Abstract
Purpose
As liquid crystal display (LCD) flat-screen televisions increase in popularity, their potential contribution to global warming has received wide attention. This study presents global warming impacts resulting from the life cycle assessment (LCA) of LCD flat-screen televisions for key global warming contributors from the “cradle-to-gate” and use stages of the product’s life cycle. The emissions from nitrogen trifluoride (NF3), a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential (GWP) 17,000 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2), are not monitored in the Kyoto Protocol. Emissions in the cradle-to-gate and use stages were modeled in this study according to their GWP (kg CO2 equivalent), focusing and analyzing the most significant source of NF3 emissions.
Materials and methods
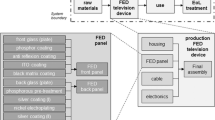
NF3 is used during the manufacturing process of LCDs to clean the vacuum chambers. In this study, a system diagram of the cradle-to-gate stage and use stage of a 40-in. LCD television was proposed using the software package Gabi®, particularly investigating NF3 to determine its possible effects on global warming based on a typical LCA.
Results and discussion
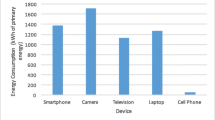
The energy inputs in the use stage of the LCD flat-screen television resulted in major global warming impacts, while the contribution of GWP resulting from NF3 was trivial. However, as energy efficiency continuously improves over time, the GWP resulting from NF3 may become significant. Findings in this study allow industry to focus on those critical stages of the production life cycle that most directly affect global warming while permitting government agencies to enact proper regulations to help decrease CO2 equivalent emissions.
Conclusions
The preliminary assessment of our LCA also offers manufacturers the ability to determine the largest sources of greenhouse gases and their connection in the life cycle analysis of a product. This extension may help guide legislation and industrial management in the future. For further decision making, an in-depth sensitivity analysis may be needed to strengthen the results.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Air Products (2009) Nitrogen trifluoride. Retrieved March 30, 2010, from Product Stewardship Summary: http://www.airproducts.com/NR/rdonlyres/75D20CE9-0D78-4255-9210-D5964972C2C3/0/NitrogenTrifluoride_ProdSum.pdf
Aoe T, Michiyasu T, Matsuoka Y, Shikata N (2003) Case study for calculation of factor x (eco-efficiency)—comparing CRT TV, PDP TV and LCD TV—Proceedings of EcoDesign 2003: 3rd International Symposium on Environmentally Conscious Design and Inverse Manufacturing. Tokyo, Japan, December 8–11, 2003
Cole S (2008) Geology.com. Retrieved March 14, 2010, from Nitrogen trifluoride: potent greenhouse gas more common in atmosphere than estimated: http://geology.com/nasa/nitrogen-trifluoride/
Conniff R (2008) YALE Environment 360. Retrieved March 26, 2010, from The greenhouse gas that nobody knew: http://e360.yale.edu/content/feature.msp?id=2085
Hischier R, Baudin I (2010) LCA study of a plasma television device. Int J Life Cycle Assess 15(5):428–438
Jeong I-T, Lee K-M (2009) Assessment of the ecodesign improvement options using the global warming and economic performance indicators. J Clean Prod 17(13):1206–1213
Patel-Predd P (2008) Retrieved Month 26, 2010, from Electronics industry changes the climate with new greenhouse gas: http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=electronics-industry-contributes-new-greenhouse-gas
PE International (2010) Gabi 4
Socolof ML, Overly GJ, Geibig JR (2005) Environmental life-cycle impacts of CRT and LCD desktop computer displays. J Clean Prod 13(13–14):1281–1294
State of California (2009) The California Energy Commission. Retrieved March 16, 2010, from Energy efficiency standards for televisions: http://www.energy.ca.gov/appliances/tv_faqs.html
Taub EA (2009) The New York Times. Retrieved March 28, 2010, from Price of flat-panel tvs rivals the old tube type : http://www.nytimes.com/2009/12/14/business/14hdtv.html
Tsai W-T (2007) Environmental and health risk analysis of nitrogen trifluoride (NF3), a toxic and potent greenhouse gas. J Hazard Mater 159:257–263
Udell E (2008) Environment. Retrieved March 14, 2010, from Your flat screen has (greenhouse) gas: http://www.alternet.org/environment/95111/your_flat_screen_has_%28greenhouse%29_gas/
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for all constructive comments provided by four anonymous referees and data and reports cited and used in this analysis. Special thanks to PE International who provides us with Gabi® education version in support of this LCA study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, N.J., Chang, NB. & Qi, C. Preliminary assessment for global warming potential of leading contributory gases from a 40-in. LCD flat-screen television. Int J Life Cycle Assess 17, 96–104 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-011-0341-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-011-0341-3