, Kundu S, Sahrawat KL, Rajasekhara Rao BK, Marimuthu S, Gopala Krishna G (2013) Heavy metals concentration in soils under rainfed agro-ecosystems and their relationship with soil properties and management practices. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:7
Steger K, Premke K, Gudasz C, Sundh I, Tranvik LJ (2011) Microbial biomass and community composition in boreal lake sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 56:725–733
Stojanovic A, Kogelnig D, Mitteregger B, Mader D, Jirsa F, Krachler R, Krachler R (2009) Major, trace element geochemistry of superficial sediments, and suspended particulate matter of shallow saline lakes in Eastern Austria. Chem Erde 69:223–234
Surakasi VP, Wani AA, Shouche YS, Ranade DR (2007) Phylogenetic analysis of methanogenic enrichment cultures obtained from Lonar lake in India: isolation o Methanocalculus sp. and Methanoculleus sp. Microb Ecol 54:697–704
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. EXS 101:133–164
Thakur SK, Tomar NK, Pandeya SB (2006) Influence of phosphate on cadmium sorption by calcium carbonate. Geoderma 130:240–249
Thiry M (2000) Palaeoclimatic interpretation of clay minerals in marine deposits: an outlook from the continental origin. Earth Sci Rev 49:201–221
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USPEA) (2001) The role of screening level risk assessments and refining contaminants of concern in baseline ecological risk assessments publications. 9345-014, EPA 540/F-01/14, June 2001
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Vega M, Pardo R, Barrado E, Deban L (1998) Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Res 32:3581–3359
Wang H, Wang J, Liu R, Yu W, Shen Z (2015) Spatial variation, environmental risk and biological hazard assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Yangtze River estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 93:250–258
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: lake and river ecosystems. Academic Press, –San Diego
Williams WD (1993) Conservation of salt lakes. Hydrobio 267:292–306
Williams WD (2002) Environmental threats to salt lakes and the likely status of inland saline ecosystems in 2025. Environ Conserv 2:154–167
Wurtsbaugh WA, Miller C, Null SE, DeRose RJ, Wilcock P, Hahnenberger M, Howe F, Moore J (2017) Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1038/NGEO3052
Xu Y, Wu Y, Han J, Li P (2017) The current status of heavy metal in lake sediments from China: pollution and ecological risk assessment. Ecol Evol 7:5454–5466
Yang J, Ma L, Jiang H, Wu G, Dong H (2016) Salinity shapes microbial diversity and community structure in surface sediments of the Qinghai-Tibetan Lakes. Sci Rep 6:25078
Yerima BPK, Calhoun FG, Senkayi AL, Dixon JB (1985) Occurrence of interstratified kaolinite–smectite in El-Salvador vertisols. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:462–466
Zhang J, Liu CL (2002) Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China – weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54:1051–1070
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Liu C, Sun C, Zhang W, Marhaba T (2018) pH effect on heavy metal release from a polluted sediment. J Chem 7597640:7
Zhang H, Walker TR, Davis E, Ma G (2019) Ecological risk assessment of metals in small craft harbour sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada. Mar Pollut Bull 146:466–475
Zhao X, Jiang T, Du B (2014) Effect of organic matter and calcium carbonate on behaviors of cadmium adsorption–desorption on/from purple paddy soils. Chemosphere 99:41–48
Zhuang Q, Li G, Liu Z (2018) Distribution, source and pollution level of heavy metals in river sediments from South China. Catena 170:386–339
Acknowledgments
EMO, SSMG, and JESD express their gratitude to Instituto Politécnico Nacional (IPN) for financial assistance. SSMG and JESD thanks IPN – Comisión de Operación y Fomento de Actividades Académicas (COFAA). SSMG wishes to thank Estímulos al Desempeño de los Investigadores (EDI). SSMG and VCS thank Sistema Nacional de Investigadores (SNI) CONACyT, México. VCS acknowledge CONACyT project Grant No. 274276 “Fase I De La Remediación de Áreas Contaminadas Con Hidrocarburos En La Refinería Gral. Lázaro Cárdenas” for postdoctoral fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Sophie Ayrault
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
Correlation matrix analysis of sediments from Texcoco saline Lake, Mexico (DOCX 15 kb)
Supplementary Figure 1
Factor score loadings for metals in sediments of Texcoco saline Lake, Mexico (JPG 44 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morales-García, S.S., Meza-Olvera, E., Shruti, V.C. et al. Assessment of metal contamination and their ecological risks in wetland sediments of the former Texcoco saline lake, Mexico. J Soils Sediments 20, 2912–2930 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02613-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02613-3