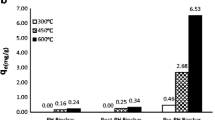
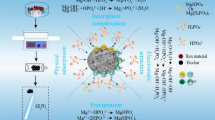
Abstract
The resource utilization of agricultural and forestry waste, especially the high-value transformation of low-grade phosphate rock and derivatives, is an important way to achieve sustainable development. This study focuses on the impregnation and co-pyrolysis of rice straw (RS) with fused calcium magnesium phosphate (FMP), FMP modified with citric acid (CA-FMP), and calcium dihydrogen phosphate (MCP) to produce three phosphorous-enriched biochars (PBC). The Cd(II) removal efficiency of biochars before and after phosphorus modification was investigated, along with the adsorption mechanism and contribution of biochars modified with different phosphorus sources to Cd(II) adsorption. The result indicated that CA-FMP and MCP could be more uniformly loaded onto biochar, effectively increasing the specific surface area (SSA) and total pore volume. The adsorption of Cd(II) onto PBC followed a mono-layer chemisorption process accompanied by intraparticle diffusion. The adsorption of Cd(II) by PBC involved ion exchange, mineral precipitation, complexation with oxygen-containing functional groups (OFGs), cation-π interaction, electrostatic interaction, and physical adsorption. Ion exchange was identified as the primary adsorption mechanism for Cd(II) by BC and FBC (51.53% and 53.15% respectively), while mineral precipitation played a major role in the adsorption of Cd(II) by CBC and MBC (51.10% and 47.98% respectively). Moreover, CBC and MBC significantly enhanced the adsorption capacity of Cd(II), with maximum adsorption amounts of 128.1 and 111.5 mg g−1 respectively.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Bekiaris G, Peltre C, Jensen LS, Bruun S (2016) Using FTIR-photoacoustic spectroscopy for phosphorus speciation analysis of biochars. Spectrochim Acta, Part A 168:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.05.049
Bruun S, Harmer SL, Bekiaris G, Christel W, Zuin L, Hu Y, Jensen LS, Lombi E (2017) The effect of different pyrolysis temperatures on the speciation and availability in soil of P in biochar produced from the solid fraction of manure. Chemosphere 169:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.058
Chen Y, Li M, Li Y, Liu Y, Chen Y, Li H, Li L, Xu F, Jiang H, Chen L (2021) Hydroxyapatite modified sludge-based biochar for the adsorption of Cu(2+) and Cd(2+): Adsorption behavior and mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 321:124413–124422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124413
Chu G, Zhao J, Huang Y, Zhou D, Liu Y, Wu M, Peng H, Zhao Q, Pan B, Steinberg CEW (2018) Phosphoric acid pretreatment enhances the specific surface areas of biochars by generation of micropores. Environ Pollut 240:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.003
Cui X, Fang S, Yao Y, Li T, Ni Q, Yang X, He Z (2016) Potential mechanisms of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by Canna indica derived biochar. Sci Total Environ 562:517–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.248
Cui H, Dong T, Hu L, Xia R, Zhou J, Zhou J (2022) Adsorption and immobilization of soil lead by two phosphate-based biochars and phosphorus release risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 824:153957–153965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153957
Deng Y, Huang S, Laird D, Wang X, Meng Z (2019) Adsorption behaviour and mechanisms of cadmium and nickel on rice straw biochars in single- and binary-metal systems. Chemosphere 218:308–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.081
Deng Y, Huang S, Dong C, Meng Z, Wang X (2020) Competitive adsorption behaviour and mechanisms of cadmium, nickel and ammonium from aqueous solution by fresh and ageing rice straw biochars. Bioresour Technol 303:122853–122861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122853
Feng D, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Sun S (2018) Catalytic effects of ion-exchangeable K+ and Ca2+ on rice husk pyrolysis behavior and its gas–liquid–solid product properties. Energy 152:166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.119
Gao R, Fu Q, Hu H, Wang Q, Liu Y, Zhu J (2019) Highly-effective removal of Pb by co-pyrolysis biochar derived from rape straw and orthophosphate. J Hazard Mater 371:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.079
Ge Q, Tian Q, Wang S, Zhang J, Hou R (2022) Highly efficient removal of lead/cadmium by phosphoric acid-modified hydrochar prepared from fresh banana peels: adsorption mechanisms and environmental application. Langmuir 38:15394–15403. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c02693
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0032-9592(98)00112-5
Hou C, Miao J, Gu S, Wang H, Wang Y, Xu X (2019) Innovation of fused calcium magnesium phosphate products to promote industry development. J Plant Nutr Fert 25:2162–2169. https://doi.org/10.11674/zwyf.19172
Huang R, Fang C, Lu X, Jiang R, Tang Y (2017) Transformation of phosphorus during (hydro)thermal treatments of solid biowastes: reaction mechanisms and implications for P reclamation and recycling. Environ Sci Technol 51:10284–10298. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02011
Huang K, Hu C, Tan Q, Yu M, Shabala S, Yang L, Sun X (2022) Highly efficient removal of cadmium from aqueous solution by ammonium polyphosphate-modified biochar. Chemosphere 305:135471–135478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135471
Lang L, Wang B, Liu T, Wang J, Zhu L, Liu Y, Niu Y (2023) Homogeneous synthesis of Schiff base modified PAMAM dendrimers/silica for efficient adsorption of Hg(II). Chem Eng J 477:147310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.147310
Liu T, Lawluvy Y, Shi Y, Ighalo J, He Y, Zhang Y, Yap P (2022) Adsorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution using modified biochar: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 10:106502–106533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106502
Meng X, Hu R (2021) Nitrogen/phosphorus enriched biochar with enhanced porosity activated by guanidine phosphate for efficient passivation of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II). J Mol Liq 323:115071–115082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115071
Shang H, Li Y, Liu J, Wan Y, Feng Y, Yu Y (2020) Preparation of nitrogen doped magnesium oxide modified biochar and its sorption efficiency of lead ions in aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 314:123708–123715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123708
