Abstract
Purpose
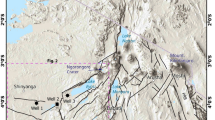
This paper investigates soils and sediments from the eastern Padanian Plain (northern Italy) in order to delineate the physiographic evolution of the area.
Materials and methods
We present new geochemical, mineralogical and textural analyses of alluvial sediments collected from a 13-m-deep section located a few kilometres south of Ferrara. The chronology of the related depositional events is provided from 14C dating of tree trunks buried at depths of ca. 9 m and organic matter from the underlying horizons.
Results and discussion
The data indicate that (1) the upper part of the sequence (down to depths of 9 m) includes sediments characterized by low nickel–chromium (Ni–Cr) concentrations ascribed to the alluvial deposits of the river Reno, deposited in the last 400 years; (2) buried soils (depths of 9–10.5 m) developed on Ni–Cr-rich sediments related to the river Po; and (3) the deeper facies (depths of 10.5–13 m) are CaCO3-free and characterized by higher amounts of organic carbon, sulphur and arsenic, reflecting episodic lacustrine/marsh environments. These wetlands probably developed in the area during the Iron and Roman ages, persisting up to the Middle Ages.
Conclusions
The data provide a contribution to the understanding of the evolution of the river network during the last 3,000 years and provide insights on the related paleohydrological framework that can be useful for geographical and historical reconstructions of the area. Results highlight the importance of investigating alluvial sediments to elucidate (1) fluctuations of environmental conditions and (2) anthropogenic impacts on the natural landscape.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JRL (1965) A review of the origin and characteristics of recent alluvial sediments. Sedimentology 5:89–191
Amorosi A (2012) Chromium and nickel as indicators of source-to-sink sediment transfer in a Holocene alluvial and coastal system (Po Plain, Italy). Sediment Geol 280:260–269
Amorosi A, Pavesi M (2010) Aquifer stratigraphy from the middle-late Pleistocene succession of the Po basin. Mem Descrittive Carta Geol Ital XC:7–20
Amorosi A, Centineo MC, Dinelli E, Lucchini F, Tateo F (2002) Geochemical and mineralogical variations as indicators of provenance changes in late Quaternary deposits of SE Po Plain. Sediment Geol 151:273–292
Amorosi A, Centineo MC, Colalongo ML, Fiorini F (2005) Millenial-scale depositional cycles from the Holocene of the Po Plain, Italy. Mar Geol 222–223:7–18
Amorosi A, Pavesi M, Ricci Lucchi M, Sarti G, Piccin A (2008) Climatic signature of cyclic fluvial architecture from the Quaternary of the central Po Plain, Italy. Sediment Geol 209:58–68
Barbafieri M, Lubrano L, Petruzzelli G (1996) Characterization of pollution in sites contaminated by heavy metals: a proposal. Ann Chim 86:585–594
Bianchini G, Laviano R, Lovo S, Vaccaro C (2002) Chemical–mineralogical characterisation of clay sediments around Ferrara (Italy): a tool for an environmental analysis. Appl Clay Sci 21:165–176
Bianchini G, Natali C, Di Giuseppe D, Beccaluva L (2012) Heavy metals in soils and sedimentary deposits of the Padanian Plain (Ferrara, Northern Italy): characterisation and biomonitoring. J Soils Sediments 12:1145–1153
Bianchini G, Di Giuseppe D, Natali C, Beccaluva L (2013) Ophiolite inheritance in the Po plain sediments: insights on heavy metals distribution and risk assessment. Ofioliti 38:1–14
Bitelli G, Cremonini S, Gatta G (2013) Cartographic heritage: toward unconventional methods for quantitative analysis of pre-geodetic maps. J Cult Herit. doi:10.1016/j.culher.2013.04.003
Blackwell PG, Buck CE, Reimer P (2006) Important features of the new radiocarbon calibration curves. Quat Sci Rev 25:408–413
Bondesan M (1989) Evoluzione geomorfologica ed idrografica della pianura ferrarese (Geomorphological and hydrographic evolution of the plain close to Ferrara). In Visser Travagli A.M. and Vighi G. (Eds), Terre ed acqua-Le bonifiche ferraresi nel delta del Po (Land and water - the reclaiming activity in the Po River Delta). Corbo G. publisher, Ferrara (Italy), pp 13–20
Bortolami GC, Fontes JC, Markgraf V, Saliege JF (1977) Land, sea and climate in the northern Adriatic region during late Pleistocene and Holocene. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 21:139–156
Bronk Ramsey C (2001) Development of the radiocarbon program OxCal. Radiocarbon 43:355–363
Calcagnile L, Quarta G, D'Elia M (2005) High-resolution accelerator-based mass spectrometry: precision accuracy and background. Appl Radiat Isot 62:623–629
Cibin U, Stefani M (2009) Note illustrative della Carta Geologica d'Italia alla scala 1:50.000 - Foglio 187 Codigoro, Firenze, 161 p (Illustrated notes of the geological map of Italy, sheet 187, scale 1:50.000). http://www.isprambiente.gov.it/Media/carg/note_illustrative/187_Codigoro.pdf. Accessed 18 Oct 2013
