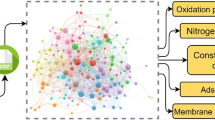
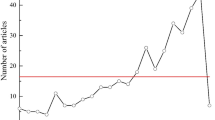
Abstract
Constructed wetland substrates (CWSs) have received considerable attention owing to their importance in adsorbing and degrading pollutants, providing growth attachment points for microorganisms, and supporting wetland plants. There are differences in the configurations and functions of constructed wetlands (CWs) for treating different water bodies and sewage, resulting in a wide variety of substrates. Research on the application and mechanism of CWSs is not sufficiently systematic. Therefore, the current research advancements and hotspots must be identified. Hence, we used CiteSpace to analyze 1955 English publications from the core collection database of the Web of Science to assess the current state of the CWS research field. Based on the cooperative network analysis, the roles of various countries, institutions, and authors in research on CWSs were reviewed. Keyword co-occurrence and cluster analyses were used to discuss the transformation of CWSs from removing traditional pollutants to emerging pollutants and the transition from incorporating natural substrates to artificial substrates. Finally, we underscored the need for more emphasis to be placed on the collocation and application of the CWSs at different latitudes. Furthermore, the substrate micro-interface process and its effects on the interaction patterns of pollutants and microorganisms should be thoroughly investigated to provide theoretical guidance for the development of wetland applications and mechanisms.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Batool A, Saleh TA (2020) Removal of toxic metals from wastewater in constructed wetlands as a green technology; catalyst role of substrates and chelators. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:109924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109924
Boucher-Carrier O, Brisson J, Abas K, Duy SV, Sauve S, Koiv-Vainik M (2022) Effects of macrophyte species and biochar on the performance of treatment wetlands for the removal of glyphosate from agricultural runoff. Sci Total Environ 838:156061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156061
Bowden LI, Jarvis AP, Younger PL, Johnson KL (2009) Phosphorus removal from waste waters using basic oxygen steel slag. Environ Sci Technol 43:2476–2481. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801626d
Brooks AS, Rozenwald MN, Geohring LD, Lion LW, Steenhuis TS (2000) Phosphorus removal by wollastonite: a constructed wetland substrate. Ecol Eng 15:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8574(99)00056-7
Bruch I, Fritsche J, Baenninger D, Alewell U, Sendelov M, Huerlimann H, Hasselbach R, Alewell C (2011) Improving the treatment efficiency of constructed wetlands with zeolite-containing filter sands. Bioresour Technol 102:937–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.041
Chen C, Ibekwe-SanJuan F, SanJuan E, Weaver C (2006) Visual analysis of conflicting opinions, 2006 IEEE Symposium On Visual Analytics Science And Technology, New York, 59–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/VAST.2006.261431
Chen CM, Hicks D (2004) Tracing knowledge diffusion. Scientometrics 59:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SCIE.0000018528.59913.48
Chen J, Li X, Jia W, Shen S, Deng S, Ji B, Chang J (2021) Promotion of bioremediation performance in constructed wetland microcosms for acid mine drainage treatment by using organic substrates and supplementing domestic wastewater and plant litter broth. J Hazard Mater 404:124125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124125
Chen M, Zhu M, Zhu Y, Wang D, Li Z, Zeng G, Zhang C, Huang J, Xu P (2019) Collision of emerging and traditional methods for antibiotics removal: Taking constructed wetlands and nanotechnology as an example. NANOIMPACT 15:100175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2019.100175
Chyan J, Senoro D, Lin C, Chen P, Chen Im (2013) A novel biofilm carrier for pollutant removal in a constructed wetland based on waste rubber tire chips. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 85:638–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.04.010
Corbella C, Guivernau M, Vinas M, Puigagut J (2015) Operational, design and microbial aspects related to power production with microbial fuel cells implemented in constructed wetlands. Water Res 84:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.06.005
Cui E, Zhou Z, Gao F, Chen H, Li J (2023) Roles of substrates in removing antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in constructed wetlands: a review. Sci Total Environ 859:160257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160257
Dan A, Zhang X, Dai Y, Chen C, Yang Y (2020) Occurrence and removal of quinolone, tetracycline, and macrolide antibiotics from urban wastewater in constructed wetlands. J Clean Prod 252:119677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119677
