Abstract
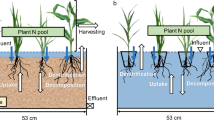
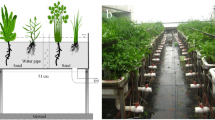
Treating wastewater with low carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratios by constructed wetlands (CWs) is still problematic. Adding chemicals is costly and may cause secondary pollution. Configuring plant diversity in substrate-based CWs has been found to be a better way to treat low-C/N wastewater, but wastewater treatment in floating CWs needs to be studied. In this study, wastewater with C/N ratios of 5 and 10 were set in simulated floating CWs, and 9 combinations with plant species richness (SR) of 1, 3, and 4 were configured. The results showed that (1) increasing SR improved the total N mass removal (NMR) by 29% at a C/N ratio of 5 but not 10; (2) the presence of Oenanthe javanica in the microcosms increased the NMR by 13% and 20% with C/N ratios of 5 and 10, respectively; (3) increasing SR mitigated the net global warming potential (GWP) by 120% at a C/N ratio of 5 but not 10; and (4) a Hemerocallis fulva × O. javanica × Echinodorus parviflours × Iris hybrids mixture resulted in a high NMR and low net GWP. In summary, assembling plant diversity in floating CWs is an efficient and clean measure during the treatment of wastewater with a C/N ratio of 5.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Abalos D, De Deyn GB, Kuyper TW, van Groenigen JW (2014) Plant species identity surpasses species richness as a key driver of N2O emissions from grassland. Glob Chang Biol 20:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12350
Abed SN, Almuktar SA, Scholz M (2017) Remediation of synthetic greywater in mesocosm—scale floating treatment wetlands. Ecol Eng 102:303–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.01.043
Afzal M, Arslan M, Müller JA, Shabir G, Islam E, Tahseen R, Anwar-ul-Haq M, Hashmat AJ, Iqbal S, Khan QM (2019) Floating treatment wetlands as a suitable option for large-scale wastewater treatment. Nat Sustain 2:863–871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0350-y
Anzola-Rojas MDP, Gonçalves Da Fonseca S, Canedo Da Silva C, Maia De Oliveira V, Zaiat M (2015) The use of the carbon/nitrogen ratio and specific organic loading rate as tools for improving biohydrogen production in fixed-bed reactors. Biotechnol Rep 5:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2014.10.010
Bunce J (2021) Carboxylation capacity can limit C3 photosynthesis at elevated CO2 throughout diurnal cycles. Plants 10:2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122603
Çakirgöz M, Bayrakdar A, Çalli B (2021) How do the influent COD/Nitrogen and internal recirculation ratios affect the oxidation ditch type pre-anoxic landfill leachate treatment? J Environ Manage 278:111598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111598
Cardinale BJ (2011) Biodiversity improves water quality through niche partitioning. Nature 472:86–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09904
Chang J, Fan X, Sun H, Zhang C, Song C, Chang SX, Gu B, Liu Y, Li D, Wang Y, Ge Y (2014) Plant species richness enhances nitrous oxide emissions in microcosms of constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 64:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.12.046
Chen X, Zhu H, Yan B, Shutes B, Tian L, Wen H (2020) Optimal influent COD/N ratio for obtaining low GHG emissions and high pollutant removal efficiency in constructed wetlands. J Clean Prod 267:122003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122003
Colares GS, Dell’Osbel N, Wiesel PG, Oliveira GA, Lemos PHZ, Da Silva FP, Lutterbeck CA, Kist LT, Machado ÊL (2020) Floating treatment wetlands: a review and bibliometric analysis. Sci Total Environ 714:136776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136776
Daelman MRJ, van Voorthuizen EM, van Dongen LGJM, Volcke EIP, van Loosdrecht MCM (2013) Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from municipal wastewater treatment - results from a long-term study. Water Sci Technol 67:2350–2355. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.109
Du Y, Pan K, Yu C, Luo B, Gu W, Sun H, Min Y, Liu D, Geng Y, Han W, Chang SX, Liu Y, Li D, Ge Y, Chang J (2018) Plant diversity decreases net global warming potential integrating multiple functions in microcosms of constructed wetlands. J Clean Prod 184:718–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.273
Du Y, Luo B, Han W, Duan Y, Yu C, Wang M, Ge Y, Chang J (2020) Increasing plant diversity offsets the influence of coarse sand on ecosystem services in microcosms of constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:34398–34411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09592-5
Du Y, Niu S, Jiang H, Luo B, Wang Q, Han W, Liu Y, Chang J, Ge Y (2021) Comparing the effects of plant diversity on the nitrogen removal and stability in floating and sand-based constructed wetlands under ammonium/nitrate ratio disturbance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:69354–69366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14829-y
Duan J, Feng Y, Yu Y, He S, Xue L, Yang L (2016) Differences in the treatment efficiency of a cold-resistant floating bed plant receiving two types of low-pollution wastewater. Environ Monit Assess 188:283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5286-3
