Abstract
The present study quantifies the environmental and sustainability impacts associated with municipal solid waste management (MSWM) in India which plays a vital environmental issue in recent times. The upsurge in population has resulted in massive waste generation, leading to a concerning rise in the level of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Therefore, the sustainable management of MSW has been discussed and highlights the conversion of MSW into refuse-derived fuel (RDF) to identify its potential for generating electricity in waste-to-energy (WtE) plants. The life cycle assessment (LCA) study has been done to identify and compare the environmental impacts associated with different scenarios (SC) as SC1: landfilling without energy recovery, SC2: open burning and SC3: processing of RDF in WtE plant by considering the nine impact categories from the inventory data obtained over a period of 12 consecutive months (Jan 2021–Jan 2022). The results exhibited that the global warming potential caused by emissions of GHG are in the order of SC1 (1188 kg CO2 eq) > SC2 (752 kg CO2 eq) > SC3 (332 kg CO2 eq), respectively from 1 t of MSW. It is concluded that the WtE plant can help in the reduction of environmental issues, strengthening the capacity of electricity generation and improving the aesthetic view of the city which is socially acceptable as well. Thus, WtE technology can help in achieving sustainable development goal 12 to regenerate the sustainable secondary resources for the twenty-first century and minimize global climate change.
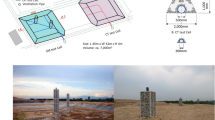
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available as per the request.
References
Abraham A, Park H, Choi O, Sang BI (2021) Anaerobic co-digestion of bioplastics as a sustainable mode of waste management with improved energy production – a review. Bioresource Technol 322(October 2020):124537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124537
Arafat HA, Jijakli K, Ahsan A (2015) Environmental performance and energy recovery potential of five processes for municipal solid waste treatment. J Clean Prod 105:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.11.071
Astrup TF, Tonini D, Turconi R, Boldrin A (2015) Life cycle assessment of thermal waste-to-energy technologies: review and recommendations. Waste Manag 37:104–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.06.011
Ayodele TR, Alao MA, Ogunjuyigbe ASO (2020) Effect of collection efficiency and oxidation factor on greenhouse gas emission and life cycle cost of landfill distributed energy generation. Sustain Cities Soc 52(September 2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101821
Bessi C, Lombardi L, Meoni R, Canovai A, Corti A (2016) Solid recovered fuel: an experiment on classification and potential applications. Waste Manag 47:184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.08.012
Beylot A, Vaxelaire S, Zdanevitch I, Auvinet N, Villeneuve J (2015) Life cycle assessment of mechanical biological pre-treatment of municipal solid waste: a case study. Waste Manag 39:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.01.033
Białowiec A, Pulka J, Stępień P, Manczarski P, Gołaszewski J (2017) The RDF/SRF torrefaction: an effect of temperature on characterization of the product – carbonized refuse derived fuel. Waste Manag 70:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.09.020
Brás I, Silva ME, Lobo G, Cordeiro A, Faria M, De Lemos LT (2017) Refuse derived fuel from municipal solid waste rejected fractions- a case study. Energy Procedia 120:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.07.227
Brunner PH, Rechberger H (2015) Waste to energy - key element for sustainable waste management. Waste Manag 37:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.02.003
Chand Malav L, Yadav KK, Gupta N, Kumar S, Sharma GK, Krishnan S, Rezania S, Kamyab H, Pham QB, Yadav S, Bhattacharyya S, Yadav VK, Bach QV (2020) A review on municipal solid waste as a renewable source for waste-to-energy project in India: current practices, challenges, and future opportunities. J Clean Prod 277:123227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123227
CPCB Report (2021) https://cpcb.nic.in/annual-report.php. Accessed 26 July 2023
CPHEEO (2018) https://cpheeo.gov.in/upload/whatsnew/5bd979e9d8ddfSBM%20RDF%20Book.pdf. Accessed 20 Oct 2023
Dong J, Tang Y, Nzihou A, Chi Y, Weiss-Hortala E, Ni M (2018) Life cycle assessment of pyrolysis, gasification and incineration waste-to-energy technologies: theoretical analysis and case study of commercial plants. Sci Total Environ 626:744–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.151
Fernández-González JM, Grindlay AL, Serrano-Bernardo F, Rodríguez-Rojas MI, Zamorano M (2017) Economic and environmental review of waste-to-energy systems for municipal solid waste management in medium and small municipalities. Waste Manag 67:360–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.05.003
Fernando Y, Tseng ML, Aziz N, Ikhsan RB, Wahyuni-TD IS (2022) Waste-to-energy supply chain management on circular economy capability: an empirical study. Sustain Prod Consum 31:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.01.032
Grzesik K, Malinowski M (2016) Life cycle assessment of refuse-derived fuel production from mixed municipal waste. Energy Sources Part A: Recover Utilization Environ Eff 38(21):3150–3157. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2015.1136976
Han Z, Liu Y, Zhong M, Shi G, Li Q, Zeng D, Zhang Y, Fei Y, Xie Y (2018) Influencing factors of domestic waste characteristics in rural areas of developing countries. Waste Manag 72:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.11.039
Havukainen J, Zhan M, Dong J, Liikanen M, Deviatkin I, Li X, Horttanainen M (2017) Environmental impact assessment of municipal solid waste management incorporating mechanical treatment of waste and incineration in Hangzhou, China. J Clean Prod 141:453–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.146
IPCC (2013) https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1/
IPCC (2006) https://www.ipcc.ch/report/2006-ipcc-guidelines-for-national-greenhouse-gas-inventories/. Accessed 9 Oct 2023
Khan S, Anjum R, Raza ST, Ahmed Bazai N, Ihtisham M (2022) Technologies for municipal solid waste management: current status, challenges, and future perspectives. Chemosphere 288(P1):132403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132403
