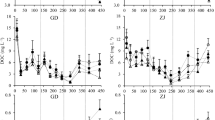
Abstract
Purpose
Crop straw return into arable land is a common method of disposing of excess straw in China and can improve soil dissolved organic matter (DOM) that is known to modify soil zinc (Zn) extractability and mobility.
Materials and methods
We conducted a soil box (internal dimensions, 160 × 140 × 80 mm3) experiment to evaluate the response of Zn extractability and transfer by diffusion to DOM after maize straw amendment (St, 0 and 15 g kg−1) in calcareous soil treated with ZnSO4·7H2O (Zn, 0 and 20 mg kg−1). Soil treated with St0Zn0 (control), St15Zn0, St0Zn20, or St15Zn20 was isolated in the 10-mm center of the box, and untreated soil was placed in compartments at either side.
Results and discussion
Results revealed that addition of St0Zn20 or St15Zn20 increased the concentration of Zn extracted with diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA-extractable Zn) in the central layer compared with control or addition of St15Zn0. Over the course of 45 days, transfer of DTPA-extractable Zn into the adjacent untreated soil was detected at 15–20 mm in soil with St15Zn20 but at 10–15 mm with St0Zn20 and only 0–5 mm with St15Zn0. Additionally, a higher amount of DTPA-extractable Zn transfer into the adjacent untreated soil also occurred in St15Zn20. This increased DTPA-extractable Zn transfer may be associated with the formation of Zn-fulvic acid complexes with the provision of DOM derived from straw.
Conclusions
Soluble Zn combined with straw return may be a promising strategy for improving both Zn mobility and extractability in calcareous soil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin KR, Shelton JE (1999) Availability of heavy metals in compost-amended soil. Bioresource Technol 69(1):1–14
Blake GR, Hartge KH (1986) Bulk density. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods, agronomy monograph no. 9, 2nd edn. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 363–375
Brown GK, MacCarthy P, Leenheer JA (1999) Simultaneous determination of Ca, Cu, Ni, Zn and Cd binding strengths with fulvic acid fractions by Schubert’s method. Anal Chim Acta 402:169–181
Cakmak I (2008) Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: agronomic or genetic biofortification? Plant Soil 302:1–17
Chantigny MH (2003) Dissolved and water-extractable organic matter in soils: a review on the influence of land use and management practices. Geoderma 113:357–380
Chen YL, Jia Z, Liu K, Tian XH, Wang S, Wang SX, Li XS, Zhao HL, Shar AG (2017) Response of exogenous zinc availability and transformation to maize straw as affected by soil organic matter. Soil Sci Soc Am J 81:814–827
Christensen JB, Christensen TH (1999) Complexation of Cd, Ni, and Zn by DOC in polluted groundwater: a comparison of approaches using resin exchange, aquifer material sorption, and computer speciation models (WHAM and MINTEQA2). Environ Science Technol 33:3857–3863
De Troyer I, Amery F, Moorleghem CV, Smolders E, Merckx R (2011) Tracing the source and fate of dissolved organic matter in soil after incorporation of a 13C labeled residue: a batch incubation study. Soil Biol Biochem 43:513–519
Deb SK, Shukla MK (2011) A review of dissolved organic matter transport processes affecting soil and environmental quality. J Environ Anal Toxicol 1:2161–2525
Degryse F, Verma VK, Smolders E (2008) Mobilization of Cu and Zn by root exudates of dicotyledonous plants in resin-buffered solutions and in soil. Plant Soil 306:69–84
Degryse F, Baird R, Mclaughlin MJ (2015) Diffusion and solubility control of fertilizer-applied zinc: chemical assessment and visualization. Plant Soil 386:195–204
Duffner A, Hoffland E, Weng L, Sjoerd TM (2013) Predicting zinc bioavailability to wheat improves by integrating pH dependent nonlinear root surface adsorption. Plant Soil 385:395–397
Fan TT, Wang YJ, Li CB, He JZ, Gao J, Zhou DM, Friedman SP, Sparks DL (2016) Effect of organic matter on sorption of Zn on soil: elucidation by Wien effect measurements and EXAFs spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 50(6):2931–2937
Feng MH, Shan XQ, Zhang S, Wen B (2005) A comparison of the rhizosphere–based method with DTPA, EDTA, CaCl2, and NaNO3 extraction methods for prediction of bioavailability of metals in soil to barley. Environ Pollut 137:231−240
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (1998) World reference base for soil resources. FAO, Rome
Gao X, Hoffland E, Stomph TJ, Grant CA, Zou C, Zhang F (2012) Improving zinc bioavailability in transition from flooded to aerobic rice. Agron Sustain Dev 32(2):465–478
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1—physical and mineralogical methods. Soil Science Society of America Book Series 5, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 383–411
Hagedorn F, Saurer M, Blaser P (2004) A 13C tracer study to identify the origin of dissolved organic carbon in forested mineral soils. Euro J Soil Sci 55:91–100
Jalali M, Khanlari ZV (2008) Effect of aging process on the fractionation of heavy metals in some calcareous soils of Iran. Geoderma 143:26–40
Kim RY, Yoon JK, Kim TS, Yang JE, Owens G, Kim KR (2015) Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils: definitions and practical implementation—a critical review. Environ Geochem Hlth 37:1041–1061
