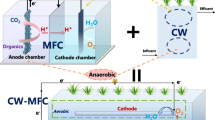
Abstract
In the field of sustainable wastewater management, electroactive wetlands (EW), or constructed wetland-microbial fuel cells (CW-MFC), are an emerging technology. With the growing problem of untreated wastewater, the emphasis must shift to decentralisation of wastewater treatment infrastructure, and CW-MFC can be an excellent choice. This review provides a chronologically organized account of the design and configuration of CW-MFCs developed between 2010 and 2023. The research on CW-MFC has mainly focused on material, positioning and number of electrodes; use of electroconductive media and filler materials; flow regime; algal-based CW-MFC and multistage setups. Compared to traditional constructed wetlands (CW) and microbial fuel cells (MFC), CW-MFCs have a number of advantages, including better treatment efficiency, faster organic matter utilisation, lower capital and land requirements and a smaller carbon footprint. However, there are some limitations as well, such as upscaling and viable electricity generation, which are covered in more detail in the article. Moreover, the economics of this technology is also evaluated. The microbiology of a CW-MFC and its influence on its performance are also elaborated. Recent advancements in this field in terms of design, configuration and performance are discussed. Finally, the knowledge gaps that must be addressed before this technique can be successfully implemented on a large scale are highlighted, along with specific recommendations. This article aims to advocate for EWs as an ideal decentralised wastewater treatment technique, while also shedding light on the areas that still need to be worked on.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be made available on request.
References
Bassi N, Gupta S, Chaturvedi K (2023) Reuse of treated wastewater in India. https://www.ceew.in/sites/default/files/scaling-wastewater-reuse-treatment-and-management-india.pdf
Bourdakos N, Marsili E, Mahadevan R (2014) A defined co-culture of Geobacter sulfurreducens and Escherichia coli in a membrane-less microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol Bioeng 111(4):709–718. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25137
Canstein HV, Ogawa J, Shimizu S, Lloyd JR (2008) Secretion of flavins by Shewanella species and their role in extracellular electron transfer. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(3):615–623. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01387-07
Choudhary M, Muduli M, Ray S (2022) A comprehensive review on nitrate pollution and its remediation: conventional and recent approaches. Sustain Water Resour Manag 8(4):113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00708-y
Corbella C, Hartl M, Fernandez-gatell M, Puigagut J (2019) MFC-based biosensor for domestic wastewater COD assessment in constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 660:218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.347
Das B, Thakur S, Chaithanya MS, Biswas P (2019) Batch investigation of constructed wetland microbial fuel cell with reverse osmosis (RO) concentrate and wastewater mix as substrate. Biomass Bioenergy 122:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.01.017
Doherty L, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Hu Y, Hao X, Xu L, Liu R (2015a) A review of a recently emerged technology: constructed wetland–microbial fuel cells. Water Res 85:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.08.016
Doherty L, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Wang W (2015b) Nutrient and organics removal from swine slurry with simultaneous electricity generation in an alum sludge-based constructed wetland incorporating microbial fuel cell technology. Chem Eng J 266:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.063
El-Naggar MY, Wanger G, Leung KM et al (2010) Electrical transport along bacterial nanowires from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(42):18127–18131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1004880107
Fang Z, Song HL, Cang N, Li XN (2013) Performance of microbial fuel cell coupled constructed wetland system for decolorization of azo dye and bioelectricity generation. Bioresour Technol 144:165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.073
Fang Z, Song HL, Cang N, Li XN (2015) Electricity production from Azo dye wastewater using a microbial fuel cell coupled constructed wetland operating under different operating conditions. Biosens Bioelectron 68:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.047
Foladori P, Ruaben J, Ortigara ARC (2013) Recirculation or artificial aeration in vertical flow constructed wetlands: a comparative study for treating high load wastewater. Bioresour Technol 149:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.099
Freguia S, Rabaey K, Yuan Z, Keller J (2008) Sequential anode–cathode configuration improves cathodic oxygen reduction and effluent quality of microbial fuel cells. Water Res 42(6–7):1387–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.007
Gupta S, Nayak A, Roy C, Yadav AK (2021) An algal assisted constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell integrated with sand filter for efficient wastewater treatment and electricity production. Chemosphere 263:128132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128132
Han J, Yang Z, Wan H, Zhong H, Xu D, Yu S, Gao L (2021) Decomposition of pollutants from domestic sewage with the combination systems of hydrolytic acidification coupling with constructed wetland microbial fuel cell. J Clean Prod 319:128650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128650
