Abstract
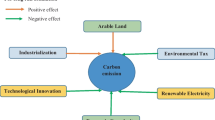
The crucial role of environmental assessment quality has been recognised by environmental and sustainable development goals in addressing climate change challenges. By focusing on the key identifier of environmental assessment, progress can be made towards overcoming climate change issues effectively. The current study considers environmental commitments under COP28 to study the role of economic complexity, greenfield investments, and energy innovation in environmental degradation in newly industrialised economies from 1995 to 2021. We employ novel panel estimations from CS-ARDL, CS-DL, AMG, and CCEMG to confirm that economic growth and greenfield investments degrade environmental quality. On the other hand, energy innovation and urbanisation improve environmental sustainability. Lastly, we confirm the EKC hypothesis for economic complexity as well. Given the reported empirical findings, the study suggests policymakers must focus on economic complexity to transform industrial sectors’ economic potential. Furthermore, foreign investment projects must be linked with environmental goals to increase renewable energy capacity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and relevant materials will be available from the corresponding author.
Notes
Turkey, Thailand, South Africa, Philippines, Mexico, Malaysia, Indonesia, India, China, Brazil.
Hydrofluorocarbons sulphur, hexafluoride, and perfluorocarbons.
References
Abu Bakar NA (2019) Greenfield, mergers and acquisitions, energy consumption, and environmental performance in selected SAARC and ASEAN countries. Int J Energy Econ Policy 9(2):216–224
Adeel-Farooq RM, Abu Bakar NA, Olajide Raji J (2018) Green field investment and environmental performance: a case of selected nine developing countries of Asia. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 37:1085–1092
Adom PK, Opoku EEO, Yan IKM (2019) Energy demand–FDI nexus in Africa: do FDIs induce dichotomous paths? Energy Econ 81:928–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.05.030
Ahmed Z, Asghar MM, Malik MN, Nawaz K (2020a) Moving towards a sustainable environment: the dynamic linkage between natural resources, human capital, urbanization, economic growth, and ecological footprint in China. Resour Policy 67:101677
Ahmed Z, Zafar MW, Ali S (2020b) Linking urbanization, human capital, and the ecological footprint in G7 countries: an empirical analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 55:102064
Akadiri S saint, Adebayo TS, Asuzu OC et al (2022) Testing the role of economic complexity on the ecological footprint in China: a nonparametric causality-in-quantiles approach. Energy Environ 34(7):2290–2316
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2015) The effect of energy consumption, urbanization, trade openness, industrial output, and the political stability on the environmental degradation in the MENA (Middle East and North African) region. Energy 84:382–389
Al-Mulali U, Weng-Wai C, Sheau-Ting L, Mohammed AH (2015) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol Indic 48:315–323
Aluko OA, Opoku EEO, Acheampong AO (2022) Economic complexity and environmental degradation: evidence from OECD countries. Bus Strategy Environ n/a.https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3269
Álvarez-Herránz A, Balsalobre D, Cantos JM, Shahbaz M (2017) Energy innovations-GHG emissions nexus: fresh empirical evidence from OECD countries. Energy Policy 101:90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.11.030
Baek J (2016) A new look at the FDI–income–energy–environment nexus: dynamic panel data analysis of ASEAN. Energy Policy 91:22–27
Bashir MF (2022) Discovering the evolution of Pollution Haven Hypothesis: a literature review and future research agenda. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:48210–48232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20782-1
Bashir MF, Ma B, Shahbaz M, Jiao Z (2020) The nexus between environmental tax and carbon emissions with the roles of environmental technology and financial development. PLoS One 15:e0242412
Bashir MF, MA B, Hussain HI et al (2022a) Evaluating environmental commitments to COP21 and the role of economic complexity, renewable energy, financial development, urbanization, and energy innovation: empirical evidence from the RCEP countries. Renew Energy 184:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.11.102
Bashir MF, Sadiq M, Talbi B et al (2022b) An outlook on the development of renewable energy, policy measures to reshape the current energy mix, and how to achieve sustainable economic growth in the post COVID-19 era. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:43636–43647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20010-w
Bashir MF, Pan Y, Shahbaz M, Ghosh S (2023) How energy transition and environmental innovation ensure environmental sustainability? Contextual evidence from Top-10 manufacturing countries. Renew Energy 204:697–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.01.049
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Toward a sustainable environment: nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Sci Total Environ 657:1023–1029
Bilgili F, Kuşkaya S, Khan M et al (2021) The roles of economic growth and health expenditure on CO2 emissions in selected Asian countries: a quantile regression model approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:44949–44972
