Abstract
Purpose
This article analyzed the use of composted sewage sludge and limestone outcrop residue as a source of saline pollution to groundwater due to their use in soil rehabilitation and land restoration.
Materials and methods
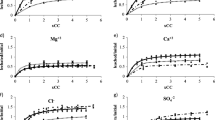
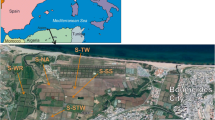
This experiment analyzed the salinity and some important anions and cations related to those wastes under an experimental design based on the use of columns (0–30 cm) formed by both wastes and a heavy irrigation regime. Two different quality waters (saline and nonsaline) were used for irrigation. The pH, electrical conductivity, anions (Cl−, SO4 2−, PO4 3−, and HCO3 −), cations (Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+), and heavy metals (Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cd, Cr, Ni, and Pb) were analyzed.
Results and discussion
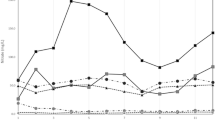
The environmental risk of salinization due to the species associated with the use of these materials was important, although chloride and sodium were the most important favoring the salinization of water. The effect was especially detected in the first weeks, while sewage sludge added important amounts of salts to leachates. After that, salinity coming from the irrigation determined the salinization of the groundwater.
Conclusions
The combination of saline water for irrigation with the compost has to be seriously considered as a source of salts and heavy metal pollution for surface and ground waters. Phosphate and trace elements pollution are clearly associated to the use of the composted sewage sludge.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad Z, Yamamoto S, Honna T (2008) Leachability and phytoavailability of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from different bio-composts under chloride- and sulfate-dominated irrigation water. J Environ Qual 37(3):1288–98
Ahmad Z, Honna T, Yamamoto S, Faridulah F, Isrhad M, El-Hassan WHA (2009) Effect of chloride and sulfate salinity on micronutrients release and uptake from different composts applied on total phosphorus basis. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 40(9–10):1566–1589
Almendro-Candel MB, Navarro-Pedreño J, Jordán Vidal MM, García Sánchez E, Mataix Solera J (2001) Ensayos de movilidad de compuestos nitrogenados en zona no saturada. In: Ballester Rodríguez A, Grima Olmedo J, López Geta JA, Rodríguez Hernández L (eds) Investigación, gestión y recuperación de acuíferos contaminados. Instituto Geológico y Minero de España, Alicante, pp 23–34
Almendro-Candel MB, Navarro-Pedreño J, Jordán Vidal MM, Gómez I (2003) Movilidad y biodisponibilidad del fósforo en un Antrosol del sureste español (Alicante) enmendado con lodo de depuradora. Edafología 10(1):7–14
Almendro-Candel MB, Jordán Vidal MM, Navarro-Pedreño J, Mataix-Solera J, Gómez I (2007) Environmental evaluation of sewage sludge application to reclaim limestone quarries wastes as soil amendments. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1328–1332
Almendro-Candel MB, Navarro-Pedreño J, Jordán Vidal MM, Gómez I, Meléndez-Pastor I (2014) Use of municipal waste compost to reclaim limestone quarries mine spoils as soil amendments: effects on Cd and Ni. J Geochem Explor 144:263–366
Alnahidh SI (1991) Effect of frequency of irrigation on sewage sludge-amended soil and corn nutrition. Arid Soil Res Rehab 5(2):137–146
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Baldantoni D, Leone A, Iovieno P, Morra L, Zaccardelli M, Alfani A (2010) Total and available soil trace element concentrations in two Mediterranean agricultural systems treated with municipal waste compost or conventional mineral fertilizers. Chemosphere 80(9):1006–1013
Brady NC, Well RR (2004) Nature and properties of soils. Potassium nature and ecological roles. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, pp 627–637
Brännvall E, Nilsson M, Sjöblom R, Skoglund N, Kumpiene J (2014) Effect of residue combinations on plant uptake of nutrients and potentially toxic elements. J Environ Manag 132:287–295
Cai H, Chen T, Liu H, Gao D, Zheng G, Zhang J (2010) The effect of salinity and porosity of sewage sludge compost on the growth of vegetable seedlings. Scientia Hort 124(3):381–386
Dolgen D, Alpaslan MN, Delenn N (2007) Agricultural recycling of treatment-plant sludge: a case study for a vegetable-processing factory. J Environ Manag 84(3):274–81
