Abstract
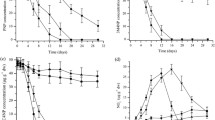
Decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) is recognized as an emerging and hazardous pollutant in numerous ecosystems. Despite this, only a few studies have concurrently investigated the biodegradation of BDE-209 by a microbial consortium comprising both bacteria and fungi. Consequently, the interactions between bacterial and fungal populations and their mutual effects on BDE-209 degradation remain unclear. Our main objective was to concurrently assess the changes and activity of bacterial and fungal communities during the biodegradation of BDE-209 in a real soil matrix. In the present study, various organic substrates were employed to promote soil biomass for the biodegradation of BDE-209. Soil respiration and molecular analysis were utilized to monitor biological activity and biomass community structure, respectively. The findings revealed that the use of wheat straw in the soil matrix resulted in the highest soil respiration and microbial activity among the treatments. This approach obviously provided suitable habitats for the soil microflora, which led to a significant increase in the biodegradability of BDE-209 (49%). Biomass survival efforts and the metabolic pathway of lignin degradation through co-metabolism contributed to the biodegradation of BDE-209. Microbial community analysis identified Proteobacteria (Alphaproteobacteria-Betaproteobacteria), Firmicutes, Bacteroides (bacterial phyla), as well as Ascomycota and Basidiomycota (fungal phyla) as the key microorganisms in the biological community involved in the biodegradation of BDE-209. This study demonstrated that applying wheat straw can improve both the biological activity and the biodegradation of BDE-209 in the soil of polluted sites.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [author initials], upon reasonable request.
References
Abtahi H, Parhamfar M, Saeedi R, Villasenor J, Sartaj M, Kumar V, Coulon F, Parhamfar M, Didehdar M, Koolivand A (2020) Effect of competition between petroleum-degrading bacteria and indigenous compost microorganisms on the efficiency of petroleum sludge bioremediation: Field application of mineral-based culture in the composting process. J Environ Manage 258:110013
Afshar S, Pashaki AS, Najafi R, Nikzad S, Amini R, Shabab N, Khiabanchian O, Tanzadehpanah H, Saidijam M (2020) Cross-resistance of acquired radioresistant colorectal cancer cell line to gefitinib and regorafenib. Iran J Med Sci 45:50
Aghadadashi V, Mehdinia A (2016) Occurrence, spatial deposition and footprint of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surficial sediments of Bushehr peninsula, the Persian Gulf. Mar Pollut Bull 112:211–217
Alef K, Nannipieri P (1995) Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic Press
Bayer K, Kamke J, Hentschel U (2014) Quantification of bacterial and archaeal symbionts in high and low microbial abundance sponges using real-time PCR. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 89:679–690
Cao Y, Yin H, Peng H, Tang S, Lu G, Dang Z (2017) Biodegradation of 2, 2′, 4, 4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium in the presence of Cd2+. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:11415–11424
Chen J, Zhou HC, Wang C, Zhu CQ, Tam NF-Y (2015) Short-term enhancement effect of nitrogen addition on microbial degradation and plant uptake of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in contaminated mangrove soil. J Hazard Mater 300:84–92
Cristale J, Belé TGA, Lacorte S, de Marchi MRR (2019) Occurrence of flame retardants in landfills: a case study in Brazil. Environ Res 168:420–427
Curiel-Alegre S, Velasco-Arroyo B, Rumbo C, Khan AHA, Tamayo-Ramos JA, Rad C, Gallego JLR, Barros R (2022) Evaluation of biostimulation, bioaugmentation, and organic amendments application on the bioremediation of recalcitrant hydrocarbons of soil. Chemosphere 307:135638
Currier HA, Fremlin KM, Elliott JE, Drouillard KG, Williams TD (2020) Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of PBDEs in a terrestrial food chain at an urban landfill. Chemosphere 238:124577
Cycoń M, Mrozik A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2017) Bioaugmentation as a strategy for the remediation of pesticide-polluted soil: A review. Chemosphere 172:52–71
de Gregoris TB, Aldred N, Clare AS, Burgess JG (2011) Improvement of phylum-and class-specific primers for real-time PCR quantification of bacterial taxa. J Microbiol Methods 86:351–356
