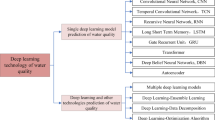
Abstract
The breathtaking economic development put a heavy toll on ecology, especially on water pollution. Efficient water resource management has a long-term influence on the sustainable development of the economy and society. Economic development and ecology preservation are tangled together, and the growth of one is not possible without the other. Deep learning (DL) is ubiquitous in autonomous driving, medical imaging, speech recognition, etc. The spectacular success of deep learning comes from its power of richer representation of data. In view of the bright prospects of DL, this review comprehensively focuses on the development of DL applications in water resources management, water environment protection, and water ecology. First, the concept and modeling steps of DL are briefly introduced, including data preparation, algorithm selection, and model evaluation. Finally, the advantages and disadvantages of commonly used algorithms are analyzed according to their structures and mechanisms, and recommendations on the selection of DL algorithms for different studies, as well as prospects for the application and development of DL in water science are proposed. This review provides references for solving a wider range of water-related problems and brings further insights into the intelligent development of water science.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data, material, or code is available associated with the manuscript.
References
Abiri N, Linse B, Edén P, Ohlsson M (2019) Establishing strong imputation performance of a denoising autoencoder in a wide range of missing data problems. Neurocomputing 365:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.07.065
Addor N, Newman AJ, Mizukami N, Clark MP (2017) The CAMELS data set: catchment attributes and meteorology for large-sample studies. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 21(10):5293–5313. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-21-5293-2017
Alvi M, Cardell-Oliver R, French T (2022a) Utilizing autoencoders to improve transfer learning when sensor data is sparse, 9th ACM International Conference on Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Cities, and Transportation (BuildSys). Assoc Computing Machinery, Boston, MA, pp 500–503. https://doi.org/10.1145/3563357.3567407
Alvi M, French T, Cardell-Oliver R, Keymer P, Ward A (2022b) Cost effective soft sensing for wastewater treatment facilities. IEEE Access 10:55694–55708. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3177201
Alvi M, Batstone D, Mbamba CK, Keymer P, French T, Ward A, Dwyer J, Cardell-Oliver R (2023a) Deep learning in wastewater treatment: a critical review. Water Res 245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120518
Alvi M, French T, Cardell-Oliver R, Batstone D, Akhtar N (2023b) Enhanced deep predictive modelling of wastewater plants with limited data. IEEE Trans Industr Inform, pp 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2023.3281835
Antanasijevic D, Pocajt V, Povrenovic D, Peric-Grujic A, Ristic M (2013) Modelling of dissolved oxygen content using artificial neural networks: Danube River, North Serbia, case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(12):9006–9013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1876-6
Ba-Alawi AH, Vilela P, Loy-Benitez J, Heo S, Yoo C (2021) Intelligent sensor validation for sustainable influent quality monitoring in wastewater treatment plants using stacked denoising autoencoders. J Water Process Eng 43:16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102206
Baek SS, Pyo J, Chun JA (2020) Prediction of water level and water quality using a CNN-LSTM combined deep learning approach. Water 12(12):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123399
Ballard DH (1987) Modular learning in neural networks. In: Proceedings of the sixth national conference on artificial intelligence- vol 1, AAAI’87. AAAI Press, Seattle, Washington, pp 279–284
Bartos M, Kerkez B (2021) Pipedream: an interactive digital twin model for natural and urban drainage systems. Environ Modell Softw 144:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2021.105120
Buonocore E, Mellino S, De Angelis G, Liu GY, Ulgiati S (2018) Life cycle assessment indicators of urban wastewater and sewage sludge treatment. Ecol Indic 94:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.04.047
Capinha C, Ceia-Hasse A, Kramer AM, Meijer C (2021) Deep learning for supervised classification of temporal data in ecology. Ecol Inform 61:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2021.101252
Castangia M, Grajales LMM, Aliberti A, Rossi C, Macii A, Macii E, Patti E (2023) Transformer neural networks for interpretable flood forecasting. Environ Modell Softw 160:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2022.105581
Chau KW (2006) A review on integration of artificial intelligence into water quality modelling. Mar Pollut Bull 52(7):726–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.04.003
Chen YY, Cheng QQ, Cheng YJ, Yang H, Yu HH (2018) Applications of recurrent neural networks in environmental factor forecasting: a review. Neural Comput 30(11):2855–2881. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco_a_01134
Chen KY, Chen HX, Zhou CL, Huang YC, Qi XY (2020) Comparative analysis of surface water quality prediction performance and identification of key water parameters using different machine learning models based on big data. Water Res 171:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115454