Cremaschi M, Pizzi C, Valsecchi V (2006) Water management and land use in the terremare and a possible climatic co-factor in their abandonment: the case study of the terramara of Poviglio Santa Rosa (northern Italy). Quatern Int 151:87–98
Cremonini S (1988) Specificità dell'Alto Ferrarese nella problematica evolutiva dell'antica idrografia padana inferiore. (Specifity of the “High Ferrara zone” within the evolution of the ancient Padanian hydrography). In "Bondeno ed il suo territorio dalle origini al Rinascimento" (The town of Bondeno and its territory from the origin to the Renaissance). Grafis Ed, Bologna, p 17-24
Cremonini S (1989) Morfoanalisi della veteroidrografia centese. Approccio semiquantitativo ad un modello evolutivo del dosso fluviale. (Morphological analysis of the ancient hydrography close to the town of Cento. Semi-quantitative approach to model the evolution of a fluvial ridge). In “Insediamenti e viabilità nell'Alto Ferrarese dall'età romana all'alto medioevo”. Atti del convegno di Cento (Proceedings of the workshop “Human settlements and road viability in the zone of Ferrara, from the Roman to the Middle Ages”) (1987). Liberty House publisher, Ferrara (Italy), pp 135–175
Cremonini S (1991a) Inquadramento geologico-ambientale della pianura bolognese in età romana (Geological and environmental framework of the plain close to Bologna during the Roman age). Civiltà Padana vol 3. Aedes Muratoriana publisher, Modena (Italy), pp 93–128
Cremonini S (1991b) Una "finestra geomorfica" d'età classica nella pianura bolognese. Inquadramento analitico del gruppo morfologico del Reno antico (A “geomorphic window” of classic age in the plain close to Bologna. Analytical framework of the morphological group of the ancient Reno). In: “Romanità della Pianura. L'ipotesi archeologica a S. Pietro in Casale come coscienza storica per una nuova gestione del territorio”, Atti Giornate di Studio, (Proceeding of the workshop “The plain in the Roman Ages. Achaeological hypothesis at S. Pietro in Casale. Historical awareness for a new management of the territory”). April 1990, Lo Scarabeo publisher, Bologna (Italy), pp 243–301
Cremonini S (1993) Dati e ipotesi sull'evoluzione dell'ambiente fisico nella pianura centropadana tra l'ultima glaciazione ed il presente (Data and hypotheses on the evolution of the physical environment in the central Padanian plain between the last glaciation and the present). Quaderni della Bassa Modenese vol 23. Gruppo Studi Bassa Modenese, San Felice Sul Panaro (MO), Italy, pp 35–46
Cremonini S (1994) Autopsia di una rotta fluviale. Note e riflessioni in margine all'evento del 1990 occorso nel fiume Reno bolognese (Chronicle of a flooding. Notes and considerations on the 1990 event occurred on River Reno). Il Carrobbio 19/20, Pàtron publisher, Bologna, Italy, pp 339–362
Cremonini S (2001) Nuovi dati per l'evoluzione paleoambientale recente da una stratigrafia centropadana (New data for the recent environmental evolution, from a central-Padanian stratigraphy), In: Materiali per una storia di Concordia sulla Secchia, vol 3. Gruppo Studi Bassa Modenese, San Felice Sul Panaro (MO), Italy, pp 37–45
Cremonini S, Scarin ML (2007) Osservazioni stratigrafiche e considerazioni paleoambientali preliminari nell'area di Galliera (Bologna); Una prospettiva di ricerca integrata nei rapporti tra insediamento e paleoambiente nella pianura d’età medievale (Stratigraphic observations and preliminary paleo-environmental considerations in the aerea of Galliera, close to Bologna; an integrated research on the relationships between settlement and paleo-environment during the Middle Ages). In: Galetti P (ed) Una terra di confine. Storia e archeologia di Galliera nel medioevo (History and archaeology of Galliera in the Middle Ages), Clueb publisher, Bologna, Italy, pp 163–220
Cremonini S, Etiope G, Italiano F, Martinelli G (2008) Evidence of possible enhanced peat burning by deep-originated methane in the Po River delta plain. J Geol 116:401–413
Di Giuseppe D, Bianchini G, Natali C, Beccaluva L (2012) Environmental geochemistry of peat-rich sediments in the Po river Delta area (Mezzano lowland, Ferrara). Rend Online Soc Geol Ital 21(part 2):860
Donnici S, Serandrei-Barbero R, Canali G (2012) Evidence of climatic changes in the Venetian coastal plain (Northern Italy) during the last 40,000 years. Sediment Geol 281:139–150
Fiorentino G, Caracuta V, Calcagnile L, D'Elia M, Matthiae P, Mavelli F, Quarta G (2008) Third millennium B.C. climate change in Syria highlighted by carbon stable isotope analysis of 14C-AMS dated plant remains from Ebla. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 266:51–58
