Abstract
Purpose
Bacterial adhesion to soil particles is fundamentally important in mineral weathering, organic matter degradation, heavy metal transformation, and fate of pollutants. However, the adhesion mechanism between bacteria and soil colloids under continuous flow systems in the natural environments remains unknown.
Materials and methods
The kinetics of Pseudomonas putida cellular adsorption and desorption on Red soil colloid films under controlled flow systems were examined using in situ attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy. Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek (DLVO) and non-DLVO interactions were employed to elucidate the cellular adsorption and desorption kinetics.
Results and discussion
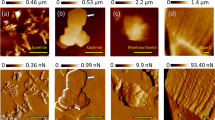
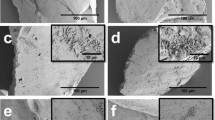
In situ ATR-FTIR spectroscopy can be used effectively to investigate the kinetics of bacterial adhesion to a soil colloid deposit. Surface proteins may be involved in the bacterial adhesion to soil colloids. The adsorption followed pseudo-first-order kinetic equation. High adsorption rate constant and great saturation coverage of adsorbed bacteria were found at high ionic strengths in dynamic systems.
Conclusions
P. putida bacterial cellular adsorption on the soil colloid deposit was irreversible in a wide range of ionic strengths under controlled flow systems. The less reversible adhesion was probably attributed to the DLVO predicted deep secondary energy minima together with non-DLVO factors including polymer bridging, local charge heterogeneities, surface roughness, and Lewis acid–base interactions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atabek A, Camesano TA (2007) Atomic force microscopy study of the effect of lipopolysaccharides and extracellular polymers on adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 189:8503–8509
Bellon-Fontaine MN, Rault J, van Oss CJ (1996) Microbial adhesion to solvents: a novel method to determine the electron-donor/electron-acceptor or Lewis acid–base properties of microbial cells. Colloids Surf B 7:47–53
Bhattacharjee S, Ko CH, Elimelech M (1998) DLVO interaction between rough surfaces. Langmuir 14:3365–3375
Bos R, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (1999) Physico-chemistry of initial microbial adhesive interactions—its mechanisms and methods for study. FEMS Microbiol Rev 23:179–230
Cai P, Huang Q, Walker S (2013) Deposition and survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on clay minerals in a parallel plate flow system. Environ Sci Technol 47:1896–1903
Chrysikopoulos CV, Syngouna VI, Vasiliadou IA, Katzourakis VE (2012) Transport of Pseudomonas putida in a 3-D bench scale experimental aquifer. Transp Porous Med 94:617–642
Crawford RJ, Webb HK, Truong VK, Hasan J, Ivanova EP (2012) Surface topographical factors influencing bacterial attachment. Adv Colloid Interfac 179–182:142–149
Elzinga EJ, Huang J, Chorover J, Kretzschmar R (2012) ATR-FTIR spectroscopy study of the influence of pH and contact time on the adhesion of Shewanella putrefaciens bacterial cells to the surface of hematite. Environ Sci Technol 46:12848–12855
Emmett PH, Brunauer S, Love KS (1938) The measurement of surface areas of soils and soil colloids by the use of low temperature van der Waals adsorption isotherms. Soil Sci 45:57–66
Gregory J (1981) Approximate expressions for retard van der Waals interaction. J Colloid Interf Sci 83:138–145
Hahn MW, O'Melia CR (2004) Deposition and reentrainment of Brownian particles in porous media under unfavorable chemical conditions: some concepts and applications. Environ Sci Technol 38:210–220
Harrick NJ, du Pré FK (1966) Effective thickness of bulk materials and thin films for internal reflection spectroscopy. Appl Optics 5:1739–1743
Hong Z, Rong X, Cai P, Liang W, Huang Q (2011) Effects of temperature, pH and salt concentrations on the adsorption of Bacillus subtilis on soil clay minerals investigated by microcalorimetry. Geomicrobiol J 28:686–691
Hong Z, Rong X, Cai P, Dai K, Liang W, Chen W, Huang Q (2012) Initial adhesion of Bacillus subtilis on soil minerals as related to their surface properties. Eur J Soil Sci 63:457–466
Hori K, Matsumoto S (2010) Bacterial adhesion: from mechanism to control. Biochem Eng J 48:424–434
Huang PM, Wang MK, Chiu CY (2005) Soil mineral–organic matter–microbe interactions: impacts on biogeochemical processes and biodiversity in soils. Pedobiologia 49:609–635
Jiang W, Saxena A, Song B, Ward BB, Beveridge TJ, Myneni SCB (2004) Elucidation of functional groups on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial surfaces using infrared spectroscopy. Langmuir 20:11433–11442
Jiang D, Huang Q, Cai P, Rong X, Chen W (2007) Adsorption of Pseudomonas putida on clay minerals and iron oxide. Colloids Surf B 54:217–221
Kang SY, Bremer PJ, Kim KW, McQuillan AJ (2006) Monitoring metal ion binding in single-layer Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms using ATR-IR spectroscopy. Langmuir 22:286–291
Kim J, Dong H, Seabaugh J, Newell SW, Eberl DD (2004) Role of microbes in the smectite-to-illite reaction. Science 303:830–832
Liu C, Li X, Xu F, Huang PM (2003) Atomic force microscopy of soil inorganic colloids. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 49:17–23