Chen C, Hui Q, Xie WX, Wan SH (2021a) Convolutional neural networks for forecasting flood process in internet-of-things enabled smart city. Comput Netw 186:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107744
Chen KH, Wang HC, Valverde-Perez B, Zhai SY (2021b) Optimal control towards sustainable wastewater treatment plants based on multi-agent reinforcement learning. Chemosphere 279:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130498
Chen Z, Xu H, Jiang P, Yu SN, Lin G (2021c) A transfer learning-based LSTM strategy for imputing large-scale consecutive missing data and its application in a water quality prediction system. J Hydrol 602:16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126573
Chen Z, Du M, Yang XD, Chen W, Li YS (2023a) Deep-learning-based automated tracking and counting of living plankton in natural aquatic environments. Environ Sci Technol 10. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c00253
Chen Z, Du M, Yang XD, Chen W, Li YS, Qian C, Yu HQ (2023b) Deep-learning-based automated tracking and counting of living plankton in natural aquatic environments. Environ Sci Technol 10. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c00253
Cho K, Van Merriënboer B, Bahdanau D, Bengio Y (2014) On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. arXiv preprint arXiv:14091259
Cho K, Kim Y (2022) Improving streamflow prediction in the WRF-Hydro model with LSTM networks. J Hydrol 605:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127297
Christin S, Hervet E, Lecomte N (2019) Applications for deep learning in ecology. Methods Ecol Evol 10(10):1632–1644. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210x.13256
Cruz AC, Luvisi A, De Bellis L, Ampatzidis Y (2017) X-FIDO: an effective application for detecting olive quick decline syndrome with deep learning and data fusion. Front Plant Sci 8:12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01741
Cui Z, Guo SL, Zhou YL, Wang J (2023) Exploration of dual-attention mechanism-based deep learning for multi-step-ahead flood probabilistic forecasting. J Hydrol 622:15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129688
Dairi A, Cheng TY, Harrou F, Sun Y, Leiknes T (2019) Deep learning approach for sustainable WWTP operation: a case study on data-driven influent conditions monitoring. Sust Cities Soc 50:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101670
Deep BV, Dash R, Ieee (2019) Underwater fish species recognition using deep learning techniques, 6th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN). Ieee, Noida, India, pp 665-669
DeLancey ER, Simms JF, Mahdianpari M, Brisco B (2020a) Comparing deep learning and shallow learning for large-scale wetland classification in Alberta, Canada. Remote Sens 12(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010002
DeLancey ER, Simms JF, Mahdianpari M, Brisco B, Mahoney C, Kariyeva J (2020b) Comparing deep learning and shallow learning for large-scale wetland classification in Alberta, Canada. Remote Sens 12(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010002
Dodangeh E, Choubin B, Eigdir AN, Nabipour N (2020) Integrated machine learning methods with resampling algorithms for flood susceptibility prediction. Sci Total Environ 705:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135983
Dong GQ, Wang N, Xu T, Liang JY, Qiao RX, Yin DQ, Lin SJ (2023) Deep learning-enabled morphometric analysis for toxicity screening using zebrafish larvae. Environ Sci Technol 12. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c00593
Du L, McCarty GW, Zhang X, Lang MW, Vanderhoof MK, Li X, Huang CQ, Lee S, Zou ZH (2020) Mapping forested wetland inundation in the Delmarva Peninsula, USA using deep convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens 12(4):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040644
Du XD, Cai YH, Wang S, Zhang LJ, Ieee (2016) Overview of deep learning, 31st Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese-Association-of-Automation (YAC). Ieee, Wuhan, Peoples R China, pp 159-164
Du BG, Zhou QL, Guo J, Guo SS, Wang L (2021) Deep learning with long short-term memory neural networks combining wavelet transform and principal component analysis for daily urban water demand forecasting. Expert Syst Appl 171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114571
Ehteram M, Ahmed AN, Khozani ZS, El-Shafie A (2023) Convolutional neural network -support vector machine model-gaussian process regression: a new machine model for predicting monthly and daily rainfall. Water Resour Manag 25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03519-8
Elman JL (1990) Finding structure in time. Cogn Sci 14(2):179–211. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15516709cog1402_1
Fabbri C, Islam M J, Sattar J, Ieee (2018) Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks, IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation ICRA. Ieee Computer Soc, Brisbane, Australia, pp 7159–7165
Fang ZC, Wang Y, Peng L, Hong HY (2021) Predicting flood susceptibility using LSTM neural networks. J Hydrol 594:20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125734
Farhi N, Kohen E, Mamane H, Shavitt Y (2021) Prediction of wastewater treatment quality using LSTM neural network. Environ Technol Innov 23:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101632
Fu G, Jin Y, Sun S, Yuan Z, Butler D (2022) The role of deep learning in urban water management: a critical review. Water Res 223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118973
