Abstract
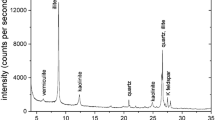
The Tunisian Lebna dam sediment was utilized to create the zeolite faujasite type Na-X. The aim of this investigation is to optimize the yield of Na-X zeolite using alkaline fusion hydrothermal treatment. Taguchi orthogonal array design was employed with nine trials to explore operating parameters including fusion temperature and time, activator type, and sediment type. The efficiency of alkaline fusion was evaluated using acid solubility. After dissolving the optimal alkali-fused sample in water, the Box–Behnken plan was used to identify the influence of L/S ratio, crystallization temperature, and time on zeolite Na-X yield. Rietveld analysis identified the mineral phases in the sediment as quartz (82.0%), calcite (8.8%), kaolinite (6.0), and illite (1.2%). With a NaOH activator, 850 °C fusion temperature for 30 min, 15 L/S ratio, and 75 °C crystallization temperature for 4 days, highly crystalline zeolite Na-X was created. FTIR, TGA, N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm, and X-ray diffraction were used to thoroughly describe this sample. The findings reveal the substantial zeolitization potential of the raw Lebna dam sediment, resulting in a high yield of zeolite Na-X.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used and analyzed during the current study were included in the article.
References
Abid R, Delahay G, Tounsi H (2019) Preparation of LTA, HS and FAU/EMT intergrowth zeolites from aluminum scraps and industrial metasilicate. J Mater Cycl Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00873-x
Anbia M, Mohammadi Nejati F, Jahangiri M, Eskandari A, Garshasbi V (2015) Optimization of synthesis procedure for NaX zeolite by Taguchi experimental design and its application in CO2 adsorption. J Sci Islam Repub Iran 26(3):213–222. http://jsciences.ut.ac.ir
Azizi D, Ibsaine F, Dionne J, Pasquier LC, Coudert L, Blais JF (2021) Microporous and macroporous materials state-of-the-art of the technologies in zeolitization of aluminosilicate bearing residues from mining and metallurgical industries: a comprehensive review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 318 (March). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111029
Bai SX, Zhou LM, Chang ZB, Zhang C, Chu M (2018) Synthesis of Na-X zeolite from Longkou oil shale ash by alkaline fusion hydrothermal method. Carbon Resour Convers 1(3):245–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crcon.2018.08.005
Bandura L, Franus M, Józefaciuk G, Franus W (2015) Synthetic zeolites from fly ash as effective mineral sorbents for land-based petroleum spills cleanup. Fuel 147:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.01.067
Bortali M, Rabouli M, Yessari M, Hajjaji A (2023) Assessment of harbor sediment contamination for a path to valorize dredged material. Arab J Chem 16 (11). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.105208
Braga BB, Anchieta TR, de Carvalho A, Brosinsky SF, Medeiros PHA (2019) From waste to resource: cost-benefit analysis of reservoir sediment reuse for soil fertilization in a semiarid catchment. Sci Total Environ 670:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.083
Burducea M, Lobiuc A, Dirvariu L, Oprea E, Olaru SM, Teliban GC, Stoleru V et al (2022) Assessment of the fertilization capacity of the aquaculture sediment for wheat grass as sustainable alternative use. Plants 11(5):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11050634
Chen J, Huang R, Ouyang He, Guangwei Yu, Liang Y, Zheng Q (2021) Utilization of dredged river sediments to synthesize zeolite for Cd(II) removal from wastewater. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128861
Chen YX, Wan C, Su XL, Zeng T, Rao SY (2014) Determination of experimental conditions of preparation of zeolites from fly ashes via alkaline fusion followed by hydrothermal crystallization. Adv Mater Res 1061–1062:342–350. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.1061-1062.342
Cundy CS, Lowe BM, Sinclair DM (1993) Crystallisation of zeolitic molecular sieves: direct measurements of the growth behaviour of single crystals as a function of synthesis conditions. Faraday Discuss 95:235–252. https://doi.org/10.1039/FD9939500235
Dar AA, Anuradha N (2018) Use of orthogonal arrays and design of experiment via Taguchi L9 method in probability of default. Accounting. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ac.2017.11.001
de Andrade FRD, Yogi MTAG, Gomes EB, Shinzato MC (2020) Extent of zeolite synthesis via alkaline fusion from tailings dam sediments. Environ Earth Sci 79(16):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09118-9
Dorleon G, Rigaud S, Techer I, Dorleon G, Rigaud S, Techer I (2023) Management of dredged marine sediments in Southern France: Main keys to large-scale beneficial re-use. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3587148/v1
Du S, Yang H, Qian K, Wang X, Chen H (2014) Fusion and transformation properties of the inorganic components in biomass ash. Fuel 117(PART B):1281–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.07.085