Madejová J, Komadel P (2001) Baseline studies of the Clay Minerals Society Source Clays: infrared meathods. Clays Clay Miner 49:410–432
McWhirter MJ, McQuillan AJ, Bremer PJ (2002a) Influence of ionic strength and pH on the first 60 min of Pseudomonas aeruginosa attachment to ZnSe and to TiO2 monitored by ATR-IR spectroscopy. Colloids Surf B 26:365–372
McWhirter MJ, Bremer PJ, McQuillan AJ (2002b) Direct infrared spectroscopic evidence of pH- and ionic strength-induced changes in distance of attached Pseudomonas aeruginosa from ZnSe surfaces. Langmuir 18:1904–1907
Mebius LJ (1960) A rapid method for the determination of organic carbon in soil. Anal Chim Acta 22:120–124
Mei L, Busscher HJ, van der Mei HC, Ren Y (2011) Influence of surface roughness on streptococcal adhesion forces to composite resins. Dent Mater 27:770–778
Mitik-Dineva N, Wang J, Truong VK, Stoddart PR, Malherbe F, Crawford RJ, Ivanova EP (2009) Differences in colonization of five marine bacteria on two types of glass. Biofouling 25:621–631
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini MT, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2003) Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur J Soil Sci 54:655–670
Ojeda JJ, Romero-Gonzalez ME, Pouran HM, Banwart SA (2008) In situ monitoring of the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas putida on hematite using flow-cell ATR-FTIR spectroscopy to investigate the formation of inner-sphere bonds between the bacteria and the mineral. Mineral Mag 72:101–106
Parikh SJ, Chorover J (2006) ATR-FTIR spectroscopy reveals bond formation during bacterial adhesion to iron oxide. Langmuir 22:8492–8500
Redman JA, Walker SL, Elimelech M (2004) Bacterial adhesion and transport in porous media: role of the secondary energy minimum. Environ Sci Technol 38:1777–1785
Rijnaarts HHM, Norde W, Bouwer EJ, Lyklema J, Zehnder AJB (1994) Reversibility and mechanism of bacterial adhesion. Colloids Surf B 4:5–22
Rong X, Huang Q, Chen W (2007) Microcalorimetric investigation on the metabolic activity of Bacillus thuringiensis as influenced by kaolinite, montmorillonite and goethite. Appl Clay Sci 38:97–103
Rong X, Huang Q, He X, Chen H, Cai P, Liang W (2008) Interaction of Pseudomonas putida with kaolinite and montmorillonite: a combination study by equilibrium adsorption, ITC, SEM and FTIR. Colloids Surf B 64:49–55
Rong X, Chen W, Huang Q, Cai P, Liang W (2010) Pseudomonas putida adhesion to goethite: studied by equilibrium adsorption, SEM, FTIR and ITC. Colloids Surf B 80:79–85
Rosenberg M, Gutnick D, Rosenberg E (1980) Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: a simple method for measuring cell-surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 9:29–33
Shephard JJ, Savory DM, Bremer PJ, McQuillan AJ (2010) Salt modulates bacterial hydrophobicity and charge properties influencing adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA01) in aqueous suspensions. Langmuir 26:8659–8665
Touhami A, Jericho MH, Boyd JM, Beveridge TJ (2006) Nanoscale characterization and determination of adhesion forces of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili by using atomic force microscopy. J Bacteriol 188:370–377
Truesdail SE, Lukasik J, Farrah SR, Shah DO, Dickinson RB (1998) Analysis of bacterial deposition on metal (hydr)oxide-coated sand filter media. J Colloid Interf Sci 203:369–378
Vasiliadou IA, Papoulis D, Chrysikopoulos CV, Panagiotaras D, Karakosta E, Fardis M, Papavassiliou G (2011) Attachment of Pseudomonas putida onto differently structured kaolinite minerals: a combined ATR-FTIR and 1H NMR study. Colloids Surf B 84:354–359
Wu H, Jiang D, Cai P, Rong X, Huang Q (2011) Effects of low-molecular-weight organic ligands and phosphate on adsorption of Pseudomonas putida by clay and iron oxide. Colloids Surf B 82:147–151
Wu H, Jiang D, Cai P, Rong X, Dai K, Liang W, Huang Q (2012) Adsorption of Pseudomonas putida on soil particle size fractions: effects of solution chemisity and organic matter. J Soil Sediment 12:143–149
Xiong Y (1985) Soil colloids, vol 2. Science Press, Beijing
Yong AG, McQuillan AJ (2009) Adsorption/desorption kinetics from ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Aqueous oxalic acid on anatase TiO2. Langmuir 25:3538–3548
Zhang W, Hughes J, Chen Y (2012) Impacts of hematite nanoparticle exposure on biomechanical, adhesive, and surface electrical properties of Escherichia coli cells. Appl Environ Microb 78:3905–3915
Zhao W, Liu X, Huang Q, Rong X, Liang W, Dai K, Cai P (2012a) Sorption of Streptococcus suis on various soil particles from an Alfisol and effects on pathogen metabolic activity. Eur J Soil Sci 63:558–564
Zhao W, Liu X, Huang Q, Walker SL, Cai P (2012b) Interactions of pathogens Escherichia coli and Streptococcus suis with clay minerals. Appl Clay Sci 69:37–42
Acknowledgments
This work was kindly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40825002) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2012YB17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Chen, W., Rong, X. et al. In situ ATR-FTIR study on the adhesion of Pseudomonas putida to Red soil colloids. J Soils Sediments 14, 504–514 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0817-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0817-9