Fukushima K (2013) Artificial vision by multi-layered neural networks: neocognitron and its advances. Neural Netw 37:103–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2012.09.016
Fulcher BD, Little MA, Jones NS (2013) Highly comparative time-series analysis: the empirical structure of time series and their methods. J R Soc Interface 10(83):12. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2013.0048
Gao S, Huang YF, Zhang S, Han JC, Wang GQ, Zhang MX, Lin QS (2020) Short-term runoff prediction with GRU and LSTM networks without requiring time step optimization during sample generation. J Hydrol 589:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125188
Gharakhanlou NM, Perez L (2023) Flood susceptible prediction through the use of geospatial variables and machine learning methods. J Hydrol 617:20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129121
Gong SM, Ball J, Surawski N (2022) Urban land-use land-cover extraction for catchment modelling using deep learning techniques. J Hydroinform 24(2):388–405. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2022.124
Goodfellow IJ, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 2. MIT Press, Montreal, Canada, pp 2672–2680
Gray PC, Fleishman AB, Klein DJ, McKown MW, Bezy VS (2019) A convolutional neural network for detecting sea turtles in drone imagery. Methods Ecol Evol 10(3):345–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210x.13132
Green AJ, Mohlenkamp MJ, Das J, Chaudhari M, Truong L, Tanguay RL, Reif DM (2021) Leveraging high-throughput screening data, deep neural networks, and conditional generative adversarial networks to advance predictive toxicology. PLoS Comput Biol 17(7):16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009135
Guang H, Tong B, Li L, Sun XY (2019) Chemical Oxygen Demand Soft-Measurement Method via Long Short-Term Memory Network, Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). Chinese Automation Congress. Ieee, Hangzhou, PEOPLES R CHINA, pp 4668–4672. https://doi.org/10.1109/cac48633.2019.8997463
Guo GC, Liu SM, Wu YP, Li JY (2018) Short-term water demand forecast based on deep learning method. J Water Resour Plann Manage 144(12). https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)wr.1943-5452.0000992
Han H, Morrison RR (2022) Improved runoff forecasting performance through error predictions using a deep-learning approach. J Hydrol 608:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127653
Han RY, Guan Y, Yu ZB, Liu P, Zheng HY (2020) Underwater image enhancement based on a spiral generative adversarial framework. IEEE Access 8:218838–218852. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3041280
Heo S, Safder U, Yoo C (2019) Deep learning driven QSAR model for environmental toxicology: effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on human health. Environ Pollut 253:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.081
Herbert ZC, Asghar Z, Oroza CA (2021) Long-term reservoir inflow forecasts: enhanced water supply and inflow volume accuracy using deep learning. J Hydrol 601:16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126676
Hernández-del-Olmo F, Gaudioso E, Dormido R, Duro N (2016) Energy and environmental efficiency for the N-ammonia removal process in wastewater treatment plants by means of reinforcement learning. Energies 9(9):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9090755
Hinton GE, Srivastava N, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov RR (2012) Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors, pp 212–223. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1207.0580
Hochreiter S (1998) The vanishing gradient problem during learning recurrent neural nets and problem solutions. Int J Uncertain Fuzz Knowl-Based Syst 06(2)
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Hosseiny B, Mahdianpari M, Brisco B, Mohammadimanesh F, Salehi B (2022) WetNet: a spatial-temporal ensemble deep learning model for wetland classification using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 60:14. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2021.3113856
Hu CH, Wu Q, Li H, Jian SQ, Li N, Lou ZZ (2018) Deep learning with a long short-term memory networks approach for rainfall-runoff simulation. Water 10(11):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111543
Hu GS, Yang XW, Zhang Y, Wan MZ (2019) Identification of tea leaf diseases by using an improved deep convolutional neural network. Sust Comput 24:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2019.100353
Hu SS, Chen P, Gu PY, Wang B (2020) A deep learning-based chemical system for QSAR prediction. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24(10):3020–3028. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2020.2977009
Huang JD, Huang Y, Hassan SG, Xu LQ, Liu SY (2021) Dissolved oxygen content interval prediction based on auto regression recurrent neural network. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03579-x
Jalwana M, Akhtar N, Bennamoun M, Mian A (2021) CAMERAS: enhanced resolution and sanity preserving class activation mapping for image saliency, IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Ieee Computer Soc, Electr Network, pp 16322–16331. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr46437.2021.01606
Jamali A, Mahdianpari M, Brisco B, Mao DH, Salehi B, Mohammadimanesh F (2022) 3DUNetGSFormer: a deep learning pipeline for complex wetland mapping using generative adversarial networks and Swin transformer. Ecol Inform 72:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2022.101904
