Abstract
Purpose
As irrigation with untreated wastewater often leads to an accumulation of contaminants in soils, nowadays, treated wastewater is increasingly used for irrigation. Here, we investigated whether and to which degree irrigation with treated wastewater might cause desorption of antibiotics from three soils (Leptosol, Phaeozem, Vertisol) and a sediment (Endhó reservoir) of the Mezquital Valley, Mexico, that were exposed to untreated wastewater in the past.
Materials and methods
We performed sequential batch desorption experiments with treated wastewater, artificial wastewater with anionic surfactants, and artificial wastewater without surfactants.
Results and discussion
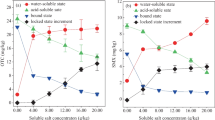
We observed no desorption, but net sorption of ciprofloxacin in contact with treated wastewater containing 3.475 μg L−1 of ciprofloxacin. Sulfamethoxazole was desorbed from the Leptosol, the Phaeozem, and the Vertisol in a similar degree with and without surfactant, but not from sediment, where no sulfamethoxazole was detected. In contact with treated wastewater containing 1.045 μg L−1 of sulfamethoxazole, it was desorbed from the Leptosol and the Phaeozem with low clay, Fe oxide, and organic matter contents, whereas the Vertisol and sediment showed a net sulfamethoxazole sorption. Desorption could be described with a bi-phasic kinetic desorption model, with most sulfamethoxazole being desorbed via a rate-limited process from poorly accessible binding sites, where it had been accumulated during the long-term irrigation in the past.
Conclusions
We conclude that a potential release of pharmaceuticals as a result from changes in wastewater irrigation is soil specific: Leptosols and Phaeozems of the Mezquital Valley might act as long-term sources of the sulfonamide sulfamethoxazole, though not of the fluoroquinolone ciprofloxacin.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano T, Levine AD (1996) Wastewater reclamation, recycle and reuse: past, present and future. Water Sci Technol 33:1–14
Barron L, Havel J, Purcell M, Szpak M, Kelleher B, Paull B (2009) Predicting sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products onto soil and digested sludge using artificial neural networks. Analyst 134:663–670
Berns AE, Philipp H, Narres HD, Burauel P, Vereecken H, Tappe W (2008) Effect of gamma-sterilization and autoclaving on soil organic matter structure as studied by solid state NMR, UV and fluorescence spectroscopy. Eur J Soil Sci 59:540–550
Carballa M, Omil F, Lema JM, Llompart M, García-Jares C, Rodríguez I, Gómez M, Ternes T (2004) Behavior of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and hormones in a sewage treatment plant. Water Res 38:2918–2926
Chefetz B, Mualem T, Ben-Ari J (2008) Sorption and mobility of pharmaceutical compounds in soil irrigated with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 73:1335–1343
Chen H, Gao B, Li H, Ma LQ (2011) Effects of pH and ionic strength on sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin transport in saturated porous media. J Contam Hydrol 126:29–36
Chen Z, Ngo HH, Guo W (2013) A critical review on the end uses of recycled water. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43:1446–1516
Dalkmann P, Broszat M, Siebe C, Willaschek E, Sakinc T, Huebner J, Amelung W, Grohmann E, Siemens J, Liles MR (2012) Accumulation of pharmaceuticals, Enterococcus, and resistance genes in soils irrigated with wastewater for zero to 100 years in central Mexico. PLoS ONE 7(9):e45397. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045397
Dalkmann P, Siebe C, Amelung W, Schloter M, Siemens J (2014a) Does long-term irrigation with untreated wastewater accelerate the dissipation of pharmaceuticals in soil? Environ Sci Technol 48:4963–4970
Dalkmann P, Willaschek E, Schiedung H, Bornemann L, Siebe C, Siemens J (2014b) Long-term wastewater irrigation reduces sulfamethoxazole sorption, but not ciprofloxacin binding, in Mexican soils. J Environ Qual 43:964–970
Deblonde T, Cossu-Leguille C, Hartemann P (2011) Emerging pollutants in wastewater: a review of the literature. Int J Hyg Environ Health 214:442–448
Edser C (2006) Latest market analysis. Focus Surfactants 5:1–2
FAO (1992) Wastewater treatment and use in agriculture. Pescod MB. FAO irrigation and drainage paper 47. Food and Agricultural Organization, Rome, 125 pp
FAO (2007) Coping with water scarcity. Challenge of the twenty-first century. Food and Agricultural Organization, Rome, 29 pp
FAO (2011) The state of the world’s land and water resources for food and agriculture. Food and Agricultural Organization, Rome, 47 pp
FAO (2012) Coping with water scarcity. An action framework for agriculture and food security. Food and Agricultural Organization, Rome, 78 pp
Fatta-Kassinos D, Kalavrouziotis LK, Koukoulakis PH, Vasquez MJ (2011) The risks associated with wastewater reuse and xenobiotics in the agroecological environment. Sci Total Environ 409:3555–3563
Figueroa-Diva RA, Vasudevan D, MacKay AA (2010) Trends in soil sorption coefficients within common antimicrobial families. Chemosphere 79:786–793
Förster M (2011) Sequestration of sulfadiazine in soils: sorption and sequestration of sulfadiazine in soils and soil fractions. Dissertation, University of Bonn, 97 pp
Gomez V, Ferreres L, Pocurull E, Borrull F (2011) Determination of non-ionic and anionic surfactants in environmental water matrices. Talanta 84:859–866
González S, Petrovic M, Barceló D (2007) Removal of a broad range of surfactants from municipal wastewater – comparison between membrane bioreactor and conventional activated sludge treatment. Chemosphere 67:335–343
Haham H, Oren A, Chefetz B (2012) Insight into the role of dissolved organic matter in sorption of sulfapyridine by semiarid soils. Environ Sci Technol 46:11870–11877
Hanjra MA, Blackwell J, Carr G, Zhang F, Jackson TM (2012) Wastewater irrigation and environmental health: implications for water governance and public policy. Int J Hyg Environ Health 215:255–269