Duan Y, Awasthi SK, Liu T, Chen H, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Taherzadeh MJ (2019) Dynamics of fungal diversity and interactions with environmental elements in responseto wheat straw biochar amended poultry manure composting. Bioresour Technol 274:410–417
Fierer N, Jackson JA, Vilgalys R, Jackson RB (2005) Assessment of soil microbial community structure by use of taxon-specific quantitative PCR assays. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4117–4120
Gentes M-L, Mazerolle MJ, Giroux J-F, Patenaude-Monette M, Verreault J (2015) Tracking the sources of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in birds: foraging in waste management facilities results in higher DecaBDE exposure in males. Environ Res 138:361–371
Gu, J.-D. (2016) Biodegradation testing: so many tests but very little new innovation. Appl Environ Biotechnol 1:92–95
He H, Li Y, Shen R, Shim H, Zeng Y, Zhao S, Lu Q, Mai B, Wang S (2021) Environmental occurrence and remediation of emerging organohalides: a review. Environ Pollut 290:118060
Kaewlaoyoong A, Chen J-R, Cheng C-Y, Lin C, Cheruiyot NK, Sriprom P (2021) Innovative mycoremediation technique for treating unsterilized PCDD/F-contaminated field soil and the exploration of chlorinated metabolites. Environ Pollut 289:117869
Kerric A, Okeme J, Jantunen L, Giroux J-F, Diamond ML, Verreault J (2021) Spatial and temporal variations of halogenated flame retardants and organophosphate esters in landfill air: potential linkages with gull exposure. Environ Pollut 271:116396
Ko C-F, Yang Y-C, Liu JIWW, Shih Y-H (2022) Thermal treatment of decabrominated diphenyl ether in its highly contaminated soil in Taiwan. Chemosphere 287:131924
Li L, He L, Li Y, Wang Y, Ashraf U, Hamoud YA, Hu X, Wu T, Tang X, Pan S (2023) Deep fertilization combined with straw incorporation improved rice lodging resistance and soil properties of paddy fields. Eur J Agron 142:126659
Li Q, Li J, Jiang L, Sun Y, Luo C, Zhang G (2021) Diversity and structure of phenanthrene degrading bacterial communities associated with fungal bioremediation in petroleum contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 403:123895
Li S, Cui Y, Xia Z, Zhang X, Zhu M, Gao Y, An S, Yu W, Ma Q (2022a) The mechanism of the dose effect of straw on soil respiration: evidence from enzymatic stoichiometry and functional genes. Soil Biol Biochem 168:108636
Li X, Chen AY, Wu Y, Wu L, Xiang L, Zhao HM, Cai QY, Li YW, Mo CH, Wong MH (2018) Applying β-cyclodextrin to amaranth inoculated with white-rot fungus for more efficient remediation of soil co-contaminated with Cd and BDE-209. Sci Total Environ 634:417–426
Li X, Wu Y, Tan Z (2022) An overview on bioremediation technologies for soil pollution in E-waste dismantling areas. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107839
Liu L, Zhang Y, Liu R, Wang Z, Xu F, Chen Y, Lin K (2016) Aerobic debromination of BDE-209 by Rhodococcus sp. coupled with zerovalent iron/activated carbon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:3925–3933
Liu Y, Liu Z, Gong A, Qiu L, Zhang W, Li J, Li F, Bai Y, Li J, Gao G (2019) Cell changes and differential proteomic analysis during biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. RSC Adv 9:25048–25055
Lu J, Li S, Wu X, Liang G, Gao C, Li J, Jin D, Wang B, Zhang M, Zheng F (2021) The dominant microorganisms vary with aggregates sizes in promoting soil carbon accumulation under straw application. Arch Agron Soil Sci 69:1–17
Lukić B, Panico A, Huguenot D, Fabbricino M, van Hullebusch ED, Esposito G (2017) A review on the efficiency of landfarming integrated with composting as a soil remediation treatment. Environ Technol Rev 6:94–116
Lv Y, Li L, Chen Y, Tang Z, Hu Y (2016) Effects of glucose and biphenyl on aerobic cometabolism of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by Pseudomonas putida: kinetics and degradation mechanism. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 108:76–84
McGrath TJ, Ball AS, Clarke BO (2017) Critical review of soil contamination by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs); concentrations, sources and congener profiles. Environ Pollut 230:741–757
Motamedi M, Yerushalmi L, Haghighat F, Chen Z (2022) A critical review of water contamination by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) and main degradation techniques. J Environ Chem Eng 10:108196
