Abstract
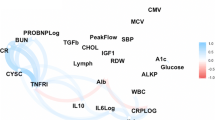
Although the number of centenarians is growing worldwide, the potential factors influencing the aging process remain only partially elucidated. Researchers are increasingly focusing toward biomarkers as tools to shed more light on the pathophysiology of complex phenotypes, including the ability to reach successful aging, i.e., free of major chronic diseases. We therefore conducted a case-control study examining the potential associations of multiple candidate biomarkers in healthy centenarians and sex-matched healthy elderly controls. Using a case-control study of 81 centenarians (aged ≥ 100 years) selected based on the fact that they were disease-free and 46 healthy elderly controls (aged 70–80 years), serum levels of 15 different candidate biomarkers involved in the regulation of metabolism, angiogenesis, inflammation, and bone formation were measured. Of the 15 biomarkers tested, four molecules (chemerin, fetuin-A, and fibroblast growth factors [FGF] 19 and 21) were found to be independently associated with successful aging regardless of sex. Logistic regression analysis confirmed that chemerin, fetuin-A, FGF19, and FGF21 were independently associated with successful aging [predicted probability (PP) = 1 / [1 + 1 / exp (11.832 − 0.027 × (chemerin) − 0.009 × (fetuin-A) + 0.014 × (FGF19) − 0.007 × (FGF21)]. The area under the curve (AUC) of predicted probability values for the four-biomarker panel revealed that it can discriminate between centenarians and elderly controls with excellent accuracy (AUC > 0.94, P < 0.001). Although preliminary in essence and limited by the low sample size and lack of replication in other independent cohorts, our data suggest an independent association between successful aging and serum chemerin, fetuin-A, FGF19, and FGF21, which may provide novel information on the mechanisms behind the human aging process. Whether the four-biomarker panel may predict successful aging deserves further scrutiny.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams AC, Cheng CC, Coskun T, Kharitonenkov A (2012) FGF21 requires betaklotho to act in vivo. PLoS ONE 7:e49977
Ailshire JA, Beltran-Sanchez H, Crimmins EM (2014) Becoming Centenarians: Disease and Functioning Trajectories of Older U.S. Adults as They Survive to 100. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci
Barutcuoglu B, Basol G, Cakir Y, Cetinkalp S, Parildar Z, Kabaroglu C, Ozmen D, Mutaf I, Bayindir O (2011) Fibroblast growth factor-19 levels in type 2 diabetic patients with metabolic syndrome. Ann Clin Lab Sci 41:390–396
Basile G, Paffumi I, D’Angelo AG, Figliomeni P, Cucinotta MD, Pace E, Ferraro M, Saitta S, Lasco A, Gangemi S (2012) Healthy centenarians show high levels of circulating interleukin-22 (IL-22). Arch Gerontol Geriatr 54:459–461
Bik W, Baranowska-Bik A, Wolinska-Witort E, Kalisz M, Broczek K, Mossakowska M, Baranowska B (2013) Assessment of adiponectin and its isoforms in Polish centenarians. Exp Gerontol 48:401–407
Christensen K, McGue M, Petersen I, Jeune B, Vaupel JW (2008) Exceptional longevity does not result in excessive levels of disability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:13274–13279
Emanuele E, Lista S, Ghidoni R, Binetti G, Cereda C, Benussi L, Maletta R, Bruni AC, Politi P (2011) Chromosome 9p21.3 genotype is associated with vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 32:1231–1235
Emanuele E, Minoretti P, Pareja-Galeano H, Sanchis-Gomar F, Garatachea N, Lucia A (2014a) Serum irisin levels, precocious myocardial infarction, and healthy exceptional longevity. Am J Med 127:888–890
Emanuele E, Minoretti P, Sanchis-Gomar F, Pareja-Galeano H, Yilmaz Y, Garatachea N , Lucia A (2014b) Can Enhanced Autophagy be Associated with Human Longevity? Serum Levels of the Autophagy Biomarker Beclin-1 are Increased in Healthy Centenarians. Rejuvenation Res
Fang Q, Li H, Song Q, Yang W, Hou X, Ma X, Lu J, Xu A, Jia W (2013) Serum fibroblast growth factor 19 levels are decreased in Chinese subjects with impaired fasting glucose and inversely associated with fasting plasma glucose levels. Diabetes Care 36:2810–2814
Fatima SS, Rehman R, Baig M, Khan TA (2014) New roles of the multidimensional adipokine: Chemerin. Peptides 62C:15–20
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A (2007) G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods 39:175–191
Gangemi S, Basile G, Merendino RA, Minciullo PL, Novick D, Rubinstein M, Dinarello CA, Lo Balbo C, Franceschi C, Basili S, DU E, Davi G, Nicita-Mauro V, Romano M (2003) Increased circulating Interleukin-18 levels in centenarians with no signs of vascular disease: another paradox of longevity? Exp Gerontol 38:669–672
Gavrilova NS, Gavrilov LA (2010) Search for mechanisms of exceptional human longevity. Rejuvenation Res 13:262–264