Engelhardt KAM, Ritchie ME (2002) The effects of aquatic plant species richness on wetland ecosystem processes. Ecology 83(10):2911–2924. https://doi.org/10.2307/3072026
Fahim R, Xiwu L, Jilani G (2021) Feasibility of using divergent plantation to aggrandize the pollutants abatement from sewage and biomass production in treatment wetlands. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 21:731–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2021.05.003
Fan X, Du Y, Luo B, Han W, Niu S, Gu W, Liu D, Chang J, Chang SX, Ge Y (2021) Increasing plant diversity to mitigate net greenhouse effect of wastewater treatment in floating constructed wetlands. J Clean Prod 314:127955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127955
Fan J, Wang W, Zhang B, Guo Y, Ngo H, Guo W, Zhang J, Wu H (2013) Nitrogen removal in intermittently aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands: impact of influent COD/N ratios. Bioresour Technol 143:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.038
Fridley JD (2002) Resource availability dominates and alters the relationship between species diversity and ecosystem productivity in experimental plant communities. Oecologia 132:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-002-0965-x
Gao X, Wang Y, Sun B, Li N (2019) Nitrogen and phosphorus removal comparison between periphyton on artificial substrates and plant-periphyton complex in floating treatment wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:21161–21171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05455-w
Geng Y, Ge Y, Luo B, Chen Z, Min Y, Schmid B, Gu B, Chang J (2019) Plant diversity increases N removal in constructed wetlands when multiple rather than single N processes are considered. Ecol Appl 29:e01965. https://doi.org/10.1002/eap.1965
Grime JP (1998) Benefits of plant diversity to ecosystems: immediate, filter and founder effects. J Eco 86:902–910. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2745.1998.00306.x
Han W, Chang J, Fan X, Du Y, Chang SX, Zhang C, Ge Y (2016) Plant species diversity impacts nitrogen removal and nitrous oxide emissions as much as carbon addition in constructed wetland microcosms. Ecol Eng 93:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.05.030
Han W, Shi M, Chang J, Ren Y, Xu R, Zhang C, Ge Y (2017) Plant species diversity reduces N2O but not CH4 emissions from constructed wetlands under high nitrogen levels. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5938–5948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8288-3
Hector A (1998) The effect of diversity on productivity: detecting the role of species complementarity. Oikos 82:597–599. https://doi.org/10.2307/3546380
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. In: Circular California Agricultural Experiment Station. 347:1e32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)73482-9
Hu S, Zhu H, Bañuelos G, Shutes B, Wang X, Hou S, Yan B (2023) Factors influencing gaseous emissions in constructed wetlands: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 20(5):3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053876
Hussain A, Iqbal MA, Javid A, Razaq A, Aslam S, Hasan A, Akmal M, Qazi JI (2019) Application of fruit wastes as cost-effective carbon sources for biological sulphate reduction. Iran J Sci Technol 43:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-017-0436-1
IPCC (2022) Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of climate change. Working group III contribution to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg3/. Accessed 14 Jan 2024
Itokawa H, Hanaki K, Matsuo T (2001) Nitrous oxide production in high-loading biological nitrogen removal process under low COD/N ratio condition. Water Res 35:657–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00309-2
Jeffrey L, Reithmaier G, Sippo J, Johnston S, Tait D, Harada Y, Maher D (2019) Are methane emissions from mangrove stems a cryptic carbon loss pathway? Insights from a catastrophic forest mortality. New Phytol 224(1):146–154. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15995
Jiang H, Du Y, Han W, Wang L, Xiang C, Ge Y, Chang J (2022) Assembling plant diversity mitigates greenhouse gas emissions and achieves high nitrogen removal when treating the low-C/N wastewater by constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:228–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22088-8
Li J, Yang X, Wang Z, Shan Y, Zheng Z (2015) Comparison of four aquatic plant treatment systems for nutrient removal from eutrophied water. Bioresour Technol 179:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.053
Licata M, Gennaro MC, Tuttolomondo T, Leto C, La Bella S (2019) Research focusing on plant performance in constructed wetlands and agronomic application of treated wastewater-a set of experimental studies in Sicily (Italy). PLoS One 14:e0219445. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219445
Liu D, Wu X, Chang J, Gu BJ, Min Y, Ge Y, Shi Y, Xue H, Peng C, Wu J (2012) Constructed wetlands as biofuel production systems. Nat Clim Chang 2:190–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1370
Luo B, Du Y, Han W, Geng Y, Wang Q, Duan Y, Ren Y, Liu D, Chang J, Ge Y (2020) Reduce health damage cost of greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions by assembling plant diversity in floating constructed wetlands treating wastewater. J Clean Prod 244:118927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118927