Jamei M, Ali M, Malik A, Karbasi M, Rai P (2023) Development of a TVF-EMD-based multi-decomposition technique integrated with Encoder-Decoder-Bidirectional-LSTM for monthly rainfall forecasting. J Hydrol 617:21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129105
Jehanzaib M, Ajmal M, Achite M, Kim TW (2022) Comprehensive review: advancements in rainfall-runoff modelling for flood mitigation. Climate 10(10):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10100147
Jiang W (2018) Object-based deep convolutional autoencoders for high-resolution remote sensing image classification. J Appl Remote Sens 12(3):1
Jiang YQ, Li CL, Sun L, Guo D (2021) A deep learning algorithm for multi-source data fusion to predict water quality of urban sewer networks. J Clean Prod 318:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128533
Kabir S, Patidar S, Xia XL, Liang QH (2020) A deep convolutional neural network model for rapid prediction of fluvial flood inundation. J Hydrol 590:16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125481
Karim F, Armin MA, Ahmedt-Aristizabal D, Tychsen-Smith L, Petersson L (2023) A review of hydrodynamic and machine learning approaches for flood inundation modeling. Water 15(3):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030566
Kavya M, Mathew A, Shekar PR, Sarwesh P (2023) Short term water demand forecast modelling using artificial intelligence for smart water management. Sust Cities Soc 95:22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2023.104610
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM 60(6):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Kumar SS, Wang MZ, Abraham DM, Jahanshahi MR, Iseley T, Cheng JCP (2020) Deep learning-based automated detection of sewer defects in CCTV videos. J Comput Civil Eng 34(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)cp.1943-5487.0000866
Kumar R, Khan FU, Sharma A, Siddiqui MH, Aziz IBA, Kamal MA, Ashraf GM, Alghamdi BS, Uddin MS (2021) A deep neural network-based approach for prediction of mutagenicity of compounds. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(34):47641–47650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14028-9
Kumar L, Afzal MS, Ahmad A (2022) Prediction of water turbidity in a marine environment using machine learning: a case study of Hong Kong. Reg Stud Mar Sci 52:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2022.102260
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Lee S, Lee D (2018) Improved prediction of harmful algal blooms in four major south korea’s rivers using deep learning models. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(7):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15071322
Li C, Bai Y, Zeng B (2016) Deep feature learning architectures for daily reservoir inflow forecasting. Water Resour Manag 30(14):5145–5161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1474-8
Li CY, Guo JC, Guo CL (2018) Emerging from water: underwater image color correction based on weakly supervised color transfer. IEEE Signal Process Lett 25(3):323–327. https://doi.org/10.1109/lsp.2018.2792050
Li LW, Yan Z, Shen Q (2019a) Water body extraction from very high spatial resolution remote sensing data based on fully convolutional networks. Remote Sens 11(10):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101162
Li LW, Yan Z, Shen Q, Cheng G, Gao LR, Zhang B (2019b) Water body extraction from very high spatial resolution remote sensing data based on fully convolutional networks. Remote Sens 11(10):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101162
Li L, Rong SM, Wang R, Yu SL (2021a) Recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning for nonlinear relationship analysis and process control in drinking water treatment: a review. Chem Eng J 405:17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126673
Li XY, Yi XH, Liu ZH, Liu HB, Chen T, Niu GQ, Yan B, Chen C, Huang MZ, Ying GG (2021b) Application of novel hybrid deep leaning model for cleaner production in a paper industrial wastewater treatment system. J Clean Prod 294:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126343
Liu P, Wang J, Sangaiah AK, Xie Y, Yin XC (2019) Analysis and prediction of water quality using LSTM deep neural networks in IoT environment. Sustainability 11(7):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072058
Liu J, Zhou XL, Zhang LQ, Xu YP (2023) Forecasting short-term water demands with an ensemble deep learning model for a water supply system. Water Resour Manag 37(8):2991–3012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03471-7
Loc HH, Do QH, Cokro AA, Irvine KN (2020) Deep neural network analyses of water quality time series associated with water sensitive urban design (WSUD) features. J Appl Water Eng Res 8(4):313–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/23249676.2020.1831976
Long Y, Xu G, Ma C, Chen L (2016) Emergency control system based on the analytical hierarchy process and coordinated development degree model for sudden water pollution accidents in the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(12):12332–12342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6448-0
Luppichini M, Barsanti M, Giannecchini R, Bini M (2022) Deep learning models to predict flood events in fast-flowing watersheds. Sci Total Environ 813:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151885
Ma J, Ding YX, Cheng JCP, Jiang FF, Xu ZR (2020) Soft detection of 5-day BOD with sparse matrix in city harbor water using deep learning techniques. Water Res 170:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115350