Gerli R, Monti D, Bistoni O, Mazzone AM, Peri G, Cossarizza A, Di Gioacchino M, Cesarotti ME, Doni A, Mantovani A, Franceschi C, Paganelli R (2000) Chemokines, sTNF-Rs and sCD30 serum levels in healthy aged people and centenarians. Mech Ageing Dev 121:37–46
Geroldi D, Falcone C, Minoretti P, Emanuele E, Arra M, D’Angelo A (2006) High levels of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products may be a marker of extreme longevity in humans. J Am Geriatr Soc 54:1149–1150
Gremeaux V, Gayda M, Lepers R, Sosner P, Juneau M, Nigam A (2012) Exercise and longevity. Maturitas 73:312–317
Hao Y, Zhou J, Zhou M, Ma X, Lu Z, Gao M, Pan X, Tang J, Bao Y, Jia W (2013) Serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 19 are inversely associated with coronary artery disease in chinese individuals. PLoS ONE 8:e72345
Heinrichsdorff J, Olefsky JM (2012) Fetuin-A: the missing link in lipid-induced inflammation. Nat Med 18:1182–1183
Kir S, Beddow SA, Samuel VT, Miller P, Previs SF, Suino-Powell K, Xu HE, Shulman GI, Kliewer SA, Mangelsdorf DJ (2011) FGF19 as a postprandial, insulin-independent activator of hepatic protein and glycogen synthesis. Science 331:1621–1624
Kuro-o M (2010) Klotho. Pflugers Arch 459:333–343
Leeson GW (2014) Future prospects for longevity. Post Reprod Health 20:11–15
Malin SK, Navaneethan SD, Mulya A, Huang H, Kirwan JP (2014) Exercise-induced lowering of chemerin is associated with reduced cardiometabolic risk and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in older adults. J Nutr Health Aging 18:608–615
Mathews ST, Rakhade S, Zhou X, Parker GC, Coscina DV, Grunberger G (2006) Fetuin-null mice are protected against obesity and insulin resistance associated with aging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 350:437–443
Mori K, Emoto M, Inaba M (2012) Fetuin-A and the cardiovascular system. Adv Clin Chem 56:175–195
Nolen B, Velikokhatnaya L, Marrangoni A, De Geest K, Lomakin A, Bast RC Jr, Lokshin A (2010) Serum biomarker panels for the discrimination of benign from malignant cases in patients with an adnexal mass. Gynecol Oncol 117:440–445
Rasul S, Wagner L, Kautzky-Willer A (2012) Fetuin-A and angiopoietins in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 42:496–505
Robert L, Fulop T (2014) Longevity and its regulation: centenarians and beyond. Interdiscip Top Gerontol 39:198–211
Stefanov T, Bluher M, Vekova A, Bonova I, Tzvetkov S, Kurktschiev D, Temelkova-Kurktschiev T (2014) Circulating chemerin decreases in response to a combined strength and endurance training. Endocrine 45:382–391
Terry DF, Sebastiani P, Andersen SL, Perls TT (2008) Disentangling the roles of disability and morbidity in survival to exceptional old age. Arch Intern Med 168:277–283
Tomiyama K, Maeda R, Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Tanaka T, Ito S, Nabeshima Y, Tomita T, Odori S, Hosoda K, Nakao K, Imura A (2010) Relevant use of Klotho in FGF19 subfamily signaling system in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:1666–1671
Trost SG, Fees BS, Haar SJ, Murray AD, Crowe LK (2012) Identification and validity of accelerometer cut-points for toddlers. Obesity (Silver Spring) 20:2317–2319
Wang D, Zhu W, Li J, An C, Wang Z (2013) Serum concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: association with insulin resistance, adiponectin, and polycystic ovary syndrome history. PLoS ONE 8:e81190
Wojcik M, Janus D, Dolezal-Oltarzewska K, Kalicka-Kasperczyk A, Poplawska K, Drozdz D, Sztefko K, Starzyk JB (2012) A decrease in fasting FGF19 levels is associated with the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese adolescents. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 25:1089–1093
Woo YC, Xu A, Wang Y, Lam KS (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 21 as an emerging metabolic regulator: clinical perspectives. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 78:489–496
Wu AL, Coulter S, Liddle C, Wong A, Eastham-Anderson J, French DM, Peterson AS, Sonoda J (2011) FGF19 regulates cell proliferation, glucose and bile acid metabolism via FGFR4-dependent and independent pathways. PLoS ONE 6:e17868
Zhang Y, Xie Y, Berglund ED, Coate KC, He TT, Katafuchi T, Xiao G, Potthoff MJ, Wei W, Wan Y, Yu RT, Evans RM, Kliewer SA, Mangelsdorf DJ (2012) The starvation hormone, fibroblast growth factor-21, extends lifespan in mice. Elife 1:e00065
Conflicts of interest
None declared. All listed authors have made a significant research contribution to the study and approved the submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Alejandro Lucia and Enzo Emanuele share senior authorship.
About this article
Cite this article
Sanchis-Gomar, F., Pareja-Galeano, H., Santos-Lozano, A. et al. A preliminary candidate approach identifies the combination of chemerin, fetuin-A, and fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 as a potential biomarker panel of successful aging. AGE 37, 42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-015-9776-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-015-9776-y