Abstract
Purpose
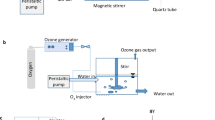
This study assesses the impacts of three different disinfection processes of sewage effluent, namely the electron beam (E-beam), ultraviolet (UV), and ozone systems, on the environment by using life cycle assessment (LCA).
Methods
The LCA employed was the comparative LCA which consists of three parts according to life cycle stages. Electricity consumption was the reference flow that can yield 99% disinfection efficiency for microorganisms present in a 1 × 105 m3 day−1 sewage treatment plant effluent over 20 years.
Results
The comparison of the LCA results indicated that the environmental impact of the UV disinfection system was the lowest, followed by the E-beam and ozone disinfection systems. The key issues of the E-beam, UV, and ozone disinfection systems are electricity consumption and SF6 usage, electricity consumption and UV lamp, and electricity consumption and liquid oxygen feeding system, respectively.
Conclusions
Electricity consumption is the key input parameter that determines the LCA results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang JC, Ossoff SF, Lobe DC, Dorfman MH, Dumais CM, Qualls RG, Johnson JD (1985) UV inactivation of pathogenic and indicator microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1361–1365
Cho M (2005) Quantitative evaluation of inactivation of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts and indicator microorganisms and investigation of inactivation mechanisms in water disinfection treatment. Doctoral dissertation, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Rice EW, Greenberg AE, Franson MAH (eds) (2005) Standard methods: for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. APHA/AWWA/WEF, Washington
Galal-Gorchev H (1996) Chlorine in water disinfection. Pure Appl Chem 68:1731–1735
Ghodke SR, Barnwal R, Kumar M, Jayaprakash D, Supriya B, Mishra R, Lawangare N, Nanu K, Puthran G, Veer VS, Abdullah KK, Kailash CM (2007) SF6 Gas handling system for 3 MeV, 30 kW electronic beam accelerator at the EBC, Kharghar, Navi Mumbai, APAC 2007. Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology(RRCAT), Indore
Glaze WH, Lay Y, Kang J (1995) Advanced oxidation processes: a kinetic model for the oxidation of 1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane in water by the combination of hydrogen peroxide and UV radiation. Ind Eng Chem Res 34:2314–2323
Goedkoop M, Spriensma R (2001a) The Eco-indicator 99: A damage oriented method for life cycle impact assessment. PRe consultants B.V, Amersfoort
Goedkoop M, Spriensma R (2001b) The Eco-indicator 99: manual for designers. A damage oriented method for life cycle impact assessment. PRe consultants B.V, Amersfoort
IPCC, Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
ISO (2006) ISO 14044: environmental management—life cycle assessment—requirements and guidelines. ISO, Geneva
Kurucz CN, Waite TD, Cooper WJ (1995) The Miami electron beam research facility: a large scale wastewater treatment application. Radiat Phys Chem 45:299–308
Lee KM, Lee SY, Hur T (2004) Life cycle inventory analysis for electricity in Korea. Energy 29:87–101
Liltved H, Landfald B (2000) Effects of high-intensity light on ultraviolet-irradiatied and non-irradiated fish pathogenic bacteria. Water Res 34:481–486
MoCT (2005) Sewage facility standards. Korea Water and Wastewater Works Association, Seoul, Korea, in Korean
MoE (2008) Statistics of sewerage 2007. Ministry of Environment, Seoul, Korea, in Korean
Ozone Engineering (2010) Ozone generator model LAB2B. http://www.ozone-engineering.com/lab2b-lab-gen.html. Accessed on 24 Feb 2010
Rakness KL, DeMers LD, Blank BD, Henry DJ (1996) Gas phase ozone concentration comparisons from a commercial UV meter and KI wet-chemistry tests. Ozone Sci Eng 18:231–249
Sampa MHO, Borrely SI, Silva BL, Vieira JM, Rela PR, Calvo WAP, Nieto RC, Duarte CL, Perez HEB, Somessari ES, Lugao AB (1995) The use of electronbeam accelerator for the treatment of erinking water and wastewater in Brazil. Radiat Phys Chem 46:1143–1146
Schmidt WP, Beyer HM (1999) Environmental considerations on battery-housing recovery. Int J Life Cycle Assess 4:107–112
Spriensma R (2004) SimaPro database manual: the BUWAL 250 library. PRe Consultants, Amersfoort
van der Zel L (2003) SF6 and the environment: guidelines for electric utility substations. Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), California
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI). Sincere thanks are extended to Mr. Tae-Hun Kim for his assistance in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Stefanie Hellweg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KM., Yu, S., Choi, YH. et al. Environmental assessment of sewage effluent disinfection system: electron beam, ultraviolet, and ozone using life cycle assessment. Int J Life Cycle Assess 17, 565–579 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-012-0388-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-012-0388-9