Mauricio-Iglesias M, Montero-Castro I, Mollerup AL, Sin G (2015) A generic methodology for the optimisation of sewer systems using stochastic programming and self-optimizing control. J Environ Manage 155:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.03.034
Meijer D, Scholten L, Clemens F, Knobbe A (2019) A defect classification methodology for sewer image sets with convolutional neural networks. Autom Constr 104:281–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2019.04.013
Merow C, Serra-Diaz JM, Enquist BJ, Wilson AM (2023) AI chatbots can boost scientific coding. Nat Ecol Evol 3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-023-02063-3
Mill L, Wolff D, Gerrits N, Philipp P, Kling L, Vollnhals F, Ignatenko A, Jaremenko C, Huang YX, De Castro O, Audinot JN, Nelissen I, Wirtz T, Maier A, Christiansen S (2021) Synthetic image rendering solves annotation problem in deep learning nanoparticle segmentation. Small Methods 5(7):13. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202100223
Mittal S, Srivastava S, Jayanth JP (2022) A survey of deep learning techniques for underwater image classification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 15. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2022.3143887
Muhammad U, Wang WQ, Chattha SP, Ali S, Ieee (2018) Pre-trained VGGNet architecture for remote-sensing image scene classification. 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Ieee, Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Automat, Beijing, Peoples R China, pp 1622–1627
Mukherjee A, Su A, Rajan K (2021) Deep learning model for identifying critical structural motifs in potential endocrine disruptors. J Chem Inf Model 61(5):2187–2197. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.0c01409
Muluye GV, Coulibaly P (2007) Seasonal reservoir inflow forecasting with low-frequency climatic indices: a comparison of data-driven methods. Hydrol Sci J-J Sci Hydrol 52(3):508–522. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.52.3.508
Niu GQ, Yi XH, Chen C (2020) A novel effluent quality predicting model based on genetic-deep belief network algorithm for cleaner production in a full-scale paper-making wastewater treatment. J Clean Prod 265:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121787
Niu GQ, Li XY, Wan X (2022) Dynamic optimization of wastewater treatment process based on novel multi-objective ant lion optimization and deep learning algorithm. J Clean Prod 345:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131140
Oh C, Dang LM, Han D, Moon H (2022) Robust sewer defect detection with text analysis based on deep learning. IEEE Access 10:46224–46237. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3168660
Olden JD, Lawler JJ, Poff NL (2008) Machine learning methods without tears: a primer for ecologists. Q Rev Biol 83(2):171–193. https://doi.org/10.1086/587826
O’Neil GL, Goodall JL, Behl M, Saby L (2020) Deep learning using physically-informed input data for wetland identification. Environ Modell Softw 126:15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2020.104665
Oulebsir R, Lefkir A, Bermad A, Safri A (2018) Optimization of energy consumption in activated sludge process using deep learning selective modeling, 2nd WaterEnergyNEXUS Conference. Advances in Science Technology & Innovation. Springer International Publishing Ag, Salerno, ITALY, pp 223–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13068-8_55
Pang J, Yang S, He L, Chen Y, Ren N (2019) Intelligent control/operational strategies in WWTPs through an integrated Q-learning algorithm with ASM2d-Guided Reward. Water 11(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050927
Peng L, Wu H, Gao M (2022) TLT: Recurrent fine-tuning transfer learning for water quality long-term prediction. Water Res 225:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119171
Perea RG, Garcia IF, Poyato EC, Diaz JAR (2023) New memory-based hybrid model for middle-term water demand forecasting in irrigated areas. Agric Water Manage 284:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2023.108367
Pham HN, Dang KB, Nguyen TV, Tran NC, Ngo XQ, Nguyen DA, Phan TTH, Nguyen TT, Guo WS, Ngo HH (2022) A new deep learning approach based on bilateral semantic segmentation models for sustainable estuarine wetland ecosystem management. Sci Total Environ 838:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155826
Pu ZH, Yan JR, Chen L (2023) A hybrid Wavelet-CNN-LSTM deep learning model for short- term urban water demand forecasting. Front Env Sci Eng 17(2):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-023-1622-3
Pyo J, Cho KH, Kim K, Baek SS, Nam G, Park S (2021) Cyanobacteria cell prediction using interpretable deep learning model with observed, numerical, and sensing data assemblage. Water Res 203:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117483
Pyo J, Hong SM, Jang J, Park S, Park J (2022) Drone-borne sensing of major and accessory pigments in algae using deep learning modeling. Gisci Remote Sens 59(1):310–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/15481603.2022.2027120
Rahimzad M, Nia AM, Zolfonoon H, Soltani J, Mehr AD (2021) Performance comparison of an LSTM-based deep learning model versus conventional machine learning algorithms for streamflow forecasting. Water Resour Manag 35(12):4167–4187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02937-w
