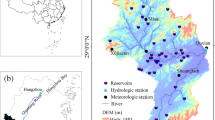
Abstract
Purpose
The trends in runoff and sediment transportation in typical Loess Plateau basins and the factors causing the changes need to be clarified.
Materials and methods
In this study, the runoff and sediment transportation data from 1960 to 2016, from hydrological stations (Wenjiachuan, Baijiachuan, Ganguyi, and Zhuangtou) based in four typical basins, were analyzed systematically using linear regression, anomaly accumulation, the Mann–Kendall test, and double accumulation curve. The characteristics of the runoff and sediment transportation and their responses to climatic and anthropogenic activities were investigated using several hydrological analytical and statistical methods.
Results and discussion
The results indicate that both runoff and sediment transportation in the four typical basins have decreased sharply from 1960 to 2016. Since the implementation of the Grain-for-Green Project in 1999, the reduction has been more marked, in particular the runoff and sediment discharge of the Kuye River (Wenjiachuan station). Compared with the period 1960–1999, the average annual runoff and sediment discharge in 2000–2016 had decreased by 76.72% and 94.50%, respectively. Apart from the Wuding River (Baijiachuan station), an abrupt change in runoff and sediment transportation in the basins occurred within 2–7 years of the implementation of the Grain-for-Green Project.
Conclusions
In general, returning farmland to forests (grass) has had a more pronounced effect on the reduction of runoff and sediment in the more northerly Kuye River (Wenjiachuan station) and Wuding River (Baijiachuan station) basins, compared with the more southerly Yanhe River (Ganguyi station) and Beiluo River (Zhuangtou station) basins.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burn DH, Elnur MAH (2002) Detection of hydrologic trends and variability. J Hydrol 255:107–122
Feng XM, Fu BJ, Lu N, Zeng Y, Wu BF (2013) How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: an analysis of carbon sequestration in China’s loess plateau. Sci Rep 3:2846
Feng XM, Cheng W, Fu BJ, Lü YH (2016a) The role of climatic and anthropogenic stresses on long-term runoff reduction from the loess plateau, China. Sci Total Environ 571:688–698
Feng XM, Fu BJ, Piao SL, Wang S, Ciais P, Zeng ZZ, Lü YH, Zeng Y, Li Y, Jiang XH, Wu BF (2016b) Revegetation in China’s loess plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat Clim Chang 6:1019–1022
Feng Q, Zhao WW, Ding JY, Fang XN, Zhang X (2017) Estimation of the cover and management factor based on stratified coverage and remote sensing indices: a case study in the loess plateau of China. J Soils Sediments 18:775–790
Fu BJ, Wang S, Liu Y, Liu JB, Liang W, Miao CY (2016) Hydrogeomorphic ecosystem responses to natural and anthropogenic changes in the loess plateau of China. Annu Rev Earth Pl Sc 45:223–243
Gao P, Mu X, Wang F, Li R (2011) Changes in streamflow and sediment discharge and the response to human activities in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 7:347–350
Gao P, Jiang GT, Wei YP, Mu XM, Wang F, Zhao GJ (2015) Streamflow regimes of the Yanhe River under climate and land use change, loess plateau, China. Hydrol Process 29:2402–2413
Gao P, Deng JC, Chai XK, Mu XM, Zhao GJ, Shao HB, Sun WY (2017) Dynamic sediment discharge in the Hekou–Longmen region of Yellow River and soil and water conservation implications. Sci Total Environ 578:56–66
Kendall MG (1990) Rank correlation methods. Brit J Psychol 25:86–91
Li BQ, Liang ZM, Zhang JY, Wang GQ, Zhao WM, Zhang HY, Wang J, Hu YM (2016) Attribution analysis of runoff decline in a semiarid region of the loess plateau, China. Theor Appl Climatol 131:845–855
Liu XY, Yang ST, Dang SZ, Luo Y, Li XY, Zhou X (2014) Response of sediment yield to vegetation restoration at a large spatial scale in the loess plateau. SCIENCE CHINA Technol Sci 57:1482–1489
Mann H (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13:245–259
Miao CY, Ni J, Borthwick AGL, Yang L (2011) A preliminary estimate of human and natural contributions to the changes in water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow River. Glob Planet Chang 76:196–205
Mu XM, Zhang L, Mcvicar TR, Chille B, Peng G (2007) Analysis of the impact of conservation measures on stream flow regime in catchments of the loess plateau, China. Hydrol Process 21:2124–2134
Mu XM, Zhang XQ, Gao P, Wang F (2010) The theory of double cumulative curves and the problems that should be paid attention to in the field of hydro-meteorology. Hydrol 30:47–51 in Chinese
Mu XM, Zhang XQ, Shao HB, Gao P, Wang F, Jiao JY, Zhu JL (2012) Dynamic changes of sediment discharge and the influencing factors in the Yellow River, China, for the recent 90 years. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 40:303–309
Ran LS, Wang SJ, Fan XL (2010) Channel change at toudaoguai station and its responses to the operation of upstream reservoirs in the upper Yellow River. J Geogr Sci 20:231–247