Deng S, Chen J, Chang J (2021) Application of biochar as an innovative substrate in constructed wetlands/biofilters for wastewater treatment: performance and ecological benefits. J Clean Prod 293:126156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126156
Ding Y, Wang W, Song X, Wang G, Wang Y (2014) Effect of spray aeration on organics and nitrogen removal in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland. Chemosphere 117:502–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.084
Dordio AV, Carvalho AJP (2013) Organic xenobiotics removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of the support matrix. J Hazard Mater 252:272–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.008
Drizo A, Frost CA, Grace J, Smith KA (2000) Phosphate and ammonium distribution in a pilot-scale constructed wetland with horizontal subsurface flow using shale as a substrate. Water Res 34:2483–2490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00424-8
Du M, Xu D, Trinh X, Liu S, Wang M, Zhang Y, Wu J, Zhou Q, Wu Z (2016) EPS solubilization treatment by applying the biosurfactant rhamnolipid to reduce clogging in constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 218:833–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.040
Engida T, Alemu T, Wu J, Xu D, Zhou Q, Wu Z (2021) Microbial community dynamics and activity in constructed wetland treating agro-industrial and domestic wastewater: a review. Appl Ecol Environ Res 19:2667–2687. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1904_26672687
Fan H, Hu Y, Tian B, Duan Y, Xue C (2023) Long-term ecological changes in China?s Ramsar sites. Ecol Indic 149:110159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110159
Ge Z, Wei D, Zhang J, Hu J, Liu Z, Li R (2019) Natural pyrite to enhance simultaneous long-term nitrogen and phosphorus removal in constructed wetland: three years of pilot study. Water Res 148:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.037
Gruneberg B, Kern J (2001) Phosphorus retention capacity of iron-ore and blast furnace slag in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Water Sci Technol 44:69–75. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2001.0811
Guan W, Yin M, He T, Xie S (2015) Influence of substrate type on microbial community structure in vertical-flow constructed wetland treating polluted river water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16202–16209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5160-9
Guo X, Cui X, Li H, Xiong B (2021) Purifying effect of biochar-zeolite constructed wetlands on arsenic-containing biogas slurry in large-scale pig farms. J Clean Prod 279:123579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123579
Haberl R, Perfler R, Mayer H (1995) Constructed wetlands in Europe. Water Sci Technol 32:305–315. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1995.0153
Hu B, Hu S, Vymazal J, Chen Z (2022) Application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for pharmaceuticals and personal care productions removal in constructed wetlands with different substrate. J Clean Prod 339:130760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130760
Hu Y, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Kumar JLG (2012) High rate nitrogen removal in an alum sludge-based intermittent aeration constructed wetland. Environ Sci Technol 46:4583–4590. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204105h
Hua GF, Zhao ZW, Kong J, Guo R, Zeng YT, Zhao LF, Zhu QD (2014) Effects of plant roots on the hydraulic performance during the clogging process in mesocosm vertical flow constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:13017–13026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3249-1
Huang J, Reneau RB, Hagedorn C (2000) Nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands employed to treat domestic wastewater. Water Res 34:2582–2588. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00018-X
Jia L, Wang R, Feng L, Zhou X, Lv J, Wu H (2018) Intensified nitrogen removal in intermittently-aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands with agricultural biomass: Effect of influent C/N ratios. Chem Eng J 345:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.087
Jia W, Sun X, Gao Y, Yang Y, Yang L (2020) Fe-modified biochar enhances microbial nitrogen removal capability of constructed wetland. Sci Total Environ 740:139534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139534
Jin F, Hu Z, Liu H, Su J, Zhang J, Wang S, Zhao Y (2023) Impact of clogging on accumulation and stability of phosphorus in the subsurface flow constructed wetland. Chemosphere 313:137429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137429
Johansson L (1999) Blast furnace slag as phosphorus sorbents - column studies. Sci Total Environ 229:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00072-8
Jorgensen C, Inglett KS, Jensen HS, Reitzel K, Reddy KR (2015) Characterization of biogenic phosphorus in outflow water from constructed wetlands. Geoderma 257:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.01.019
