Abstract
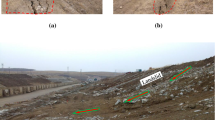
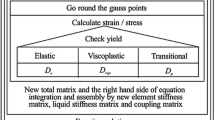
The formation of interflow is of great significance for the stability of mountain slopes and soil erosion. Hillsides are often covered with a certain amount of gravel, and research on interflow of slope land with different gravel ratios needs to be carried out. This article is based on indoor experiments and numerical models to study the formation law of interflow in hillside soil under different gravel coverage ratios. It was found that the interflow in the soil rapidly increased in the early stage and began to decrease after briefly reaching equilibrium. The formation of interflow is a complex process that is related to slope, soil characteristics, and rainfall intensity, but the correlation is not high when viewed separately. The lattice Boltzmann model can effectively simulate such problems and achieve high simulation accuracy. The \({R}^{2}\) of the simulated data and measured data ranged from 0.5217 to 0.7403, and \(RMSE\) of the simulated data and measured data ranged from 0.4051 to 0.5711.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Azuka CV, Igué AM (2020) Surface runoff as influenced by slope position and land use in the Koupendri catchment of northwest Benin: field observation and model validation. Hydrol Sci J 65(6):995–1004
Bai Y, Cui H (2021) An improved vegetation cover and management factor for RUSLE model in prediction of soil erosion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:21132–21144
Barthel R, Banzhaf S (2016) Groundwater and surface water interaction at the regional-scale–a review with focus on regional integrated models. Water Resour Manag 30(1):1–32
Beven K (1989) Changing ideas in hydrology—the case of physically-based models. J Hydrol 105(1–2):157–172
Carroll RW, Deems JS, Niswonger R, Schumer R, Williams KH (2019) The importance of interflow to groundwater recharge in a snowmelt-dominated headwater basin. Geophys Res Lett 46(11):5899–5908
Deng L, Fei K, Sun T, Zhang L, Fan X, Ni L (2019) Phosphorus loss through overland flow and interflow from bare weathered granite slopes in southeast China. Sustainability 11(17):4644
Espinha Marques J, Samper J, Pisani B, Alvares D, Carvalho JM, Chaminé HI, Marques JM, Vieira GT, Mora C, Sodré Borges F (2011) Evaluation of water resources in a high-mountain basin in Serra da Estrela, Central Portugal, using a semi-distributed hydrological model. Environ Earth Sci 62:1219–1234
Geng C, Lu D, Qian J, Xu C, Li D, Ou J, Ye Z (2023) A review on process-based groundwater vulnerability assessment methods. Processes 11(6):1610
Hua K, Zhu B, Wang X, Tian L (2016) Forms and fluxes of soil organic carbon transport via overland flow, interflow, and soil erosion. Soil Sci Soc Am J 80(4):1011–1019
Huntington JL, Niswonger RG (2012) Role of surface‐water and groundwater interactions on projected summertime streamflow in snow dominated regions: an integrated modeling approach. Water Resour Res 48(11), W11524, https://doi.org/10.1029/2012WR012319
Klaus J, Jackson CR (2018) Interflow is not binary: a continuous shallow perched layer does not imply continuous connectivity. Water Resour Res 54(9):5921–5932
Lee RM, McGuire KJ, Strahm BD, Knoepp JD, Jackson CR, Stewart RD (2020) Revisiting the Hewlett and Hibbert (1963) hillslope drainage experiment and modeling effects of decadal Pedogenic processes and leaky soil boundary conditions. Water Resour Res 56(1):e2019WR025090
Liu Q, Zhu B, Tang J, Huang W, Zhang X (2017) Hydrological processes and sediment yields from hillslope croplands of regosol under different slope gradients. Soil Sci Soc Am J 81(6):1517–1525
Lu D, Wang H, Geng N, Xia Y, Xu C, Hua E (2022) Imaging and characterization of the preferential flow process in agricultural land by using electrical resistivity tomography and dual-porosity model. Ecol Ind 134:108498
Meles Bitew M, Jackson CR, Goodrich DC, Younger SE, Griffiths NA, Vaché KB, Rau B (2020) Dynamic domain kinematic modelling for predicting interflow over leaky impeding layers. Hydrol Process 34(13):2895–2910
Ni CF, Tran QD, Lee IH, Truong MH, Hsu SM (2021) Mapping interflow potential and the validation of index-overlay weightings by using coupled surface water and groundwater flow model. Water 13(17):2452
Samper J, Pisani B, Espinha Marques J (2015) Hydrological models of interflow in three Iberian mountain basins. Environ Earth Sci 73:2645–2656
Shan C, Guo H, Dong Z, Liu L, Lu D, Hu J (2022) Study on the river habitat quality in Luanhe based on the eco-hydrodynamic model. Ecol Ind 142:109262
Sun T, Gui N, Yang X, Tu J, Jiang S (2017a) Numerical study of patterns and influencing factors on flow boiling in vertical tubes by thermal LBM simulation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 86:32–41
Sun Z, Lotz T, Chang NB (2017b) Assessing the long-term effects of land use changes on runoff patterns and food production in a large lake watershed with policy implications. J Environ Manag 204:92–101
Sunada K, Hong TF (1988) Effects of slope conditions on direct runoff characteristics by the interflow and overland flow model. J Hydrol 102(1–4):323–334
Tang J, Zhu B, Wang T, Cheng X, Gao M, Lin H (2012) Subsurface flow processes in sloping cropland of purple soil. J Mt Sci 9:1–9
Tao W, Bo Z, Fuhong K (2012) Reducing interflow nitrogen loss from hillslope cropland in a purple soil hilly region in southwestern China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 93:285–295
Watanabe S, Fujisaki S, Hu C (2021) Numerical simulation of dam break flow impact on vertical cylinder by cumulant lattice Boltzmann method. J Hydrodyn 33(2):185–194
Wencai D, Fangfei C, Quanjiu W, Qiang F, Weiyu S, Likun W (2019) Modeling interflow under the influence of plough pans for a sloping field. Soil Sci Soc Am J 83(5):1468–1478
Wu Y, Xu Y (2005) Snow impact on groundwater recharge in Table Mountain Group aquifer systems with a case study of the Kommissiekraal River catchment South Africa. Water SA 31(3):275–282
Xie H, Liu J (2020) A modeling study of the interflow in the green roof. Urban For Urban Green 54:126760
Yang T, Wang Q, Su L, Wu L, Zhao G, Liu Y, Zhang P (2016) An approximately semi-analytical model for describing surface runoff of rainwater over sloped land. Water Resour Manag 30:3935–3948
Zhang Y, Baeumer B, Chen L, Reeves DM, Sun H (2017) A fully subordinated linear flow model for hillslope subsurface stormflow. Water Resour Res 53(4):3491–3504
Zhu B, Wang T, Kuang F, Luo Z, Tang J, Xu T (2009) Measurements of nitrate leaching from a hillslope cropland in the Central Sichuan Basin, China. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73(4):1419–1426
Funding
Funding by Scholars of Nanxun; Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation Project LZJWY22E090009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YB analyzed and interpreted the data and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. HW and DH performed the calculation of the model. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
wang, H., Bai, Y. & Huang, D. Study of experimental and numerical simulation on the influence of gravel on the interflow of slope land. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 11716–11726 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31808-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31808-7