Higinbotham N (1970) Movement of ions and electrogenesis in higher plant cells. Americ Zool 10(3):393–403. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/10.3.393
Holmes DE, Bond DR, O’neil RA, Reimers CE, Tender LR, Lovley DR, (2004) Microbial communities associated with electrodes harvesting electricity from a variety of aquatic sediments. Microb Ecol 48:178–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-0004-4
Ilyas H, Masih I (2017) Intensification of constructed wetlands for land area reduction: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:12081–12091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8740-z
Jatoi AS, Akhter F, Mazari SA et al (2021) Advanced microbial fuel cell for waste water treatment—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:5005–5019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11691-2
Jayaraman PP, Yavari A, Georgakopoulos D, Morshed A, Zaslavsky A (2016) Internet of things platform for smart farming: experiences and lessons learnt. Sensors 16(11):1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111884
Ji B, Zhao Y, Vymazal J, Mander Ü, Lust R, Tang C (2021) Mapping the field of constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell: a review and bibliometric analysis. Chemosphere 262:128366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128366
Kiely PD, Regan JM, Logan BE (2011) The electric picnic: synergistic requirements for exoelectrogenic microbial communities. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(3):378–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.03.003
Kong Q, Shi Q, Guo W, Qi X, Zhao Z, Qin M (2023) Synergistic effect of zero-valent iron and static magnetic field on wastewater purification and bioelectricity generation in electroactive constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 385:129417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129417
Kuleshova TE, Galushko AS, Panova GG, Volkova EN, Apollon W, Shuang C, Sevda S (2022) Bioelectrochemical systems based on the electroactivity of plants and microorganisms in the root environment. Selskokhoziaistvennaia Biol [Agricul Biol] 57(3):425–440. https://doi.org/10.15389/agrobiology.2022.3.425eng
Kulshreshtha NM, Verma V, Soti A, Brighu U, Gupta AB (2022) Exploring the contribution of plant species in the performance of constructed wetlands for domestic wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol Rep 18:101038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2022.101038
Kumar VK, Manangath SP, Gajalakshmi S (2023) Innovative pilot-scale constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell system for enhanced wastewater treatment and bioelectricity production. Chem Eng J 460:141686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.141686
Liu S, Song H, Li X, Yang F (2013) Power generation enhancement by utilizing plant photosynthate in microbial fuel cell coupled constructed wetland system. Int J Photoenergy 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/172010
Liu S, Song H, Wei S, Yang F, Li X (2014) Bio-cathode materials evaluation and configuration optimization for power output of vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland—microbial fuel cell systems. Bioresour Technol 166:575–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.104
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R et al (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5181–5192. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0605016
Logan BE, Rossi R, Ragab AA, Saikaly PE (2019) Electroactive microorganisms in bioelectrochemical systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 17(5):307–319. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0173-x
Lovley DR (2006) Bug juice: harvesting electricity with microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(7):497–508. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1442
Lovley DR (2012) Electromicrobiology. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:391–409. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150104
Malvankar NS, Lau J, Nevin KP, Franks AE, Tuominen MT, Lovley DR (2012) Electrical conductivity in a mixed-species biofilm. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(16):5967–5971. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01803-12
Manmohan K, Kumar KV, Harindran SV, Gajalakshmi S (2021) Biosorptionally treated dye wastewater employed in “Olla-pot coupled microbial fuel cell” for tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) irrigation and bio-electricity production. Bioresour Technol Rep 13:100626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100626
Man Mohan K, Kiran Kumar V, Gajalakshmi S (2023) Biosorption of AB-193 Dye using rice straw biomass and post-biosorption application of treated wastewater in olla-pot coupled microbial fuel cells (OPMFCs). Waste Biomass Valori 14(5):1539–1549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01993-6
Mittal Y, Dash S, Srivastava P, Mishra PM, Aminabhavi TM, Yadav AK (2022) Azo dye containing wastewater treatment in earthen membrane based unplanted two chambered constructed wetlands-microbial fuel cells: a new design for enhanced performance. Chem Eng J 427:131856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131856
Mohyudin S, Farooq R, Jubeen F, Rasheed T, Fatima M, Sher F (2022) Microbial fuel cells a state-of-the-art technology for wastewater treatment and bioelectricity generation. Environ Res 204:112387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112387