Hirsch R, Ternes T, Haberer K, Kratz KL (1999) Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 225:109–118
IMS (2005) IMS chemical country profile Mexico. Database. IMS Health Incorporated, London
Jiménez B, Chávez A (2004) Quality assessment of an aquifer recharged with wastewater for its potential use as drinking source: “El Mezquital Valley” case. Water Sci Technol 50:269–276
Jiménez B, Mara D, Carr R, Brissaud F (2010) Wastewater treatment for pathogen removal and nutrient conservation: suitable systems for use in developing countries. In: Drechsel P, Scott CA, Raschid-Sally L, Redwood M, Bahri A (eds) Wastewater irrigation and health: assessing and mitigating risk in low-income countries. Earthscan, London, pp 149–169
Katsoyiannis A, Samara C (2007) The fate of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the wastewater treatment process and its importance in the removal of wastewater contaminants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 14:284–292
Leal RMP, Alleoni LRF, Tornisielo VL, Regitano JB (2013) Sorption of fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides in 13 Brazilian soils. Chemosphere 92:979–985
Lindberg RH, Olofsson U, Rendahl P, Johansson M, Andersson BAV (2006) Behavior of fluoroquinolones and trimethoprim during mechanical, chemical, and active sludge treatment of sewage water and digestion of sludge. Environ Sci Technol 40:1042–1048
OECD (2000) Test No. 106: adorption - desorption using a batch equilibrium method, OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 1. OECD Publishing, Paris
Pedrero F, Kalavrouziotis I, Alarcón JJ, Koukoulakis P, Asano T (2010) Use of treated municipal wastewater in irrigated agriculture—review of some practices in Spain and Greece. Agric Water Manag 97:1233–1241
Qadir M, Wichelns D, Raschid-Sally L (2010) The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric Water Manag 97:561–568
Raschid-Sally L, Jayakody P (2008) Drivers and characteristics of wastewater agriculture in developing countries-results from a global assessment. International Water Management Institute, Colombo
Rosendahl I, Siemens J, Groeneweg J, Linzbach E, Laabs V, Herrmann C, Vereecken H, Amelung W (2011) Dissipation and sequestration of the veterinary antibiotic sulfadiazine and its metabolites under field conditions. Environ Sci Technol 45:5216–5222
Schaumann GE, Thiele-Bruhn S (2011) Molecular modeling of soil organic matter: squaring the circle? Geoderma 166:1–14
Siebe C (1994) Akkumulation, Mobilität und Verfügbarkeit von Schwermetallen in langjährig mit städtischen Abwässern bewässerten Böden in Zentralmexiko. Hohenheimer Bodenkundliche Hefte Nr. 17, 213 pp
Siemens J, Huschek G, Siebe C, Kaupenjohann M (2008) Concentrations and mobility of human pharmaceuticals in the world’s largest wastewater irrigation system, Mexico City-Mezquital Valley. Water Res 42:2124–2134
Sukul P, Lamshöft M, Zühlke S, Spiteller M (2008) Sorption and desorption of sulfadiazine in soil and soil-manure systems. Chemosphere 73:1344–1350
Thiele-Bruhn S, Aust MO (2004) Effect of pig slurry on the sorption of sulfonamide antibiotics in soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 47:31–39
Thiele-Bruhn S, Seibicke T, Schulten HR, Leinweber P (2004) Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particle size fractions. J Environ Qual 33:1331–1342
UNDP (2006) Human development report 2006. Beyond scarcity: power, poverty and the global water crisis. Palgrave Macmillan, New York
UNESCO (2009) Water in a changing world. The united nations world water development report 3. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Paris
Vasudevan D, Bruland GL, Torrance BS, Upchurch VG, MacKay AA (2009) pH-dependent ciprofloxacin sorption to soils: interaction mechanisms and soil factors influencing sorption. Geoderma 151:68–76
Vo PT, Ngo HH, Guo W, Zhou JL, Nguyen PD, Listowoski A, Wang XC (2014) A mini-review on the impacts of climate change on wastewater reclamation and reuse. Sci Total Environ 494–495:9–17
WHO (2006) Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater, excreta and graywater. Volume 1: Policy and regulatory aspects. 100 pp
Yu Z, Yediler A, Yang M, Schulte-Hostede S (2012) Leaching behavior of enrofloxacin in three different soils and the influence of a surfactant on its mobility. J Environ Sci 24:435–439
Zhang D, Pan B, Zhang H, Ning P, Xing B (2010) Contribution of different sulfamethoxazole species to their overall adsorption on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 44:3806–3811
Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhong Z, Guo C, Li L, He Y, Fan W, Chen Y (2013) Degradation of sulfonamides antibiotics in lake water and sediment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2372–2380
Zheng H, Wang Z, Zhao J, Herbert S, Xing B (2013) Sorption of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole varies with biochars produced at different temperatures. Environ Pollut 181:60–67
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge funding for a scholarship for M.C. by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD, Ref. Nr. A/11/79684). Furthermore, this work was jointly co-funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG, grant no. SI 1106/5-1,2) and the Mexican Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT, grant no. I 0110-193-10). We thank to Dr. Alexander Correa-Metrio and his team for supporting the sediment sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Dong-Mei Zhou
Manuel Carrillo and Gianna Carina Braun contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrillo, M., Braun, G.C., Siebe, C. et al. Desorption of sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin from long-term wastewater-irrigated soils of the Mezquital Valley as affected by water quality. J Soils Sediments 16, 966–975 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1292-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1292-2