Jozwiakowski K, Gajewska M, Pytka A, Marzec M, Gizinska-Gorna M, Jucherski A, Walczowski A, Nastawny M, Kaminska A, Baran S (2017) Influence of the particle size of carbonate-siliceous rock on the efficiency of phosphorous removal from domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 98:290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.006
Kang Y, Guo Z, Ma H, Wu H, Zhang J (2023) Enhanced removal of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in constructed wetlands: iron cycling and microbial mechanisms. Acs Est Water 3:287–297. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestwater.2c00250
Kang Y, Sun H, Gao B, Dang J, Zhang M, Li M, Dong J, Wu H, Zhang J, Guo Z (2022) Enhanced reduction of Cr(VI) in iron-carbon micro-electrolysis constructed wetlands: Mechanisms of iron cycle and microbial interactions. Chem Eng J 439:135742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135742
Kataki S, Chatterjee S, Vairale MG, Dwivedi SK, Gupta DK (2021) Constructed wetland, an eco-technology for wastewater treatment: a review on types of wastewater treated and components of the technology (macrophyte, biolfilm and substrate). J Environ Manage 283:111986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.111986
Kong F, Zhang Y, Wang H, Tang J, Li Y, Wang S (2020) Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by artificial zeolite spheres loaded with nano Fe-Al bimetallic oxide in constructed wetland. Chemosphere 257:127224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127224
Li H, Cai Y, Gu Z, Yang Y, Zhang S, Yang X, Song H (2020) Accumulation of sulfonamide resistance genes and bacterial community function prediction in microbial fuel cell-constructed wetland treating pharmaceutical wastewater. Chemosphere 248:126014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126014
Liang M, Han Y, Easa SM, Chu P, Wang Y, Zhou X (2020) New solution to build constructed wetland in cold climatic region. Sci Total Environ 719:137124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137124
Liu M, Wu S, Chen L, Dong R (2014a) How substrate influences nitrogen transformations in tidal flow constructed wetlands treating high ammonium wastewater? Ecol Eng 73:478–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.09.111
Liu S, Song H, Wei S, Yang F, Li X (2014b) Bio-cathode materials evaluation and configuration optimization for power output of vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland - microbial fuel cell systems. Bioresour Technol 166:575–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.104
Liu T, Lu S, Wang R, Xu S, Qin P, Gao Y (2020) Behavior of selected organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) and their influence on rhizospheric microorganisms after short-term exposure in integrated vertical-flow constructed wetlands (IVCWs). Sci Total Environ 710:136403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136403
Liu X, Guo X, Liu Y, Lu S, Xi B, Zhang J, Wang Z, Bi B (2019a) A review on removing antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater by constructed wetlands: performance and microbial response. Environ Pollut 254:112996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.112996
Liu X, Yang X, Hu X, He Q, Zhai J, Chen Y, Xiong Q, Vymazal J (2019b) Comprehensive metagenomic analysis reveals the effects of silver nanoparticles on nitrogen transformation in constructed wetlands. Chem Eng J 358:1552–1560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.151
Lu H, Xiao L, Wang T, Lu S, Wang H, Guo X, Li J (2021) The application of steel slag in a multistage pond constructed wetland to purify low-phosphorus polluted river water. J Environ Manage 292:112578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112578
Meng P, Pei H, Hu W, Shao Y, Li Z (2014) How to increase microbial degradation in constructed wetlands: Influencing factors and improvement measures. Bioresour Technol 157:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.095
Moore MT, Schulz R, Cooper CM, Smith S, Rodgers JH (2002) Mitigation of chlorpyrifos runoff using constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 46:827–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00189-8
Nguegang B, Masindi V, Makudali TAM, Tekere M (2022) Effective treatment of acid mine drainage using a combination of MgO-nanoparticles and a series of constructed wetlands planted with Vetiveria zizanioides: a hybrid and stepwise approach. J Environ Manage 310:114751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114751
Ravichandran MK, Yoganathan S, Philip L (2021) Removal and risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a decentralized greywater treatment system serving an Indian rural community. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106832
Ren Y, Zhang H, Wang C, Yang Y, Qin Z, Ma Y (2011) Effects of the substrate depth on purification performance of a hybrid constructed wetland treating domestic sewage. J. Environ. Sci Health Part -ToxicHazardous Subst Environ Eng 46:777–782. https://doi.org/10.1080/13632469.2011.571960