Bukhari WAA, Pervaiz A, Zafar M et al (2023) Role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption in environmental quality and their subsequent effects on average temperature: an assessment of sustainable development goals in South Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30493-w
Can M, Gozgor G (2017) The impact of economic complexity on carbon emissions: evidence from France. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:16364–16370
Charfeddine L (2017) The impact of energy consumption and economic development on ecological footprint and CO2 emissions: evidence from a Markov switching equilibrium correction model. Energy Econ 65:355–374
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:138–154
Chu LK (2021) Economic structure and environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: new evidence from economic complexity. Appl Econ Lett 28:612–616
Chu LK, Le NTM (2022) Environmental quality and the role of economic policy uncertainty, economic complexity, renewable energy, and energy intensity: the case of G7 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:2866–2882
Danish, Wang Z (2019) Investigation of the ecological footprint’s driving factors: what we learn from the experience of emerging economies. Sustain Cities Soc 49:101626
Destek MA, Manga M (2021) Technological innovation, financialization, and ecological footprint: evidence from BEM economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:21991–22001
Dogan E, Ulucak R, Kocak E, Isik C (2020) The use of ecological footprint in estimating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for BRICST by considering cross-section dependence and heterogeneity. Sci Total Environ 723:138063
Doğan B, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Nasir MA (2020) European commitment to COP21 and the role of energy consumption, FDI, trade and economic complexity in sustaining economic growth. J Environ Manag 273:111146
Doğan B, Driha OM, Balsalobre Lorente D, Shahzad U (2021) The mitigating effects of economic complexity and renewable energy on carbon emissions in developed countries. Sustain Dev 29:1–12
Doytch N (2020) The impact of foreign direct investment on the ecological footprints of nations. Environ Sustain Indic 8:100085
Doytch N, Ashraf A (2022) The ecological footprints of greenfield FDI and cross-border M&A Sales. Environ Model Assess 27:935–951
Doytch N, Narayan S (2016) Does FDI influence renewable energy consumption? An analysis of sectoral FDI impact on renewable and non-renewable industrial energy consumption. Energy Econ 54:291–301
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Model 29:1450–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2012.02.014
García-Quevedo J, Jové-Llopis E (2021) Environmental policies and energy efficiency investments. An industry-level analysis. Energy Policy 156:112461
Gormus S, Aydin M (2020) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis using innovation: new evidence from the top 10 innovative economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:27904–27913
Hassan ST, Wang P, Khan I, Zhu B (2023) The impact of economic complexity, technology advancements, and nuclear energy consumption on the ecological footprint of the USA: Towards circular economy initiatives. Gondwana Res 113:237–246
He K, Ramzan M, Awosusi AA et al (2021) Does globalization moderate the effect of economic complexity on CO2 emissions? Evidence from the top 10 energy transition economies. Front Environ Sci 9:778088
IEA (2020) World energy outlook 2020. International Energy Agency: Paris, France, p 2050
Ke H, Yang W, Liu X, Fan F (2020) Does innovation efficiency suppress the ecological footprint? Empirical evidence from 280 Chinese cities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:6826
Khezri M, Heshmati A, Khodaei M (2022) Environmental implications of economic complexity and its role in determining how renewable energies affect CO2 emissions. Appl Energy 306:117948
Kihombo S, Ahmed Z, Chen S et al (2021) Linking financial development, economic growth, and ecological footprint: what is the role of technological innovation? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:61235–61245
Kosifakis G, Kampas A, Papadas CT (2020) Economic complexity and the environment: some estimates on their links. Int J Sustain Agric Manag Inform 6:261–271
Lee C-C, Chen M-P, Wu W (2022) The criticality of tourism development, economic complexity, and country security on ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:37004–37040
Leitão NC, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Cantos-Cantos JM (2021) The impact of renewable energy and economic complexity on carbon emissions in BRICS countries under the EKC scheme. Energies (basel) 14:4908
Li S, Sun H, Sharif A et al (2024) Economic complexity, natural resource abundance and education: implications for sustainable development in BRICST economies. Resour Policy 89:104572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.104572
Liang W, Yang M (2019) Urbanization, economic growth and environmental pollution: evidence from China. Sustai Comput: Inform Syst 21:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2018.11.007