Moon H, Chang IS, Kim BH (2006) Continuous electricity production from artificial wastewater using a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 97(4):621–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.03.027
Mu C, Wang L, Wang L (2021) Removal of Cr (VI) and electricity production by constructed wetland combined with microbial fuel cell (CW-MFC): influence of filler media. J Clean Prod 320:128860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128860
Muduli M, Chanchpara A, Choudhary M, Saravaia H, Haldar S, Ray S (2022a) Critical review on sustainable bioreactors for wastewater treatment and water reuse. Sustain Water Resour Manag 8:159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00747-5
Muduli M, Choudhary M, Haldar S, Ray S (2022b) Monitoring and assessment of Dracaena-based constructed vertical flow wetlands treating textile dye wastewater. Environ Monit Assess 194(727):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10415-y
Muduli M, Choudhary M, Ray S (2023a) Remediation and characterization of emerging and environmental pollutants from residential wastewater using a nature-based system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(16):45750–45767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25553-0
Muduli M, Choudharya M, Ray S (2023b) A review on constructed wetlands for environmental and emerging contaminants removal from wastewater: traditional and recent developments. Environ Dev and Sus 1–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04190-0
Muduli M, Vasavdutta S, Ray S, Haldar S (2022c) In-depth performance study of an innovative decentralized multistage constructed wetland system treating real institutional wastewater. Environ Res 210:112896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112896
Myers JM, Myers CR (2001) Role for outer membrane cytochromes OmcA and OmcB of Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1 in reduction of manganese dioxide. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(1):260–269. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.1.260-269.2001
Oon YL, Ong SA, Ho LN et al (2020) Constructed wetland–microbial fuel cell for azo dyes degradation and energy recovery: influence of molecular structure, kinetics, mechanisms and degradation pathways. Sci Total Environ 720:137370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137370
Orio-de-la-Rosa E, Vazquez-Castillo J, Castillo-Atoche A, Heredia-Lozano J, CastilloAtoche A, Becerra-Nunez G, Barbosa R (2021) Arrays of plant microbial fuel cells for implementing self-sustainable wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sens J 21(2):1965–1974. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3019986
Patel D, Bapodra SL, Madamwar D, Desai C (2021) Electroactive bacterial community augmentation enhances the performance of a pilot scale constructed wetland microbial fuel cell for treatment of textile dye wastewater. Bioresour Technol 332:125088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125088
Paucar NE, Sato C (2022) An overview of microbial fuel cells within constructed wetland for simultaneous nutrient removal and power generation. Energies 15(18):6841. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15186841
Pirbadian S, Barchinger SE, Leung KM et al (2014) Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 nanowires are outer membrane and periplasmic extensions of the extracellular electron transport components. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(35):12883–12888. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1410551111
Qu Y, Feng Y, Wang X, Logan BE (2012) Use of a coculture to enable current production by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(9):3484–3487. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00073-12
Ren B, Wang T, Zhao Y (2021) Two-stage hybrid constructed wetland-microbial fuel cells for swine wastewater treatment and bioenergy generation. Chemosphere 268:128803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128803
Rozendal RA, Hamelers HV, Rabaey K, Keller J, Buisman CJ (2008) Towards practical implementation of bioelectrochemical wastewater treatment. Trends Biotechnol 26(8):450–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2008.04.008
Saeed T, Yadav AK, Miah MJ (2022) Influence of electrodes and media saturation in horizontal flow wetlands employed for municipal sewage treatment: a comparative study. Environ Technol Innov 25:102160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102160
Srivastava P, Abbassi R, Yadav AK, Garaniya V, Kumar N, Khan SJ, Lewis T (2020) Enhanced chromium (VI) treatment in electroactive constructed wetlands: influence of conductive material. J Hazard Mater 387:121722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121722
Srivastava P, Yadav AK, Mishra BK (2015) The effects of microbial fuel cell integration into constructed wetland on the performance of constructed wetland. Bioresour Technol 195:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.05.072
Tamta P, Rani N, Mittal Y, Yadav AK (2023) Evaluating the potential of multi-anodes in constructed wetlands coupled with microbial fuel cells for treating wastewater and bioelectricity generation under high organic loads. Energies 16(2):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020784