Ren T, Liu XF, Niu JW, Lei XH, Zhang Z (2020) Real-time water level prediction of cascaded channels based on multilayer perception and recurrent neural network. J Hydrol 585:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124783
Riedmiller M (1994) Advanced supervised learning in multi-layer perceptrons—from backpropagation to adaptive learning algorithms. Int J Comput Stand Interfaces 16(3):265–278
Rodrigues NM, Batista JE, Mariano P, Fonseca V, Duarte B, Silva S (2021) Artificial Intelligence meets marine ecotoxicology: applying deep learning to bio-optical data from marine diatoms exposed to legacy and emerging contaminants. Biology-Basel 10(9):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090932
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ (1986) Learning representations by back propagating errors. Nature 323(6088):533–536
Sabour S, Frosst N, Hinton GE (2017) Dynamic Routing Between Capsules, 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Neural Information Processing Systems (Nips), Long Beach, CA
Sadeghi M, Asanjan AA, Faridzad M, Nguyen P, Hsu K (2019) PERSIANN-CNN: precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks-convolutional neural networks. J Hydrometeorol 20(12):2273–2289. https://doi.org/10.1175/jhm-d-19-0110.1
Safder U, Loy-Benitez J, Nguyen HT, Yoo C (2022) A hybrid extreme learning machine and deep belief network framework for sludge bulking monitoring in a dynamic wastewater treatment process. J Water Process Eng 46:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102580
Sagan V, Peterson KT, Maimaitijiang M, Sidike P, Sloan J (2020) Monitoring inland water quality using remote sensing: potential and limitations of spectral indices, bio-optical simulations, machine learning, and cloud computing. Earth-Sci Rev 205:31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103187
Salloom T, Kaynak O, He W (2021) A novel deep neural network architecture for real-time water demand forecasting. J Hydrol 599:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126353
Mitrović S, Andreoletti D, Ayoub O (2023) ChatGPT or Human? Detect and Explain. Explaining Decisions of Machine Learning Model for Detecting Short ChatGPT-generated Text
Schuegraf P, Bittner K (2019) Automatic building footprint extraction from multi-resolution remote sensing images using a hybrid FCN. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 8(4):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8040191
Shao ZY, Xu L, Chai HX, Yost SA, Zheng ZL (2021) A Bayesian-SWMM coupled stochastic model developed to reconstruct the complete profile of an unknown discharging incidence in sewer networks. J Environ Manage 297:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113211
Sharma A, Liu XW, Yang XJ (2018) Land cover classification from multi-temporal, multi-spectral remotely sensed imagery using patch-based recurrent neural networks. Neural Netw 105:346–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.05.019
Shen CP (2018) A transdisciplinary review of deep learning research and its relevance for water resources scientists. Water Resour Res 54(11):8558–8593. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018wr022643
Shen C, Zhu KY, Ruan JP, Li JL, Wang Y, Zhao MR, He CY, Zuo ZH (2021) Screening of potential oestrogen receptor a agonists in pesticides via in silico, in vitro and in vivo methods. Environ Pollut 270:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116015
Shi XY, Lv FS, Seng DW, Zhang JM (2021) Visualizing and understanding graph convolutional network. Multimed Tools Appl 80(6):8355–8375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09885-4
Singha S, Pasupuleti S, Singha SS, Singh R, Kumar S (2021) Prediction of groundwater quality using efficient machine learning technique. Chemosphere 276:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130265
Sit M, Demiray BZ, Xiang ZR, Ewing GJ, Sermet Y (2020) A comprehensive review of deep learning applications in hydrology and water resources. Water Sci Technol 82(12):2635–2670. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.369
Song SR, Liu JH, Liu Y, Feng GQ, Han H (2020) Intelligent object recognition of urban water bodies based on deep learning for multi-source and multi-temporal high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Sensors 20(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020397
Song HM, Woo DK, Yan Q (2021) Detecting subsurface drainage pipes using a fully convolutional network with optical images. Agric Water Manage 249:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106791
Sun LP, Zhu JJ, Tan JX, Li XF, Li RH, Deng HZ, Zhang XY, Liu BY, Zhu XZ (2023) Deep learning-assisted automated sewage pipe defect detection for urban water environment management. Sci Total Environ 882:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163562
Syafiie S, Tadeo F, Martinez E, Alvarez T (2011) Model-free control based on reinforcement learning for a wastewater treatment problem. Appl Soft Comput 11(1):73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.10.018
Tian WC, Liao ZL, Wang X (2019) Transfer learning for neural network model in chlorophyll-a dynamics prediction. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(29):29857–29871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06156-0
Tu JC, Yang XQ, Chen CB, Gao S, Wang JC, Sun C, Ieee (2019) Water quality prediction model based on CNN-GRU hybrid network, chinese automation congress (CAC). Chinese automation congress. Ieee, Hangzhou, peoples r china, pp 1893–1898
Uddin MG, Nash S, Olbert AI (2021) A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol Indic 122:21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107218