Franceschini A (1983a) Una storia di acque (A history of water). Sitti R (ed) “Vigarano - Storia/attualità”. Arstudio publisher, Portomaggiore (FE), Italy, pp 21–49
Franceschini A (1983b) Note introduttive alla storia di un paese che non c'era: S. Bartolomeo in Bosco (Notes to the history of a town that didn’t exist: S. Bartolomeo in Bosco) Gruppo culturale “In Nemore” (Ed.), In quel giorno si raccapitolò tutto l'inverno…, S. Bartolomeo in Bosco (In that day all the winter was condensed… S. Bartolomeo in Bosco). Liberty House publisher, Ferrara, Italy, pp 3–71
Guzmán G, Quinton JN, Nearing MA, Mabit L, Gómez JA (2013) Sediment tracer in water erosion studies: current approaches and challenges. J Soils Sediments 13:816–833
Marchetti M (2002) Environmental changes in the central Po Plain (northern Italy) due to fluvial modifications and anthropogenic activities. Geomorphology 44:361–373
Moldenhauer KM, Zielhofer C, Faust D (2008) Heavy metals as indicators for Holocene sediment provenance in a semi-arid Mediterranean catchment in northern Tunisia. Quat Int 189:129–134
Navratil O, Evrand O, Esteves M, Ayrault S, Lefèvre I, Legout C, Reyss J-L, Gratiot N, Nemery J, Mathys N, Poirel A, Bonté P (2012) Core-derived historical record of suspended sediment origin in a mesoscale mountainous catchment: the River Bléone, French Alps. J Soils Sediments 12:1463–1478
Nichols GJ, Fisher JA (2007) Processes, facies and architecture of fluvial distributary system deposits. Sediment Geol 195:75–90
Oldfield F, Asioli A, Accorsi CA, Mercuri AM, Juggins S, Langone L, Rolph T, Trincardi F, Wolff G, Gibbs Z, Vigliotti L, Frignani M, van der Post K, Branch N (2003) A high resolution late Holocene palaeo environmental record from the central Adriatic Sea. Quat Sci Rev 22:319–342
Pennisi M, Bianchini G, Kloppmann W, Muti A (2009) Chemical and isotopic (B, Sr) composition of alluvial sediments as archive of a past hydrothermal outflow. Chem Geol 266:114–125
Ravazzi C, Marchetti M, Zanon M, Perego R, Quirino T, Deaddis M, De Amicis M, Margaritora D (2013) Lake evolution and landscape history in the lower Mincio River valley, unravelling drainage changes in the central Po Plain (N-Italy) since the Bronze Age. Quatern Int 88:195–205
Romans B (2007) Sediment accumulation rates and bias: the Sadler effect. http://clasticdetritus.com/2007/07/03/. Accessed 18 Oct 2013
Sadler PM (1981) Sediment accumulation rates and the completeness of stratigraphic sections. J Geol 89:569–584
Simonneau A, Doyen E, Chapron E, Millet L, Vannière B, Di Giovanni C, Bossard N, Tachikawa K, Bard E, Albéric P, Desmet M, Roux G, Lajeunesse P, Berger JF, Arnaud F (2013) Holocene land-use evolution and associated soil erosion in the French Prealps inferred from Lake Paladru sediments and archaeological evidences. J Archaeol Sci 40:1636–1645
Smólczyñski S, Orzechowski M (2010) Sorptive properties of upper-silted organic soils in various landscapes of north-eastern Poland. Pol J Soil Sci XLIII(2):129–140
Stefani M, Zuppiroli M (2010) The interaction of geological and anthropic processes shaping the urban growth of Ferrara and the evolution of the surrounding plain. Il Quaternario. Ital J Quat Sci 23:355–372
Stuiver M, Polach HA (1977) Discussion: reporting of 14C data. Radiocarbon 19:355–363
Tolksdorf JF, Turner F, Kaiser K, Eckmeier E, Stahlschmidt M, Housley RA, Breest K, Veil S (2013) Multiproxy analyses of stratigraphy and palaeoenvironment of the late Palaeolithic Grabow floodplain site, northern Germany. Geoarchaeology 28:50–65
Van Den Berg GA, Loch JPG (2000) Decalcification of soils subject to periodic waterlogging. Eur J Soil Sci 51:27–33
Vittori Antisari L, Cremonini S, Desantis P, Calastri C, Vianello G (2013) Chemical characterisation of anthro-technosols from Bronze to Middle Age in Bologna (Italy). J Archaeol Sci 40:3660–3671
Woodward J, Huckleberry G (2011) The geoarchaelogy of river basin systems: an introduction. Geoarchaeology 26:611–615
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. C. Cornelio and Dr. M. Marchesini of the Superintendence to Archaeological properties of Emilia–Romagna (SAER) that promoted this research. The authors thank Dr. R. Tassinari for the analytical support and the referees and editors for their constructive comments that helped to improve earlier versions of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcel van der Perk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bianchini, G., Cremonini, S., Di Giuseppe, D. et al. Multiproxy investigation of a Holocene sedimentary sequence near Ferrara (Italy): clues on the physiographic evolution of the eastern Padanian Plain. J Soils Sediments 14, 230–242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0791-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0791-2