Saeed T, Miah MJ, Kumar Yadav A (2022) Development of electrodes integrated hybrid constructed wetlands using organic, construction, and rejected materials as filter media: landfill leachate treatment. Chemosphere 303:135273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135273
Sakadevan K, Bavor HJ (1998) Phosphate adsorption characteristics of soils, slags and zeolite to be used as substrates in constructed wetland systems. Water Res 32:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00271-6
Seo DC, Hwang SH, Kim HJ, Cho JS, Lee HJ, DeLaune RD, Jugsujinda A, Lee ST, Seo JY, Heo JS (2008) Evaluation of 2-and 3-stage combinations of vertical and horizontal flow constructed wetlands for treating greenhouse wastewater. Ecol Eng 32:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2007.10.007
Shen C, Zhao Y, Liu W, Liu R, Zhang F, Shi Y, Wang J, Tang Q, Yang Y, Man YB, Zhang J (2023) Plants boost pyrrhotite-driven nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 367:128240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128240
Si Z, Song X, Wang Y, Cao X, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Ge X, Sand W (2020) Untangling the nitrate removal pathways for a constructed wetland- sponge iron coupled system and the impacts of sponge iron on a wetland ecosystem. J Hazard Mater 393:122407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122407
Stefanakis AI, Akratos CS, Gikas GD, Tsihrintzis VA (2009) Effluent quality improvement of two pilot-scale, horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands using natural zeolite (clinoptilolite). Microporous Mesoporous Mater 124:131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.05.005
Vallee R, Dousset S, Billet D, Benoit M (2014) Sorption of selected pesticides on soils, sediment and straw from a constructed agricultural drainage ditch or pond. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:4895–4905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1840-5
Vymazal J (2013) Emergent plants used in free water surface constructed wetlands: A review. Ecol Eng 61:582–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.06.023
Vymazal J (2011a) Plants used in constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow: a review. Hydrobiologia 674:133–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0738-9
Vymazal J (2011b) Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: five decades of experience. Environ Sci Technol 45:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101403q
Vymazal J (2007) Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 380:48–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.09.014
Wang R, Zhao X, Wang T, Guo Z, Hu Z, Zhang J, Wu S, Wu H (2022) Can we use mine waste as substrate in constructed wetlands to intensify nutrient removal? A critical assessment of key removal mechanisms and long-term environmental risks. WATER Res 210:118009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.118009
Westholm LJ (2006) Substrates for phosphorus removal - potential benefits for on-site wastewater treatment? Water Res 40:23–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.11.006
Wieder R (1990) Metal cation binding to sphagnum peat and sawdust - relation to wetland treatment of metal-polluted waters. Water Air Soil Pollut 53:391–400
Wu H, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Guo W, Hu Z, Liang S, Fan J, Liu H (2015) A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: design and operation. Bioresour Technol 175:594–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.068
Wu J, Xu D, Zhou Q, Zhang L, He F, Wu Z (2019) Effects of layered combined substrates on plant growth and treatment performance and its spatiotemporal variation of vertical-flow constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:23082–23094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05593-1
Wu S, Austin D, Liu L, Dong R (2011) Performance of integrated household constructed wetland for domestic wastewater treatment in rural areas. Ecol Eng 37:948–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.02.002
Xie T, Jing Z, Hu J, Yuan P, Liu Y, Cao S (2018) Degradation of nitrobenzene-containing wastewater by a microbial-fuel-cell-coupled constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 112:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.12.018
Xu G, Li Y, Hou W, Wang S, Kong F (2021) Effects of substrate type on enhancing pollutant removal performance and reducing greenhouse gas emission in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland. J Environ Manage 280:111674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111674
Xu L, Zhao Y, Doherty L, Hu Y, Hao X (2016) The integrated processes for wastewater treatment based on the principle of microbial fuel cells: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46:60–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1061884
Yang R, Liu M, Yang Q (2022) Microbial fuel cell affected the filler pollution accumulation of constructed wetland in the lab-scale and pilot-scale coupling reactors. Chem Eng J 429:132208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132208