Vaishya R, Misra A, Vaish A (2023) ChatGPT: is this version good for healthcare and research? Diabetes Metab Syndr-Clin Res Rev 17(4):6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2023.102744
Van Hasselt H, Guez A, Silver D (2015) Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 30. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v30i1.10295
Wai KP, Chia MY, Koo CH, Huang YF, Chong WC (2022) Applications of deep learning in water quality management: a state-of-the-art review. J Hydrol 613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128332
Wang KF, Gou C, Duan YJ, Lin YL, Zheng XH, Wang FY (2017) Generative adversarial networks: introduction and outlook. IEEE-CAA J Automatica Sin 4(4):588–598. https://doi.org/10.1109/jas.2017.7510583
Wang GM, Qiao JF, Bi J, Li WJ, Zhou MC (2019a) TL-GDBN: growing deep belief network with transfer learning. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 16(2):874–885. https://doi.org/10.1109/tase.2018.2865663
Wang ZF, Man Y, Hu YS, Li JG, Hong MN, Cui PZ (2019b) A deep learning based dynamic COD prediction model for urban sewage. Environ Sci-Wat Res Technol 5(12):2210–2218. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ew00505f
Wang J, Li P, Deng JH, Du YZ (2020a) CA-GAN: class-condition attention GAN for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Access 8:130719–130728. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3003351
Wang ZB, Gao X, Zhang YN, Zhao GH (2020b) MSLWENet: A Novel Deep Learning Network for Lake Water Body Extraction of Google Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens 12(24):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244140
Wang GM, Jia QS, Zhou MC, Bi J, Qiao JF (2021a) Soft-sensing of wastewater treatment process via deep belief network with event-triggered learning. Neurocomputing 436:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.12.108
Wang LG, Zhao L, Liu X, Fu JJ, Zhang AQ (2021b) SepPCNET: deeping learning on a 3D surface electrostatic potential point cloud for enhanced toxicity classification and its application to suspected environmental estrogens. Environ Sci Technol 55(14):9958–9967. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c01228
Wang Y, Cao Y, Zhang J, Wu F, Zha ZJ (2021c) Leveraging deep statistics for underwater image enhancement. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl 17(3):20. https://doi.org/10.1145/3489520
Wang YJ, Li SC, Lin YH, Wang MJ (2021d) Lightweight deep neural network method for water body extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images with multisensors. Sensors 21(21):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217397
Wang GM, Jia QS, Zhou MC, Bi J, Qiao JF (2022) Artificial neural networks for water quality soft-sensing in wastewater treatment: a review. Artif Intell Rev 55(1):565–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10038-8
Wang MZ, Cheng JCP (2018) Development and improvement of deep learning based automated defect detection for sewer pipe inspection using faster R-CNN, 25th Workshop of the European-Group-for-Intelligent-Computing-in-Engineering (EG-ICE). Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer International Publishing Ag, Lausanne, Switzerland, pp 171–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91638-5_9
Wang HW, Yang M, Yin G, Dong JN (2023) Self-adversarial generative adversarial network for underwater image enhancement. IEEE J Ocean Eng 12. https://doi.org/10.1109/joe.2023.3297731
Xiao X, He JY, Huang HM, Miller TR, Christakos G, Reichwaldt ES, Ghadouani A, Lin SP, Xu XH, Shi JY (2017) A novel single-parameter approach for forecasting algal blooms. Water Res 108:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.10.076
Xu CW, Wang YZ, Fu H, Yang JS (2022) Comprehensive analysis for long-term hydrological simulation by deep learning techniques and remote sensing. Front Earth Sci 10:16. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.875145
Xu GY, Cheng Y, Liu F, Ping P, Sun J, Ieee (2019) A water level prediction model based on ARIMA-RNN, 5th IEEE International Conference on Big Data Computing Service and Applications (IEEE BigDataService) / Workshop on Big Data in Water Resources, Environment, and Hydraulic Engineering / Workshop on Medical, Healthcare, Using Big Data Technologies. Ieee Computer Soc, San Francisco, CA, pp. 221-226. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigDataService.2019.00038
Yan XB, Song J, Liu YXY, Lu SL, Xu YY, Ma CY, Zhu YQ (2023) A Transformer-based method to reduce cloud shadow interference in automatic lake water surface extraction from Sentinel-2 imagery. J Hydrol 620:18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129561
Yang F, Xie H, Li HX (2019) RETRACTED ARTICLE: video associated cross-modal recommendation algorithm based on deep learning. Appl Soft Comput 82:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105597
Yang BW, Xiao ZJ, Meng QJ, Yuan Y, Wang WQ (2023a) Deep learning-based prediction of effluent quality of a constructed wetland. Env Sci Ecotechnol 13:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2022.100207
Yang MY, Wang WS, Gao Q, Zhao C, Li CL, Yang XF, Li JX, Li XG, Cui JL, Zhang LT, Ji YP, Geng SQ (2023b) Automatic identification of harmful algae based on multiple convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):15311–15324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23280-6