EC (2003) European Communities (Water Policy) Regulations 2003. Official Journal of the European Communities 722/2003
EC (2005) European Communities (Water Policy) (Amendment) Regulations, 2005. Official Journal of the European Communities 413/2005
EC (2008) European Communities (Water Policy) (Amendment) Regulations, 2008. Official Journal of the European Communities 219/2008
EC (2009) European Communities Environmental Objectives (Surface Waters) Regulations, 2009. Official Journal of the European Communities 272/2009
EC (2010a) European Communities Environmental Objectives (Groundwater) Regulations, 2010. Official Journal of the European Communities 9/2010
EC (2010b) European Communities (Good Agricultural Practice for Protection of Waters) Regulations, 2010. Official Journal of the European Communities 610/2010
EC (2010c) Water is for life: how the Water Framework Directive helps safeguard Europe’s resources. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, p 28
EC (2011) European Communities (TechnicalSpecifications for the Chemical Analysis and Monitoring of Water Status) Regulations, 2011. Official Journal of the European Communities 489/2011
EC/2000/60 (2000) Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October, 2000, establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Communities 327/2000
EC/2008/98 (2008) Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on waste and repealing certain Directives. Official Journal of the European Communities 312/2008
EC/2014/350 (2014) European Union (Water Policy) Regulations 2014. Official Journal of the European Communities 350/2014
Eldridge SM, Chan KY, Barchia I, Pengelly PK, Katupitiya S, Davis JM (2009) A comparison of surface applied granulated biosolids and poultry litter in terms of risk to runoff water quality on turf farms in Western Sydney, Australia. Agr Ecosyst Environ 134(3–4):243–50
EU (2001) Report from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions on the Thematic Strategy on the Prevention and Recycling of Waste. Brussels 19.1.2011 COM (2011) 13 final
Galbally P, Ryan D, Fagan CC, Finnan J, Grant J, McDonnell K (2013) Biosolid and distillery effluent amendments to Irish short rotation coppiced willow plantations: impacts on groundwater quality and soil. Agri Water Manag 116:193–203
Hall SJ (2014) Soils and the future of food. Challenges and opportunities for feeding nine billion people. In: Churchman JG, Landa ER (eds) The soil underfoot: infinite possibilities for a finite resource. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 17–36
Jordán MM, Almendro-Candel MB, Pina S, García-Orenes F, García-Sánchez E, Sabater MC, Navarro-Pedreño J, Gómez I (2006) Sewage sludge application for soil reclamation of limestone quarries. Test in columns using a calcareous mineral rejection. In: Water management and soil conservation in semi-arid environments. INRA, Marrakech
Jordán MM, Pina S, García-Orenes F, Almendro-Candel MB, García-Sánchez E (2008) Environmental risk evaluation of the use of mine spoils and treated sewage sludge in the ecological restoration of limestone quarries. Environ Geol 55(2):453–462
Jordán MM, Rincón-Mora B, Almendro-Candel MB (2014) Heavy metal distribution and electrical conductivity measurements in biosolid pellets. J Soil Sediments doi: 10.1007/s11368-014-1021-2
Jordão CP, Cecon PR, Pereira JL (2003) Evaluation of metal concentrations in edible vegetables grown in compost amended soil. Int J Environ Stud 60(6):547–562
Karef S, Kettab A, Nakib M (2014) Characterization of byproducts from wastewater treatment of medea (Algeria) with a view to agricultural reuse. Desalin Water Treat 52(10–12):2201–2207
Klay S, Charef A, Ayed L, Houman B, Rezgui F (2010) Effect of irrigation with treated wastewater on geochemical properties (saltiness, C, N and heavy metals) of isohumic soils (Zaouit Sousse perimeter, Oriental Tunisia). Desalination 253(1):180–187
Lag-Brotons AJ, Soriano-Disla JM, Gómez I, Navarro-Pedreño J (2013) Saline irrigation effects on Cynara cardunculus L. plants grown in Mediterranean soils. Hort Sci 48(6):762–767
Navarro-Pedreño J, Gómez I, Moral R, Palacios G, Mataix J (1997) Heavy metals and plant nutrition and development. Recent Res Devel in Phytochem 1:173–179
Navarro-Pedreño J, Almendro-Candel MB, Jordán-Vidal MM, Mataix-Solera J, Garcia-Sánchez E (2003) Mobility of cadmium, chromium, and nickel through the profile of a calcisol treated with sewage sludge in the southeast of Spain. Environ Geol 44:545–553