El Bojaddayni I, Küçük ME, El Ouardi Y, Jilal I, El Barkany S, Moradi K, Repo E, Laatikainen K, Ouammou A (2023) A review on synthesis of zeolites from natural clay resources and waste ash: recent approaches and progress. Miner Eng 198(April):108086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2023.108086
El-Radaideh N, Al-Taani AA, Al Khateeb WM (2017) Characteristics and quality of reservoir sediments, Mujib Dam, Central Jordan, as a case study. Environ Monit Assess 189 (4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5836-3
Ferone C, Colangelo F, Cioffi R, Montagnaro F, Santoro L (2013) Use of reservoir clay sediments as raw materials for geopolymer binders. Adv Appl Ceram 112(4):184–189. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743676112Y.0000000064
Gao J, Yin J, Zhu F, Chen X, Tong M, Kang W, Zhou Y, Jun Lu (2016) Orthogonal test design to optimize the operating parameters of a hybrid solvent MEA–methanol in an absorber column packed with three different packing: Sulzer BX500, Mellapale Y500 and Pall Rings 16 × 16 for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 68:218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.08.040
Georgiev D, Bogdanov B, Markovska I, Hristov Y (2013) A study on the synthesis and structure of zeolite NaX. J Chem Technol Metall 48(2):168–173
Ghasemi Z, Sourinejad I, Kazemian H, Rohani S (2018) Application of zeolites in aquaculture industry: a review. Rev Aquac 10(1):75–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12148
Ghasemi Z, Sourinejad I, Kazemian H, Hadavifar M, Rohani S, Younesi H (2020) Kinetics and thermodynamic studies of Cr(VI) adsorption using environmental friendly multifunctional zeolites synthesized from coal fly ash under mild conditions. Chem Eng Commun 207(6):808–825. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2019.1630389
Guaya D, Cobos H, Camacho J, López CM, Valderrama C, Cortina JL (2022) LTA and FAU-X iron-enriched zeolites: use for phosphate removal from aqueous medium. Materials 15(15):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155418
Habibi MY, Samet B, El Hafiane Y, Smith A (2023a) Synthesis and characterization of cement clinker based on Tunisian dam sediments. Constr Build Mater 394(June):132254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132254
Habibi MY, Samet B, El Hafiane Y, Smith A (2023b) Synthesis and characterization of cement clinker based on Tunisian dam sediments. Constr Build Mater 394 (August). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132254
Haryani N, Harahap H, Taslim, Irvan (2020) Biogasoline production via catalytic cracking process using zeolite and zeolite catalyst modified with metals: a review. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 801 (1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/801/1/012051
He K, Chen Y, Tang Z, Yongyou Hu (2016) Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by zeolite synthesized from fly ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(3):2778–2788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5422-6
He Y, Tang S, Yin S, Li S (2021) Research progress on green synthesis of various high-purity zeolites from natural material-kaolin. J Clean Prod 306:127248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127248
Hu T, Gao W, Liu X, Zhang Y, Meng C (2017) Synthesis of zeolites Na-A and Na-X from tablet compressed and calcinated coal fly ash. R Soc Open Sci 4 (10). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.170921
Hussan A, Levacher D, Mezazigh S, Jardin L (2023) Co-valorization of sediments incorporating high and low organic matter with alkali-activated GGBS and hydraulic binder for use in road construction. J Build Eng 66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.105848
Jafari S, Ghorbani F, Bahrami A, Kazemian H, Yousefinejad S (2017) Removal of toluene from air by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8: synthesis, characterization, and experimental breakthrough curve. Int J Sci Stud 5(July):1073–82. https://doi.org/10.17354/ijssI/2017/143
Jafari S, Ghorbani-Shahna F, Bahrami A, Kazemian H (2018) Adsorptive removal of toluene and carbon tetrachloride from gas phase using zeolitic imidazolate framework-8: effects of synthesis method, particle size, and pretreatment of the adsorbent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 268(October 2017):58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.04.013
Jiménez A, Misol A, Morato A, Rives V, Vicente MA, Gil A (2021) Synthesis of pollucite and analcime zeolites by recovering aluminum from a saline slag. J Clean Prod 297 (May). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126667
Jraba N, Tounsi H, Makhlouf T (2018) Valorization of aluminum chips into γ-Al2O3 and η-Al2O3 with high surface areas via the precipitation route. Waste Biomass Valorization 9(6):1003–1014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9786-8
Khaleque A, Alam MdM, Hoque M, Mondal A, Haider JB, Xu B, Johir MAH et al. (2020) Zeolite synthesis from low-cost materials and environmental applications: a review. Environ Adv 2 (October). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2020.100019