Kumar A, Samadder SR (2023) Development of lower heating value prediction models and estimation of energy recovery potential of municipal solid waste and RDF incineration. Energy 274:127273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127273
Kumar A, Samadder SR, Kumar N, Singh C (2018) Estimation of the generation rate of different types of plastic wastes and possible revenue recovery from informal recycling. Waste Manag 79:781–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.08.045
Kumari K, Kumar S, Rajagopal V, Khare A, Kumar R (2019) Emission from open burning of municipal solid waste in India. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 40(17):2201–2214. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1351489
Malav LC, Yadav K, Gupta N (2020) A review on MSW as a renewable source for waste-to-energy project in India; current practices, challenges, and future oppurtunities. J Clean Prod 277:123227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123227
Nanda S, Berruti F (2021) Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(2):1433–1456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01100-y
Nate S, Bilan Y, Cherevatskyi D, Kharlamova G, Lyakh O, Wosiak A (2021) The impact of energy consumption on the three pillars of sustainable development. Energies 14(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051372
Nowakowski P, Wala M (2023) The evaluation of energy consumption in transportation and processing of municipal waste for recovery in a waste-to-energy plant: a case study of Poland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(4):8809–8821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21220-y
Nwaokorie KJ, Bareither CA, Mantell SC, Leclaire DJ (2018) The influence of moisture enhancement on landfill gas generation in a full-scale landfill. Waste Manag 79:647–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.08.036
Oliver-Tomas B, Hitzl M, Owsianiak M, Renz M (2019) Evaluation of hydrothermal carbonization in urban mining for the recovery of phosphorus from the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Resour Conserv Recycl 147(April):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.04.023
Pujara Y, Pathak P, Sharma A, Govani J (2019) Review on Indian municipal solid waste management practices for reduction of environmental impacts to achieve sustainable development goals. J Environ Manag 248:109238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.07.009
Pujara Y, Govani J, Patel HT, Pathak P, Mashru D, Ganesh PS (2023) Quantification of environmental impacts associated with municipal solid waste management in Rajkot city, India using life cycle assessment. Environ Adv 12:100364
Shah VA, Srivastava VK et al (2021) Municipal solid waste as a sustainable resource for energy production: state of the art review. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105717
Shehata N, Obaideen K, Sayed ET, Abdelkareem MA, Mahmoud MS, El-Salamony ALHR, Mahmoud HM, Olabi AG (2022) Role of refuse-derived fuel in circular economy and sustainable development goals. Process Saf Environ Prot 163(May):558–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.05.052
Srivastava RR, Rajak DK, Ilyas S, Kim H, Pathak P (2022) Challenges, regulations, and case studies on sustainable management of industrial waste. Minerals 13(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010051
SWM, UN Environmental Programme (2016) https://leap.unep.org/countries/in/national-legislation/solid-waste-management-rules-2016. Accessed 20 Sept 2023
Talang RPN, Sirivithayapakorn S (2022) Comparative analysis of environmental costs, economic return and social impact of national-level municipal solid waste management schemes in Thailand. J Clean Prod 343(January):131017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131017
Tejaswini MSSR, Pathak P (2023) Co-combustion thermogravimetric process to optimize the energy potential of multilayered plastic waste. Fuel 337:127168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.127168UN
Tejaswini MSSR, Pathak P, Gupta DK (2022a) Sustainable approach for valorization of solid wastes as a secondary resource through urban mining. J Environ Manag 319:115727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115727
Tejaswini MSSR, Pathak P, Ramkrishna S, Ganesh PS (2022b) A comprehensive review on integrative approach for sustainable management of plastic waste and its associated externalities. Sci Total Environ 825:153973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153973
Xiao S, Dong H, Geng Y, Francisco MJ, Pan H, Wu F (2020) An overview of the municipal solid waste management modes and innovations in Shanghai China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(24):29943–29953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09398-5
Zhang X, Liu C, Chen Y et al (2022) Source, separation, transportantion, pretreatment, and valorization of municipal solid waste: a critical review. 24:11471-11513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01932-w.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to their organization for continuous research support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP: conceptualization, data curation and writing — original draft. TMSSR: writing and editing. GN: writing and editing. NP: review and editing. DB: conceptualization, review and editing. PP: supervision, conceptualization, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Each author has participated and contributed adequately to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Loubet
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Management of 1 Mt of heterogeneous municipal solid waste (MSW).
• Segregation of MSW processed 65% refuse-derived fuel (RDF).
• Physio-chemical characterization determined the potential of RDF as a secondary resource.
• 1 Mt of MSW yields 0.45 MW of energy.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, H., MSSR, T., Nandikes, G. et al. Techno-environmental analysis to valorize the secondary energy resources from refuse-derived fuel-based waste to energy plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 22441–22452 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32544-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32544-2