Navarro-Pedreño J, Almendro-Candel MB, Jordán-Vidal MM, Mataix-Solera J, García-Sánchez E (2004) Risk areas in the application of sewage sludge on degraded soils in Alicante province (Spain). In: Martin JF, Brebbia CA, Godfrey AE (eds) Díaz de Terán JR (eds) Geo-Environment. WIT Press, Southampton, pp 293–302
Palazzo AJ, Reynolds SM (1991) Long-term changes in soil and plant metal concentrations in an acidic dredge disposal site receiving sewage sludge. Water Air Soil Pollut 57–58:839–848
Pepper IL, Zerghi H, Brooks JP, Gerba CP (2008) Sustainability of land application of class B biosolids. J Environ Qua 37(5):58–67
Qiang Z, Speir TW, Van Schaik AP (2004) Leaching of nutrients from soil cores treated with a single large dose of digested sewage sludge. Biol Fert Soils 40:284–289
R.D. 824/2005. 2005. Real Decreto 824/2005 de 8 Julio sobre productos fertilizantes. Boletín Oficial del Estado 171, 25592–25669, Anexo VI
Rains DW, Goyal SS (2003) Strategies for managing crop production in saline environments: an overview. In: Goyal SS, Sharma SK, Rains DW (eds) Crop Production in Saline Environments. The Haworth Press, Binghamton, pp 1–10
Raveendran E, Grieve JC, Madamy IM (1994) Effects of organic amendments and irrigation waters on the physical and chemical-properties of 2 calcareous soils in Bahrain. Environ Monit Assess 30(2):177–196
Reddy N, Crohn DM (2012) Compost induced soil salinity: a new prediction method and its effect on plant growth. Compost Sci Util 20(3):133–140
Saveyn H, Eder P (2014) End-of-waste criteria for biodegradable waste subjected to biological treatment (compost & digestate): technical proposals. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg
Soriano-Disla JM, Speir TW, Gómez I, Clucas LM, McLaren RG, Navarro-Pedreño J (2010) Evaluation of Different Extraction Methods for the Assessment of Heavy Metal Bioavailability in Various Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 213(1–4):471–483
Soriano-Disla JM, Gómez I, Navarro-Pedreño J (2011) The influence of soil properties on the mobility of metals following a single application of polluted sewage sludge to seventy agricultural topsoils: a laboratory column study. Soil Sediment Cont 20(8):961–976
Soriano-Disla JM, Gómez I, Navarro-Pedreño J, Jordán MM (2014) The transfer of heavy metals to barley plants from soils amended with sewage sludge with different heavy metal burdens. J Soils Sediments 14:687–696
Speir TW, van Schaik AP, Hunter LC, Ryburn JL, Percival HJ (2007) Attempts to derive EC50 values for heavy metals from land applied Cu-, Ni-, and Zn-spiked sewage sludge. Soil Biol Biochem 39(2):539–549
Tedesco MJ, Teixeira EC, Medina C, Bugin A (1999) Reclamation of spoil and refuse material produced by coal mining using bottom ash and lime. Environ Technol 20(5):523–529
Trudgill ST, Burt TP, Heathwaite AL, Arkell BP (1991) Soil nitrate sources and nitrate leaching losses, Slapton, South Devon. Soil Use Manag 7:200–206
Valdez-Gonzalez J, Lopez-Chuken U, Guzman-Mar J, Flores-Banda F, Hernandez-Ramirez A, Hinojosa-Reyes L (2014) Saline irrigation and Zn amendment effect on Cd phytoavailability to Swiss chard (Beta vulgaris L.) grown on a long-term amended agricultural soil: a human risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(9):5909–16
Veeresh H, Tripathy S, Chaudhuri D, Ghosh BC, Hart BR, Powell MA (2003) Changes in physical and chemical properties of three soil types in India as a result of amendment with fly ash and sewage sludge. Environ Geol 43:513–520
Wahla IH, Kirkham MB (2008) Heavy metal displacement in salt-water-irrigated soil during phytoremediation. Environ Pollut 155(2):271–83
Wong JWC, Ho G (1994) Sewage sludge as organic ameliorant for revegetation of fine bauxite refining residue. Res Conserv Recyc 11(1–4):297–309
Yazdanpanah N, Mahmoodabadi M (2013) Reclamation of calcareous saline-sodic soil using different amendments: time changes of soluble cations in leachate. Arab J Geosci 6:2519–2528
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Claudio Bini
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Gimeno, A., Navarro-Pedreño, J., Almendro-Candel, M.B. et al. Environmental consequences of the use of sewage sludge compost and limestone outcrop residue for soil restoration: salinity and trace elements pollution. J Soils Sediments 16, 1012–1021 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1288-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1288-y