Maucieri C, Barbera AC, Vymazal J, Borin M (2017) A review on the main affecting factors of greenhouse gases emission in constructed wetlands. Agric For Meteorol 236:175–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.01.006
Mo Y, Deng Z, Gao J, Guo Y, Yu F (2015) Does richness of emergent plants affect CO2 and CH4 emissions in experimental wetlands? Freshw Biol 60:1537–1544. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12586
Moreira F, Dias E (2020) Constructed wetlands applied in rural sanitation: a review. Environ Res 190:110016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110016
Nema A, Yadav KD, Christian RA (2020) A small-scale study of plant orientation in treatment performance of vertical flow constructed wetland in continuous flow. Int J Phytoremediat 22:849–856. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2020.1715918
Nguyen TNP, Chao SJ, Chen PC, Huang C (2018) Effects of C/N ratio on nitrate removal and floc morphology of autohydrogenotrophic bacteria in a nitrate-containing wastewater treatment process. J Environ Sci 69:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.04.002
Nuamah LA, Li Y, Pu Y, Nwankwegu AS, Haikuo Z, Norgbey E, Banahene P, Bofah-Buoh R (2020) Constructed wetlands, status, progress, and challenges. The need for critical operational reassessment for a cleaner productive ecosystem. J Clean Prod 269:122340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122340
Palmborg C, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Jumpponen A, Carlsson G, Huss-Danell K, Högberg P (2005) Inorganic soil nitrogen under grassland plant communities of different species composition and diversity. Oikos 110:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.13673.x
Pang J, Yang M, Tong D, Fu X, Huang L, Sun B, Pan J (2020) Does influent C/N ratio affect pollutant removal and greenhouse gas emission in wastewater ecological soil infiltration systems with/without intermittent aeration? Water Sci. Technol 81:668–678. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.141
Park JBK, Sukias JPS, Tanner CC (2019) Floating treatment wetlands supplemented with aeration and biofilm attachment surfaces for efficient domestic wastewater treatment. Ecol Eng 139:105582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105582
Pelaz L, Gómez A, Letona A, Garralón G, Fdz-Polanco M (2018) Nitrogen removal in domestic wastewater. Effect of nitrate recycling and COD/N ratio. Chemosphere 212:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.052
Perdana MC, Sutanto HB, Prihatmo G (2018) Vertical subsurface flow (VSSF) constructed wetland for domestic wastewater treatment. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 148:012025. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/148/1/012025
Prata RCC, Matos ATD, Cecon PR, Monaco PAVL, Pimenta LA (2013) Sewage treatment in wetlands cultivated with yellow lily. Eng Agríc 33:1144–1155. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-69162013000600007
Ravenek JM, Bessler H, Engels C, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Gessler A, Gockele A, De Luca E, Temperton VM, Ebeling A, Roscher C, Schmid B, Weisser WW, Wirth C, de Kroon H, Weigelt A, Mommer L (2014) Long-term study of root biomass in a biodiversity experiment reveals shifts in diversity effects over time. Oikos 123:1528–1536. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.01502
Reich PB (2014) The world-wide ‘fast-slow’ plant economics spectrum: a traits manifesto. J Ecol 102:275–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12211
Rodriguez M, Brisson J (2016) Does the combination of two plant species improve removal efficiency in treatment wetlands? Ecol Eng 91:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.02.047
Saliu T, Oladoja N (2021) Nutrient recovery from wastewater and reuse in agriculture: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:2299–2316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01159-7
Schwammberger PF, Yule CM, Tindale NW (2020) Rapid plant responses following relocation of a constructed floating wetland from a construction site into an urban stormwater retention pond. Sci Total Environ 699:134372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134372
Song S, Wang P, Liu Y, Zhao D, An S (2019) Effects of Oenanthe javanica on nitrogen removal in free-water surface constructed wetlands under low-temperature conditions. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081420
Sooknah R, Wilkie A (2004) Nutrient removal by floating aquatic macrophytes cultured in anaerobically digested flushed dairy manure wastewater. Ecol Eng 22(1):27–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2004.01.004
Stadmark J, Leonardson L (2005) Emissions of greenhouse gases from ponds constructed for nitrogen removal. Ecol Eng 25:542–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.07.004
Sun Y, Chen Z, Wu G, Wu Q, Zhang F, Niu Z, Hu H (2016) Characteristics of water quality of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: implications for resources utilization and management. J Clean Prod 131:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.068
Sun S, Liu J, Zhang M, He S (2019) Simultaneous improving nitrogen removal and decreasing greenhouse gas emission with biofilm carriers addition in ecological floating bed. Bioresour Technol 292:121944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121944