Yaseen ZM (2021) An insight into machine learning models era in simulating soil, water bodies and adsorption heavy metals: review, challenges and solutions. Chemosphere 277:22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130126
Yin XF, Chen Y, Bouferguene A, Zaman H, Al-Hussein M, Kurach L (2020) A deep learning-based framework for an automated defect detection system for sewer pipes. Autom Constr 109:17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2019.102967
Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y, Lipson H (2014) How transferable are features in deep neural networks ?, 28th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Neural Information Processing Systems (Nips), Montreal, Canada
Yu JW, Kim JS, Li X, Jong YC (2022) Water quality forecasting based on data decomposition, fuzzy clustering and deep learning neural network. Environ Pollut 303:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119136
Zanfei A, Brentan BM, Menapace A, Righetti M, Herrera M (2022) Graph convolutional recurrent neural networks for water demand forecasting. Water Resour Res 58(7):14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022wr032299
Zhang JF, Zhu Y, Zhang XP, Ye M, Yang JZ (2018) Developing a long short-term memory (LSTM) based model for predicting water table depth in agricultural areas. J Hydrol 561:918–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.065
Zhang C, Patras P, Haddadi H (2019) Deep learning in mobile and wireless networking: a survey. IEEE Commun Surve Tutor 21(3):2224–2287. https://doi.org/10.1109/comst.2019.2904897
Zhang HQ, Yu FS, Sun JC, Shen XQ, Li K (2020) Deep learning for sea cucumber detection using stochastic gradient descent algorithm. Eur J Remote Sens 53:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/22797254.2020.1715265
Zhang JS, Xing MD, Sun GC, Chen JL, Li MY (2021) Water body detection in high-resolution SAR images with cascaded fully-convolutional network and variable focal loss. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 59(1):316–332. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2020.2999405
Zhang YT, Li CL, Duan HP, Yan KF (2023) Deep learning based data-driven model for detecting time-delay water quality indicators of wastewater treatment plant influent. Chem Eng J 467:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.143483
Zhi W, Feng D, Tsai W-P, Sterle G, Harpold A, Shen C, Li L (2021) From hydrometeorology to river water quality: can a deep learning model predict dissolved oxygen at the continental scale? Environ Sci Technol 55(4):2357–2368. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c06783
Zhong HF, Sun Q, Sun HM, Jia RS (2022) NT-Net: a semantic segmentation network for extracting lake water bodies from optical remote sensing images based on transformer. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 60:13. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2022.3197402
Zhu H, Ma MR, Ma WP (2021a) A spatial-channel progressive fusion ResNet for remote sensing classification. Inf Fusion 70:72–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.12.008
Zhu NY, Ji X, Tan JL, Jiang YN, Guo Y (2021b) Prediction of dissolved oxygen concentration in aquatic systems based on transfer learning. Comput Electron Agric 180:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105888
Zhu S, Wei JA, Zhang HR, Xu Y, Qin H (2023) Spatiotemporal deep learning rainfall-runoff forecasting combined with remote sensing precipitation products in large scale basins. J Hydrol 616:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128727
Zhuang FZ, Qi ZY, Duan KY, Xi DB, Zhu YC, Zhu HS, Xiong H, He Q (2021) A comprehensive survey on transfer learning. Proc IEEE 109(1):43–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/jproc.2020.3004555
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all members of for their friendly cooperation in completing this study.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2017ZX07101003), National Key Research and Development Project (2019YFC1804800), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Forestry Administration (2020-KYXM-08), Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou, China (No. 201710010065), Youth Foundation of SCIES (PM-zx097-202304-147), and European Social Fund via IT Academy Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaohua Fu: initial idea and conceptualization, investigation, and visualization. Jie Jiang: methodology, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. Xie Wu: methodology and formal analysis. Lei Huang: resources, formal analysis, writing—review and editing, and conceptualization. Rui Han: reviewing and writing—review and editing. Kun Li: reviewing and writing—review and editing. Chang Liu: reviewing and writing—review and editing. Nesma Talaat Abbas Mahmoud: data curation, software, reviewing, and writing—literature review. Jianyu Chen: reviewing and writing—review and editing. Zhenxing Wang: supervision, funding acquisition, project administration, and review and editing. Kallol Roy: conceptualization, validation, review and editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
This article has not been published before and its publication has been approved by all co-authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Jiang, J., Wu, X. et al. Deep learning in water protection of resources, environment, and ecology: achievement and challenges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 14503–14536 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31963-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31963-5