Tang C, Zhao Y, Kang C, Yang Y, Morgan D, Xu L (2019) Towards concurrent pollutants removal and high energy harvesting in a pilot-scale CW-MFC: insight into the cathode conditions and electrodes connection. Chem Eng J 373:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.035
Türker OC, Yakar A (2017) A hybrid constructed wetland combined with microbial fuel cell for boron (B) removal and bioelectric production. Ecol Eng 102:411–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.02.034
Villasenor J, Capilla P, Rodrigo MA, Canizares P, Fernández FJ (2013) Operation of a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland–microbial fuel cell treating wastewater under different organic loading rates. Water Res 47(17):6731–6738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.02.034
Wang J, Long Y, Yu G et al (2022a) A review on microorganisms in constructed wetlands for typical pollutant removal: species, function, and diversity. Front Microbiol 13:845725. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.845725
Wang W, Wang J, Wang X, Cui Y, Zhai T, Wu H, Wang S (2022b) Performance and mechanism of azo dyes degradation and greenhouse gases reduction in single-chamber electroactive constructed wetland system. Bioresour Technol 365:128142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128142
Wang X, Tian Y, Liu H, Zhao X, Peng S (2019) The influence of incorporating microbial fuel cells on greenhouse gas emissions from constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 656:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.328
Wang Y, Song X, Cao X, Xu Z, Huang W, Wang Y, Ge X (2022c) Integration of manganese ores with activated carbon granules into CW-MFC to trigger anoxic electron transfer and removal of ammonia nitrogen. J Clean Prod 334:130202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130202
Wu H, Fan J, Zhang J et al (2015) Strategies and techniques to enhance constructed wetland performance for sustainable wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:14637–14650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5151-x
Xu F, Ouyang DL, Rene ER, Ng HY, Guo LL, Zhu YJ et al (2019) Electricity production enhancement in a constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell system for treating saline wastewater. Bioresour Technol 288:121462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121462
Xu F, Sun R, Wang H, Wang Y, Liu Y, Jin X et al (2021) Improving the outcomes from electroactive constructed wetlands by mixing wastewaters from different beverage-processing industries. Chemosphere 283:131203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131203
Xu L, Zhao Y, Fan C, Fan Z, Zhao F (2017) First study to explore the feasibility of applying microbial fuel cells into constructed wetlands for COD monitoring. Bioresour Technol 243:846–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.179
Xu L, Zhao Y, Tang C, Doherty L (2018) Influence of glass wool as separator on bioelectricity generation in a constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell. J Environ Manage 207:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.035
Xu S, Jangir Y, El-Naggar MY (2016) Disentangling the roles of free and cytochrome-bound flavins in extracellular electron transport from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Electrochim Acta 198:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.03.074
Yadav AK (2010) Design and development of novel constructed wetland cum microbial fuel cell for electricity production and wastewater treatment. 12th IWA International Conference on Wetland Systems for Water Pollution Control, October 4-8, Venice, Italy, Palombi, Italy, (pp. 1085-1089)
Yadav AK, Dash P, Mohanty A, Abbassi R, Mishra BK (2012) Performance assessment of innovative constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell for electricity production and dye removal. Ecol Eng 47:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.06.029
Yi H, Nevin KP, Kim BC, Franks AE, Klimes A, Tender LM, Lovley DR (2009) Selection of a variant of Geobacter sulfurreducens with enhanced capacity for current production in microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 24(12):3498–3503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.05.004
Zhang K, Wu X, Luo H et al (2020) CH4 control and associated microbial process from constructed wetland (CW) by microbial fuel cells (MFC). J Environ Manage 260:110071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110071
Zhi W, Ji G (2012) Constructed wetlands, 1991–2011: a review of research development, current trends, and future directions. Sci Total Environ 441:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.09.064
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely acknowledge Dr. S. Kannan, Director, CSIR-CSMCRI, for providing in-house facilities and infrastructure. The manuscript has been assigned CSIR-CSMCRI-123/2023 registration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Palindhi Verma: conceptualization, data curation and writing—original draft. Sanak Ray: conceptualization, visualization, data curation, review, supervision, editing and fund acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that affect the work reported in this article.
Consent for publication
We do not have any person’s data.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, P., Ray, S. Critical evaluation of electroactive wetlands: traditional and modern advances. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 14349–14366 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32115-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32115-5