Tilman D (1982) Resource competition and community structure. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Tilman D, Lehman CL, Thomson KT (1997) Plant diversity and ecosystem productivity: theoretical considerations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1857–1861. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.5.1857
Tilman D, Hill J, Lehman C (2006) Carbon-negative biofuels from low-input high-diversity grassland biomass. Science 314:1598–1600. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1133306
Tilman D, Isbell F, Cowles JM (2014) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 45:471e493. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-120213-091917
Tondera K, Shang K, Vincent G, Chazarenc F, Hu Y, Brisson J (2020) Effect of plant species and nutrient loading rates in treatment wetlands for polluted river water under a subtropical climate. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04830-5
Tripathi BD, Upadhyay AR (2003) Dairy effluent polishing by aquatic macrophytes. Water Air Soil Pollut 143:377–385. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022813125339
Vymazal J (2007) Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 380:48–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.09.014
Vymazal J (2014) Constructed wetlands for treatment of industrial wastewaters: a review. Ecol Eng 73:724–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.09.034
Wang Y, Inamori R, Kong H, Xu K, Inamori Y, Kondo T, Zhang J (2008) Nitrous oxide emission from polyculture constructed wetlands: effect of plant species. Environ Pollut 152:351–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.017
Wang P, Jeelani N, Zuo J, Zhang H, Zhao D, Zhu Z, Leng X, An S (2018) Nitrogen removal during the cold season by constructed floating wetlands planted with Oenanthe javanica. Mar Freshw Res 69:635–647. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF17156
Wang X, Luo B, Wang L, Zhao Y, Wang Q, Li D, Gu B, Min Y, Chang SX, Ge Y, Chang J (2020) Plant diversity improves the effluent quality and stability of floating constructed wetlands under increased ammonium/nitrate ratio in influent. J Environ Manage 266:110607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110607
Wang L, Luo B, Du Y, Jiang H, Chang SX, Fan X, Chang J, Ge Y (2022) Carbon nanotubes and plant diversity reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve nitrogen removal efficiency of constructed wetlands. J Clean Prod 380:135023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135023
Yan C, Zhang H, Li B, Wang D, Zhao Y, Zheng Z (2012) Effects of influent C/N ratios on CO2 and CH4 emissions from vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands treating synthetic municipal wastewater. J Hazard Mater 203–204:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.002
Yu C, Huang X, Chen H, Godfray HCJ, Wright JS, Hall JW, Gong P, Ni S, Qiao S, Huang G, Xiao Y, Zhang J, Feng Z, Ju X, Ciais P, Stenseth NC, Hessen DO, Sun Z, Yu L, Cai W, Fu H, Huang X, Zhang C, Liu H, Taylor J (2019) Managing nitrogen to restore water quality in China. Nature 567:516–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1001-1
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Ge Z, Hu C, Zhang H (2014) Effects of influent C/N ratios on wastewater nutrient removal and simultaneous greenhouse gas emission from the combinations of vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands and earthworm eco-filters for treating synthetic wastewater. Environ Sci Process Impacts 16:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3em00655g
Zhao Z, Chang J, Han W, Wang M, Ma D, Du Y, Qu Z, Chang SX, Ge Y (2016) Effects of plant diversity and sand particle size on methane emission and nitrogen removal in microcosms of constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 95:390–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.047
Zurita F, De Anda J, Belmont MA (2009) Treatment of domestic wastewater and production of commercial flowers in vertical and horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 35:861–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.12.026
Acknowledgements
We thank Lei He, Bin Luo, Shaodan Niu, and Lichunxiao Wang for their assistance in the field and laboratory works.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 41901242 and 31770434) and “Pioneer” and “Leading Goose” R&D Program of Zhejiang (2022C02038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ying Ge, Jie Chang, and Yuanyuan Du designed the experiments. Chenxu Xiang, Hang Jiang, Hua Liu, Yu An, and Yu Liu performed the experiments. Chenxu Xiang analyzed the data. Chenxu Xiang, Ying Ge, and Jie Chang wrote the first manuscript. Yuanyuan Du, Wenjuan Han, and Baohua Guan provided editorial advice in the process of writing the article, and all authors provided insights throughout the completion of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, C., Du, Y., Han, W. et al. Proper C/N ratio enhances the effect of plant diversity on nitrogen removal and greenhouse effect mitigation in floating constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 12036–12051 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31985-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31985-z