Paliya S, Mandpe A, Bhisikar D, Kumar MS, Kumar S (2022) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Indian wastewater treatment plant: occurrence, mass flow and removal. Chemosphere 303:135055
Pfaffl, M. W. (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45–e45
Sahu RS, Peng Y-H, Ko C-F, Chou T-H, Catherine HN, Yang C-Y, Tso C-P, Su Y-F, Shih Y-H (2021) Processes driving the degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in terrestrial environment. Trends Environ Anal Chem 30:e00126
Sarkar D, Haldar A (2005) Physical and Chemical Methods in Soil Analysis. New age international (p) limited, publishers
Scully ED, Geib SM, Hoover K, Tien M, Tringe SG, Barry KW, GLAVINA DEL RIO, T., CHOVATIA, M., HERR, J. R. & CARLSON, J. E. (2013) Metagenomic profiling reveals lignocellulose degrading system in a microbial community associated with a wood-feeding beetle. PLoS ONE 8:e73827
Shore JL, M’Coy WS, Gunsch CK, Deshusses MA (2012) Application of a moving bed biofilm reactor for tertiary ammonia treatment in high temperature industrial wastewater. Biores Technol 112:51–60
Silva JP, Ticona AR, Hamann PR, Quirino BF, Noronha EF (2021) Deconstruction of lignin: from enzymes to microorganisms. Molecules 26:2299
Stiborova H, Vrkoslavova J, Lovecka P, Pulkrabova J, Hradkova P, Hajslova J, Demnerova K (2015) Aerobic biodegradation of selected polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in wastewater sewage sludge. Chemosphere 118:315–321
Wang L, Tang L, Wang R, Wang X, Ye J, Long Y (2016) Biosorption and degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether by Brevibacillus brevis and the influence of decabromodiphenyl ether on cellular metabolic responses. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:5166–5178
Wang S, Li W, Liu L, Qi H, You H (2022) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) by white-rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus: characteristics, mechanisms, and toxicological response. J Hazard Mater 424:127716
Wu Q, Lian R, Bai M, Bao J, Liu Y, Li S, Liang C, Qin H, Chen J, Xu Q (2021) Biochar co-application mitigated the stimulation of organic amendments on soil respiration by decreasing microbial activities in an infertile soil. Biol Fertil Soils 57:793–807
Wu X, Liu P, Zhao X, Wang J, Teng M, Gao S (2022) Critical effect of biodegradation on long-term microplastic weathering in sediment environments: a systematic review. J Hazard. Mater 437:129287
Wu Z, Xie M, Li Y, Gao G, Bartlam M, Wang Y (2018) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) by a newly isolated bacterium from an e-waste recycling area. AMB Express 8:1–12
Xiang L, Harindintwali JD, Wang F, Bian Y, Zhao Z, Wang Z, Wang Y, Mei Z, Jiang X, Schäffer A (2023) Manure-and straw-derived biochars reduce the ecological risk of PBDE and promote nitrogen cycling by shaping microbiomes in PBDE-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 312:137262
Xiang L, Sheng H, Gu C, Marc R-G, Wang Y, Bian Y, Jiang X, Wang F (2019) Biochar combined with compost to reduce the mobility, bioavailability and plant uptake of 2, 2’, 4, 4’-tetrabrominated diphenyl ether in soil. J Hazard Mater 374:341–348
Xiang X, Liu J, Zhang J, Li D, Xu C, Kuzyakov Y (2020) Divergence in fungal abundance and community structure between soils under long-term mineral and organic fertilization. Soil Tillage Res 196:104491
Xiao D, He X, Wang G, Xu X, Hu Y, Chen X, Zhang W, Su Y, Wang K, Soromotin AV (2022) Network analysis reveals bacterial and fungal keystone taxa involved in straw and soil organic matter mineralization. Appl Soil Ecol 173:104395
Xu G, Wang J (2014) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by white-rot fungus Phlebia lindtneri. Chemosphere 110:70–77
Xu M, Huang Q, Xiong Z, Liao H, Lv Z, Chen W, Luo X, Hao X (2021) Distinct responses of rare and abundant microbial taxa to in situ chemical stabilization of cadmium-contaminated soil. Msystems 6:e01040-e1121
Xu W, Pang K-L, Luo Z-H (2014) High fungal diversity and abundance recovered in the deep-sea sediments of the Pacific Ocean. Microb Ecol 68:688–698
Yan D, Long X-E, Ye L, Zhang G, Hu A, Wang D, Ding S (2021) Effects of salinity on microbial utilization of straw carbon and microbial residues retention in newly reclaimed coastal soil. Eur J Soil Biol 107:103364