Krishnamurti GSR, Naidu R (2000) Speciation and phytoavailability of cadmium in selected surface soils of South Australia. Aust J Soil Res 38:991–1004
Krishnamurti GS, Naidu R (2002) Solid‒solution speciation and phytoavailability of copper and zinc in soils. Environ Sci Technol 36:2645–2651
Lal R (2007) Farming carbon. Soil Till Res 96:1–5
Li T, Di Z, Yang X, Sparks DL (2011) Effects of dissolved organic matter from the rhizosphere of the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii on sorption of zinc and cadmium by different soils. J Hazard Mater 192:1616–1622
Li M, Wang SX, Tian XH, Zhao JH, Li HY, Guo CH, Chen YL, Zhao AQ (2015) Zn distribution and bioavailability in whole grain and grain fractions of winter wheat as affected by applications of soil N and foliar Zn combined with N or P. J Cereal Sci 61:26–32
Liebich J, Vereecken H, Burauel P (2006) Microbial community changes during humification of 14C-labelled maize straw in heat-treated and native Orthic Luvisol. Eur J Soil Sci 57:446–455
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J42:421–428
Liu DY, Zhang W, Pang LL, Zhang YQ, Wang XZ, Liu YM, Chen XP, Zhang FS, Zou CQ (2017) Effects of zinc application rate and zinc distribution relative to root distribution on grain yield and grain Zn concentration in wheat. Plant Soil 411(1):1–12
Lu XC, Cui J, Tian XH, Ogunniyi JE, Gale WJ, Zhao AQ (2012) Effects of zinc fertilization on zinc dynamics in potentially zinc-deficient calcareous soil. Agron J 104:963–969
Ma YB, Uren NC (2006) Effect of aging on the availability of zinc added to a calcareous clay soil. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 76:11–18
Mcbeath TM, Mclaughlin MJ, Kirby JK, Armstrong RD (2012) Dry soil reduces fertilizer phosphorus and zinc diffusion but not bioavailability. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76:1301–1310
Mesquita M, Carranca C (2005) Effect of dissolved organic matter on copper–zinc competitive adsorption by a sandy soil at different pH values. Environ Technol 26:1065−1072
Modaihsh AS (1990) Zinc diffusion and extractability as affected by zinc carrier and soil chemical properties. Fert Res 25:85–91
Montalvo D, Degryse F, Da Silva RC, Baird R, McLaughlin MJ (2016) Agronomic effectiveness of zinc sources as micronutrient fertilizer. Adv Agron 139:215–267
Naomi H, Andy B, Darren R (2007) Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters—a review. River Res Appl 23:631–649
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1973) Determination of total nitrogen in plant material. Agron J 65:109–112
Pérez-Esteban J, Escolástico C, Masaguer A, Moliner A (2012) Effects of sheep and horse manure and pine bark amendments on metal distribution and chemical properties of contaminated mine soils. Eur J Soil Sci 63:733–742
Rayment GE, Higginson FR (1992) Australian laboratory handbook of soil and water chemical methods. Inkata Press, Melbourne
Sinha MK, Prasad B (1977) Effect of chelating agents on the kinetics of diffusion of zinc to a simulated root system and its uptake by wheat. Plant Soil 48:599–612
Smith SR (2009) A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge. Environ Int 35:142–156
Snyder JD, Trofymow JA (1984) A rapid accurate wet oxidation diffusion procedure for determining organic and inorganic carbon in plant and soil samples. Commun Soil Sci Plant 15:587–597
Soil Survey Staff (2006) Keys to soil taxonomy, 10th edn. United States Department of Agriculture, Washington
Sun JH, Li ZH, Li X, Liu ZL, Guo ZD (2012) Influence of high application of Zn fertilizers on absorption and accumulation of Zn content and maize yield. J Soil Water Conser 26(4):212–215
Sun HY, Wang CX, Wang XD, Rees RM (2014) Changes in soil organic carbon and its chemical fractions under different tillage practices on loess soils of the Guanzhong plain in Northwest China. Soil Use Manage 29(3):344–353
Tan WF, Zhang R, Cao H, Huang CQ, Yang QK, Wang MK, Koopal LK (2014) Soil inorganic carbon stock under different soil types and land uses on the Loess Plateau region of China. Catena 121:22–30
Tang X, Li Z, Chen Y (2009) Adsorption behavior of Zn (II) on calcinated Chinese loess. J Hazard Mater 161:824–834
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Weng LP, Temminghoff EJ, Lofts S, Tipping E, Van Riemsdijk WH (2002) Complexation with dissolved organic matter and solubility control of heavy metals in a sandy soil. Environ Sci Technol 36:4804–4810
Zsolnay Á (2003) Dissolved organic matter: artefacts, definitions, and functions. Geoderma 113:187–209
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (41371288, 31662233) and the National Key Technologies R&D Programs (2012BAD14B11) of China during the 12th Five-Year Plan period.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhenli He
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 57 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Shi, J., Tian, X. et al. Impact of dissolved organic matter on Zn extractability and transfer in calcareous soil with maize straw amendment. J Soils Sediments 19, 774–784 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2060-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2060-x