Larouci A, Senhadji Y, Laoufi L, Benazzouk A (2020) Valorisation of natural waste: dam sludge for road construction. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 19(3):1075–83. https://doi.org/10.46488/NEPT.2020.v19i03.018
Larouci A, Senhadji Y, Laoufi L, Benazzouk A (2021) Dredged dam raw sediments geotechnical characterization for beneficial use in road construction. Int J Eng Res Afr 57(November):81–98. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JERA.57.81
Lee YR, Soe JT, Zhang A, Ahn JW, Park MB, Ahn WS (2017) Synthesis of nanoporous materials via recycling coal fly ash and other solid wastes: a mini review. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.124
Liu W, Aldahri T, Chunbao Xu, Li C, Rohani S (2021) Synthesis of sole gismondine-type zeolite from blast furnace slag during CO2 mineralization process. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104652
Mamedova G, Nasirli G (2021) Investigation of various influencing factors of hydrothermal synthesis of analcime zeolite. Chem J Moldova 16(1):60–67
Marzouki M, Samet B, Tounsi H (2022) Application of Plackett-Burman and Box-Behnken designs for the optimization of Tunisian dam sediment-based geopolymers. J Build Eng 50(March):104162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2022.104162
Matlob S, Abdul RA, Kamarudin ZJ, Ramli Z (2011) Optimized conditions for synthesis of Na-A zeolite from coal fly ash by applying the response surface methodology. Solid State Sci Technol 19(1):88–100
Matlob AS, Kamarudin RA, Jubri Z, Ramli Z (2013) Response surface methodology for optimizing zeolite Na-A synthesis. Arab J Sci Eng 38(7):1713–1720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0382-3
Mesrar H, Mesrar L, Jabrane R (2023) Physicochemical and mechanical characterization of ceramic materials from Meknes Region (Morocco). J Ecol Eng 24(8):183–97. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/166393
Mohamed G, Fathy M (2023) Advanced chemical leaching process of wadi el dakhal silica sand to produce a high concentration of SiO2 for electronic industry. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2685990/v1
Mouna S, Hajji S, Tounsi H (2024) Waste to health: green synthesis of Zn loaded LTA zeolite prepared from waste glass and aluminum scrap with high antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. J Clean Prod 434(January):139946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139946
Musyoka NM, Petrik LF, Hums E, Kuhnt A, Schwieger W (2015) Thermal stability studies of zeolites A and X synthesized from South African coal fly ash. Res Chem Intermed 41(2):575–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-013-1211-3
Nakhli SAA, Delkash M, Bakhshayesh BE, Kazemian H (2017) Application of Zeolites for Sustainable Agriculture: A Review on Water and Nutrient Retention. Water Air Soil Pollut 228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3649-1
Nazir M, Salwa L, Yeong YF, Chew TL (2020) Controlled growth of faujasite zeolite with NaX topology by manipulating solution aging and Na2O/Al2O3 ratios. Colloids Surf, A 600(March):124803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124803
Noroozi R, Al-Musawi TJ, Kazemian H, Kalhori EM, Zarrabi M (2018) Removal of cyanide using surface-modified linde type-A zeolite nanoparticles as an efficient and eco-friendly material. Jo Water Process Eng 21(October 2017):44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.11.011
Raabe D, Ponge D, Uggowitzer PJ, Roscher M, Paolantonio M, Liu C, Antrekowitsch H et al (2022) Making sustainable aluminum by recycling scrap: the science of ‘dirty’ alloys. Progress in Materials Science. Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.100947
Rache ML, García AR, Zea HR, Silva AMT, Madeira LM, Ramírez JH (2014) Azo-Dye Orange II degradation by the heterogeneous Fenton-like process using a zeolite Y-Fe catalyst-kinetics with a model based on the Fermi’s equation. Appl Catal B 146:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.04.028
Renella G (2021) Recycling and reuse of sediments in agriculture: where is the problem? Sustainability (switzerland) 13(4):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041648
Sadok H, Rachid NB, Tahlaiti M, Mazouzi R (2021) Reusing calcined sediments from Chorfa II dam as partial replacement of cement for sustainable mortar production. J Build Eng 40(December 2020):102273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102273
Safhi AeM, Benzerzour M, Rivard P, Abriak NE, Ennahal I (2019) Development of self-compacting mortars based on treated marine sediments. J Build Eng 22:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2018.12.024
Saputera WH, Putrie AS, Esmailpour AA, Sasongko D, Suendo V, Mukti RR (2021) Technology advances in phenol removals: current progress and future perspectives. Catalysts 11 (8). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11080998
Sayehi M, Garbarino G, Delahay G, Busca G, Tounsi H (2020) Synthesis of high value-added Na–P1 and Na-FAU zeolites using waste glass from fluorescent tubes and aluminum scraps. Mater Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122903