Shrestha R, Ban S, Devkota S, Sharma S, Joshi R, Tiwari A, Kim H, Joshi M (2021) Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105688–105705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105688
Sun K, Qiu M, Han L, Jin J, Wang Z, Pan Z, Xing B (2018) Speciation of phosphorus in plant- and manure-derived biochars and its dissolution under various aqueous conditions. Sci Total Environ 634:1300–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.099
Wang J, Guo X (2022) Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: interpretation, solving methods and applications. Chemosphere 309:136732–136745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136732
Wang Q, Duan C, Xu CY, Geng Z (2022) Efficient removal of Cd(II) by phosphate-modified biochars derived from apple tree branches: processes, mechanisms, and application. Sci Total Environ 819:152876–152887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152876
Wang B, Wu K, Liu T, Cheng Z, Liu Y, Liu Y, Niu Y (2023) Feasible synthesis of bifunctional polysilsesquioxane microspheres for robust adsorption of Hg(II) and Ag(I): behavior and mechanism. J Hazard Mater 442:130121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130121
Wu J, Wang T, Wang J, Zhang Y, Pan WP (2021) A novel modified method for the efficient removal of Pb and Cd from wastewater by biochar: enhanced the ion exchange and precipitation capacity. Sci Total Environ 754:142150–142159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142150
Xu X, Hou C, Wang H, Tang J (2010) Structure of phosphate-containing aluminosilicate vitreous body of complex components with low chemical stability: model of phosphate-containing aluminosilicate vitreous structure and fertilizer development. Sci China: Chem 40:922–926. https://doi.org/10.1360/zb2010-40-7-922
Yang F, Lv J, Zhou Y, Wu S, Sima J (2023) Co-pyrolysis of biomass and phosphate tailing to produce potential phosphorus-rich biochar: efficient removal of heavy metals and the underlying mechanisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:17804–17816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23128-z
Yu Y, Du C (2023) A review on the P enrichment and recovery from steelmaking slag: towards a sustainable P supply and comprehensive utilization of industrial solid wastes. Sci Total Environ 891:164578–164591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164578
Yu Y, Liu D, Wu H (2013) Formation and characteristics of reaction intermediates from the fast pyrolysis of NaCl- and MgCl2-loaded celluloses. Energy Fuels 28:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef401483u
Yuan Q, Wang P, Wang X, Hu B, Wang C, Xing X (2023) Nano-chlorapatite modification enhancing cadmium(II) adsorption capacity of crop residue biochars. Sci Total Environ 865:161097–161107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161097
Zamora-Ledezma C, Negrete-Bolagay D, Figueroa F, Zamora-Ledezma E, Ni M, Alexis F, Guerrero V (2021) Heavy metal water pollution: a fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ Technol Innovation 22:101504–101529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101504
Zhang S, Zhang H, Cai J, Zhang X, Zhang J, Shao J (2017) Evaluation and prediction of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by phosphate-modified activated bamboo biochar. Energy Fuels 32:4469–4477. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b03159
Zhang A, Li X, Xing J, Xu G (2020a) Adsorption of potentially toxic elements in water by modified biochar: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104196–104205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104196
Zhang H, Shao J, Zhang S, Zhang X, Chen H (2020b) Effect of phosphorus-modified biochars on immobilization of Cu (II), Cd (II), and As (V) in paddy soil. J Hazard Mater 390:121349–121356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121349
Zhang H, Ke S, Xia M, Bi X, Shao J, Zhang S, Chen H (2021) Effects of phosphorous precursors and speciation on reducing bioavailability of heavy metal in paddy soil by engineered biochars. Environ Pollut 285:117459–117469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117459
Zhang H, Liao W, Zhou X, Shao J, Chen Y, Zhang S, Chen H (2022a) Coeffect of pyrolysis temperature and potassium phosphate impregnation on characteristics, stability, and adsorption mechanism of phosphorus-enriched biochar. Bioresour Technol 344:126273–126282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126273
Zhang Z, Li Y, Zong Y, Yu J, Ding H, Kong Y, Ma J, Ding L (2022b) Efficient removal of cadmium by salts modified-biochar: performance assessment, theoretical calculation, and quantitative mechanism analysis. Bioresour Technol 361:127717–127728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127717
Zhang K, Yi Y, Fang Z (2023) Remediation of cadmium or arsenic contaminated water and soil by modified biochar: a review. Chemosphere 311:136914–136928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136914
Zhao X, Cai M, Dong Q, Li Y, Sheng J (2018) Advances of mechanisms and technology pathway of efficient utilization of medium-low grade phosphate rock resources. J Plant Nutr Fert 24:1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.11674/zwyf.17418
Zhou X, Xu D, Yang J, Yan Z, Zhang Z, Zhong B, Wang X (2023) Treatment of distiller grain with wet-process phosphoric acid leads to biochar for the sustained release of nutrients and adsorption of Cr(VI). J Hazard Mater 441:129949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129949
Funding
This study was supported by the Chongqing Graduate Scientific Research Innovation Project (CYB22212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang Zeng (first author): conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. Yuhan Lin: data curation—original draft. Ming Ma: visualization and writing—review and editing. Hong Chen (corresponding author): conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, supervision, and writing—review and editing. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent when it is submitted.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Lin, Y., Ma, M. et al. Adsorption effect and mechanism of Cd(II) by different phosphorus-enriched biochars. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 16642–16652 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32308-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32308-y