Ran DC, Zuo ZG, Wu YH, Li XM, Li ZH (2012) Recent change of streamflow and sediment responding to human activities in the middle Yellow River Basin. Science Press, Beijing, pp 71–76 in Chinese
Sun QH, Miao CY, Duan QY, Wang YF (2015) Temperature and precipitation changes over the loess plateau between 1961 and 2011, based on high-density gauge observations. Glob Planet Chang 132:1–10
Wang HJ, Yang ZS, Saito Y, Liu JP, Sun XX (2006a) Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50years: connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams. Glob Planet Chang 50:212–225
Wang L, Shao MA, Wang QJ, Gale WJ (2006b) Historical changes in the environment of the Chinese loess plateau. Environ Sci Pol 9:675–684
Wang GL, Liu GB, Xu MX (2009) Above-and belowground dynamics of plant community succession following abandonment of farmland on the loess plateau, China. Plant Soil 322:343–343
Wang HJ, Saito Y, Zhang Y, Bi NS, Sun XX, Yang ZS (2011a) Recent changes of sediment flux to the western Pacificocean from major rivers in east and Southeast Asia. Earth-Sci Rev 108:80–100
Wang L, Wei SP, Horton R, Shao MA (2011b) Effects of vegetation and slope aspect on water budget in the hill and gully region of the loess plateau of China. Catena 87:90–100
Wang F, Mu XM, Li R, Fleskens L, Stringer LC, Ritsema CJ (2015) Co-evolution of soil and water conservation policy and human–environment linkages in the Yellow River basin since 1949. Sci Total Environ 508:166–177
Wang S, Fu BJ, Liang W, Liu Y, Wang YF (2017) Driving forces of changes in the water and sediment relationship in the Yellow River. Sci Total Environ 576:453–461
Xin ZB, Ran LS, Lu XX (2012) Soil erosion control and sediment load reduction in the loess plateau: policy perspectives. Int J Water Resour D 28:325–341
Xu JX (2000) The wind-water two-phase erosion and sediment-producing processes in the middle Yellow River basin, China. Sci China Earth Sci 43:176–186
Xu JX (2011) Variation in annual runoff of the Wudinghe River as influenced by climate change and human activity. Quat Int 244:230–237
Yang KJ, Lu CH (2018) Evaluation of land-use change effects on runoff and soil erosion of a hilly basin — the Yanhe River in the Chinese loess plateau. Land Degrad Dev 29:58–61
Yao HF, Shi CX, Shao WW, Bai JB, Yang H (2016) Changes and influencing factors of the sediment load in the Xiliugou basin of the upper Yellow River, China. Catena 142:1–10
Yu PS, Yang TC, Wu CK (2002) Impact of climate change on water resources in southern Taiwan. J Hydrol 260:161–175
Yu YG, Wang HJ, Shi XF, Ran XB, Cui TW, Qiao SQ, Liu YG (2013) New discharge regime of the Huanghe (Yellow River): causes and implications. Cont Shelf Res 69:62–72
Yu GQ, Zhang MS, Li ZB, Li P, Zhang X, Cheng SD (2015) Piecewise prediction model for watershed-scale erosion and sediment yield of individual rainfall events on the loess plateau. China Hydrol Process 28:5322–5336
Zhang CC (2017) Soil moisture effect on the conversion of cropland to forest in the loess plateau. Dissertation, Center for Soil and Water Conservation and ecological environment research, Ministry of Education, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese)
Zhang XP, Zhang L, Zhao J, Rustomji P, Hairsine P (2008) Responses of streamflow to changes in climate and land use/cover in the loess plateau, China. Water Resour Res 44:2183–2188
Zhang C, Liu GB, Xue S, Wang GL (2015) Changes in rhizospheric microbial community structure and function during the natural recovery of abandoned cropland on the loess plateau, China. Ecol Eng 75:161–171
Zhang BQ, He CS, Burnham M, Zhang LH (2016) Evaluating the coupling effects of climate aridity and vegetation restoration on soil erosion over the loess plateau in China. Sci Total Environ 539:436–449
Zhang JQ, Yang MY, Sun XJ, Zhang FB (2017) Estimation of wind and water erosion based on slope aspects in the crisscross region of the Chinese loess plateau. J Soils Sediments 3–4:1–12
Zhao GJ, Mu XM, Strehmel A, Tian P (2014) Temporal variation of streamflow, sediment load and their relationship in the Yellow River basin, China. PLoS One 9:e91048
Zhou YY, Shi CX, Du J, Fan XL (2013) Characteristics and causes of changes in annual runoff of the Wuding river in 1956-2009. Environ Earth Sci 69:225–234
Zuo DP, Xu ZX, Yao WY, Jin SY, Xiao PQ, Ran DC (2016) Assessing the effects of changes in land use and climate on runoff and sediment yields from a watershed in the loess plateau of China. Sci Total Environ 544:238–250
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0501604), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41771545; 41530854), and the State Key Laboratory of Urban and Regional Ecology Open Foundation (No. SKLURE2016-2-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Rajith Mukundan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Q., Wang, L., Liu, H. et al. Runoff and sediment variation and attribution over 60 years in typical Loess Plateau basins. J Soils Sediments 19, 3631–3647 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02345-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02345-z