Long X, Ji X, Ulgiati S (2017) Is urbanization eco-friendly? An energy and land use cross-country analysis. Energy Policy 100:387–396
Luo W, Bai H, Jing Q et al (2018) Urbanization-induced ecological degradation in Midwestern China: an analysis based on an improved ecological footprint model. Resour Conserv Recycl 137:113–125
Ma B, Lin S, Bashir MF et al (2023a) Revisiting the role of firm-level carbon disclosure in sustainable development goals: research agenda and policy implications. Gondwana Res 117:230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2023.02.002
Ma B, Sharif A, Bashir M, Bashir MF (2023b) The dynamic influence of energy consumption, fiscal policy and green innovation on environmental degradation in BRICST economies. Energy Policy 183:113823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2023.113823
Mahmood N, Zhao Y, Lou Q, Geng J (2022) Role of environmental regulations and eco-innovation in energy structure transition for green growth: evidence from OECD. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 183:121890
Majeed MT, Mazhar M, Samreen I, Tauqir A (2022) Economic complexities and environmental degradation: evidence from OECD countries. Environ Dev Sustain 24:5846–5866
Martins JM, Adebayo TS, Mata MN et al (2021) Modeling the relationship between economic complexity and environmental degradation: evidence from top seven economic complexity countries. Front Environ Sci 9(2021):744781
Mealy P, Teytelboym A (2022) Economic complexity and the green economy. Res Policy 51:103948
Mensah CN, Long X, Boamah KB et al (2018) The effect of innovation on CO2 emissions of OCED countries from 1990 to 2014. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:29678–29698
Mrabet Z, AlSamara M, Hezam Jarallah S (2017) The impact of economic development on environmental degradation in Qatar. Environ Ecol Stat 24:7–38
Nathaniel S, Khan SAR (2020) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy, trade, and ecological footprint in ASEAN countries. J Clean Prod 272:122709
Neagu O (2021) Economic complexity: a new challenge for the environment. Earth 2:1059–1076
Okamoto S (2013) Impacts of growth of a service economy on CO 2 emissions: Japan’s case. J Econ Struct 2:1–21
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Economet 22:265–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.951
Ponce P, Álvarez-García J, Álvarez V, Irfan M (2022) Analysing the influence of foreign direct investment and urbanization on the development of private financial system and its ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(4):9624–9641
Rafei M, Esmaeili P, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) A step towards environmental mitigation: How do economic complexity and natural resources matter? Focusing on different institutional quality level countries. Resour Policy 78:102848
Sadiq M, Wen F, Bashir MF, Amin A (2022) Does nuclear energy consumption contribute to human development? Modeling the effects of public debt and trade globalization in an OECD heterogeneous panel. J Clean Prod 375:133965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133965
Shahbaz M, Balsalobre D, Shahzad SJH (2019) The influencing factors of CO 2 emissions and the role of biomass energy consumption: statistical experience from G-7 countries. Environ Model Assess 24:143–161
Shahbaz M, Sinha A, Raghutla C, Vo XV (2022) Decomposing scale and technique effects of financial development and foreign direct investment on renewable energy consumption. Energy 238:121758
Swart J, Brinkmann L (2020) Economic complexity and the environment: evidence from Brazil. In: Universities and sustainable communities: meeting the goals of the agenda 2030. pp 3–45. Springer International Publishing, 2020
Wang Y, Kang L, Wu X, Xiao Y (2013) Estimating the environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint at the global level: a spatial econometric approach. Ecol Indic 34:15–21
World Bank (2022) World development indicators 2022. The World Bank 2022
Yahya F, Rafiq M (2020) Brownfield, greenfield, and renewable energy consumption: moderating role of effective governance. Energy Environ 31:405–423
Yilanci V, Pata UK (2020) Investigating the EKC hypothesis for China: the role of economic complexity on ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:32683–32694
Yu Y, Jiang T, Li S et al (2020) Energy-related CO2 emissions and structural emissions’ reduction in China’s agriculture: an input–output perspective. J Clean Prod 276:124169
Funding
Moreover, we acknowledge funding support from Project (Grant No:2023JJ40061) supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Farhan Bashir: conceptualization, methodology, writing draft, writing—revision; Roula Inglesi-Lotz: data curation, writing draft, methodology, data analysis; Ummara Razi: writing draft; Luqman Shahzad: data curation; methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
N/A.
Consent to participate
N/A.
Consent for publication
N/A.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, M.F., Inglesi-Lotz, R., Razi, U. et al. Economic complexity, greenfield investments, and energy innovation: policy implications for sustainable development goals in newly industrialised economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 36013–36027 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33433-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33433-4