Shao Q, Mingming Lu, Zhou J, Zhu Z, Song Y (2019) Preparation of non-sintered fly ash filter (NSFF) for ammonia nitrogen adsorption. Environ Technol (united Kingdom) 40(15):1988–1999. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1435733
Sivalingam S, Sen S (2018) Optimization of synthesis parameters and characterization of coal fly ash derived microporous Zeolite X. Appl Surf Sci 455:903–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.05.222
Soudejani HT, Kazemian H, Inglezakis VJ, Zorpas AA (2019) Application of zeolites in organic waste composting: a review. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 22(October):101396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101396
Soudejani T, Hajar MS, Kazemian H, Heidarpour M, Rutherford M (2020) Effect of co-composting municipal solid waste with mg-modified zeolite on soil water balance components using HYDRUS-1D. Comput Electron Agric 176(July):105637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105637
Soudejani HT, Heidarpour M, Shayannejad M, George P (2018) Incorporation of Mg-modified zeolite in municipal solid waste compost reduces heavy metal concentration in soil and corn plant. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331686691
Tabit K, Waqif M, Saâdi L (2019) Application of the Taguchi method to investigate the effects of experimental parameters in hydrothermal synthesis of Na-P1 zeolite from coal fly ash. Res Chem Intermed 45(9):4431–4447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03840-1
Taheri-Sodejani H, Ghobadinia M, Tabatabaei SH, Kazemian H (2015) Using natural zeolite for contamination reduction of agricultural soil irrigated with treated urban wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 54(10):2723–2730. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.904818
Taheri-Soudejani H, Heidarpour M, Shayannejad M, Shariatmadari H, Kazemian H, Afyuni M (2019) Composts containing natural and mg-modified zeolite: the effect on nitrate leaching, drainage water, and yield. Clean - Soil, Air, Water 47 (8). https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201800257
Tounsi H, Mseddi S, Djemal S (2010) Hydrothermal synthesis of Na-LTA, Na-X and HS zeolites from Tunisian sand and aluminum scraps 637:1389–96.https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.636-637.1389
Usachev NY, Belanova EP, Krukovsky IM, Kanaev SA, Atal’yan OK, Kazakov AV (2003) Thermal transformations in systems based on zeolites Y, X, and A containing zinc and sodium nitrates. Russ Chem Bull 52(9):1940–49. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUCB.0000009636.89718.56
Wu D, Yikai Lu, Kong H, Ye C, Jin X (2008) Synthesis of zeolite from thermally treated sediment. Ind Eng Chem Res 47(2):295–302. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie071063u
Yang L, Qian X, Yuan P, Bai H, Miki T, Men F, Li H, Nagasaka T (2019) Green synthesis of zeolite 4A using fly ash fused with synergism of NaOH and Na2CO3. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.259
Yilmaz B, Müller U (2009) Catalytic applications of zeolites in chemical industry. Top Catal 52(6–7):888–895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-009-9226-0
Yue Y, Kang Y, Bai Y, Gu L, Liu H, Bao J, Wang T et al (2018) Seed-assisted, template-free synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from natural aluminosilicate minerals. Appl Clay Sci 158(November 2017):177–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.03.025
Zouch A, Mamindy-Pajany Y, Bouchikhi A, Abriak NE, Ksibi M (2022) Valorization of marine sediments in geopolymer mortars: physico-mechanical, microstructural and environmental investigations at laboratory scale. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 24(3):1109–1123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-022-01382-0
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully recognize the support that was provided by the Laboratory of Advanced Materials (LAMA) at the University of Sfax, Tunisia, and the Northern Analytical Lab Services (NALS) at the University of Northern British Columbia (UNBC), Canada, for the instrumentation’s facility and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Leila Doudey: conceptualization, doing experiments, analysis, and writing original draft. Basma Samet: conceptualization, software, validation, and writing—review and editing. Hassib Tounsi: supervision, conceptualization, formal analysis, visualization, and writing—review and editing. Hossein Kazemian: supervision, formal analysis, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Doudey, L., Samet, B., Tounsi, H. et al. Unlocking the potential of Tunisian dam sediment: optimizing zeolite X synthesis via Taguchi and Box–Behnken methods for sustainable resource recovery and versatile applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 14574–14592 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31944-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31944-8