Yang Y, Zhao Y, Liu R, Morgan D (2018) Global development of various emerged substrates utilized in constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 261:441–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.085
Zhang H, Tang W, Wang W, Yin W, Liu H, Ma X, Zhou Y, Lei P, Wei D, Zhang L, Liu C, Zha J (2021a) A review on China’s constructed wetlands in recent three decades: application and practice. J Environ Sci 104:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.11.032
Zhang S, Yang X, Li H, Song H, Wang R, Dai Z (2017) Degradation of sulfamethoxazole in bioelectrochemical system with power supplied by constructed wetland-coupled microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 244:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.143
Zhang X, Wang T, Xu Z, Zhang L, Dai Y, Tang X, Tao R, Li R, Yang Y, Tai Y (2020) Effect of heavy metals in mixed domestic-industrial wastewater on performance of recirculating standing hybrid constructed wetlands (RSHCWs) and their removal. Chem Eng J 379:122363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122363
Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang J, Wang X, Liu Y, Wang S, Kong F (2021b) Interactions of chlorpyrifos degradation and Cd removal in iron-carbon-based constructed wetlands for treating synthetic farmland wastewater. J Environ Manage 299:113559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113559
Zhao M, Wang S, Wang H, Qin P, Yang D, Sun Y, Kong F (2019) Application of sodium titanate nanofibers as constructed wetland fillers for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Environ Pollut 248:938–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.040
Zhao YQ, Babatunde AO, Hu YS, Kumar JLG, Zhao XH (2011) Pilot field-scale demonstration of a novel alum sludge-based constructed wetland system for enhanced wastewater treatment. Process Biochem 46:278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.08.023
Zhao YQ, Babatunde AO, Zhao XH, Li WC (2009a) Development of alum sludge-based constructed wetland: an innovative and cost effective system for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Sci Health Part -ToxicHazardous Subst Environ Eng 44:827–832. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520902928685
Zhao YQ, Zhao XH, Babatunde AO (2009b) Use of dewatered alum sludge as main substrate in treatment reed bed receiving agricultural wastewater: long-term trial. Bioresour Technol 100:644–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.040
Zhong H, Hu N, Wang Q, Chen Y, Huang L (2022) How to select substrate for alleviating clogging in the subsurface flow constructed wetland? Sci Total Environ 828:154529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154529
Zhu H, Yu X, Xu Y, Yan B, Banuelos G, Shutes B, Wen Z (2021) Removal of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolytic metabolite in microcosm-scale constructed wetlands under soda saline-alkaline condition: mass balance and intensification strategies. Sci Total Environ 777:145956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145956
Zhu J, You H, Ng HY, Li Z, Xie B, Chen H, Ding Y, Tan H, Liu F, Zhang C (2022) Impacts of bio-carriers on the characteristics of cake layer and membrane fouling in a novel hybrid membrane bioreactor for treating mariculture wastewater. Chemosphere 300:134593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134593
Zhu W, Cui L, Ouyang Y, Long C, Tang X (2011) Kinetic adsorption of ammonium nitrogen by substrate materials for constructed wetlands. Pedosphere 21:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(11)60147-1
Zou Y, Yang Y, Wu S, Chen F, Zhu R (2022) Effect of steel slag on ammonia removal and ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in zeolite-based tidal flow constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 309:136727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136727
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yongqiang Wang: writing—original draft preparation; Yi Chen: supervision, writing—Reviewing; Xiaochun Guo: writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition; Shaoyong Lu: conceptualization, writing—reviewing and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Bibliometrics was initially used to analyze substrates in CWs.
• Important countries, institutions, and authors in this field are highlighted.
• Research in this field focuses on developing new substrates and removing emerging pollutants.
• The research prospects of constructed wetland substrates are reviewed.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Chen, Y., Lu, S. et al. Development and trends of constructed wetland substrates over the past 30 years: a literature visualization analysis based on CiteSpace. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 14537–14552 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32139-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32139-x