Yang C, Wang X, Miao F, Li Z, Tang W, Sun J (2020) Assessing the effect of soil salinization on soil microbial respiration and diversities under incubation conditions. Appl Soil Ecol 155:103671
Yu Y, Yin H, Peng H, Lu G, Dang Z (2019) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) using a novel microbial consortium GY1: cells viability, pathway, toxicity assessment, and microbial function prediction. Sci Total Environ 668:958–965
Yu Y, Yin H, Peng H, Lu G, Dang Z (2020) Proteomic mechanism of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) biodegradation by Microbacterium Y2 and its potential in remediation of BDE-209 contaminated water-sediment system. J Hazard Mater 387:121708
Zeng W, Bai X, Zhang L, Wang A, Peng Y (2014) Population dynamics of nitrifying bacteria for nitritation achieved in Johannesburg (JHB) process treating municipal wastewater. Biores Technol 162:30–37
Zhang J, Shen C, Shang TH, Liu JL (2022) Difference responses of soil fungal communities to cattle and chicken manure composting application. J Appl Microbiol 133:323–339
Zhang Y, Xi B, Tan W (2021) Release, transformation, and risk factors of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from landfills to the surrounding environments: a review. Environ Int 157:106780
Zhao C, Yan M, Zhong H, Liu Z, Shi L, Chen M, Zeng G, Song B, Shao B, Feng H (2018) Biodegradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and strategies for acceleration: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 129:23–32
Zhao W, Deng J, Chi S, Wang W, Xu L, Huang Q, Zhang Y, Yu X, Xu J, Chen Y (2022) Sustainability assessment of topsoil ecology in Chongqing, China based on the application of livestock and poultry manure. J Clean Prod 358:131969
Zhu B, Wu S, Xia X, Lu X, Zhang X, Xia N, Liu T (2016) Effects of carbonaceous materials on microbial bioavailability of 2, 2′, 4, 4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) in sediments. J Hazard Mater 312:216–223
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Iran (9907154913, 9907154912). The authors are thankful to the Iran National Science Foundation (99007108).
Funding
This work was supported by Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Iran (Grant numbers: 9907154913, 9907154912) and Iran National Science Foundation (Grant number: 99007108). The corresponding author (Dr Alireza Rahmani) has received research support from “Hamadan University of Medical Sciences” and “Iran National Science Foundation.” The other authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.Z.: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, software, writing-original draft.
A.R.: formal analysis, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision.
V.A.: conceptualization, formal analysis, supervision, methodology, writing-review and editing.
M.K.: data curation, project administration, writing-original draft.
M.T.S.: project administration, validation.
M.L.: investigation, validation, writing-original draft.
A.A.S.S.: formal analysis, methodology.
S.A.: methodology, software, writing-review and editing.
P.K.: resources, methodology.
D.Z.: investigation, resources, writing-review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
We hereby certify that this manuscript represents original work and has not been submitted or published elsewhere. We confirm that all data and information presented in this manuscript are accurate and authentic to the best of our knowledge.
Consent to participate
As part of this study, no human or animal participants were involved at any stage.
Consent for publication
The authors of this manuscript, titled “Investigation of the effects of different substrates on the promotion of the soil microbial consortium, encompassing bacteria and fungi, in the bioremediation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209)” hereby provide their full consent for its publication in the Journal of Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gerald Thouand
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zabihollahi, S., Rahmani, A., Aghadadashi, V. et al. Investigation of the effects of different substrates on the promotion of the soil microbial consortium, encompassing bacteria and fungi, in the bioremediation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209). Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 16359–16374 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32152-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32152-0