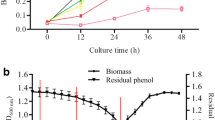
Abstract
The ability of bacteria to efficiently remove phenolic pollutants depends on their genetic makeup and environmental conditions. This study examined a novel strain, Pseudomonas aeruginosa STV1713, for degrading higher concentrations of phenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol. After optimization, a combination of degradation parameters, such as pH (7.0), temperature (32.5 °C), and ammonium nitrate concentration (0.7 g/L), was found to reduce degradation time while promoting cell growth. Under these optimal conditions, the bacterium effectively degraded up to 2000 mg/L of phenol and 1400 mg/L of 2,4-dichlorophenol, while maximum tolerance was observed till 2100 mg/L and 1500 mg/L, respectively. Metabolic profiling identified crucial metabolites in the ortho-degradation pathway during pollutant removal. Additionally, transcriptome analysis revealed that P. aeruginosa STV1713 utilizes different branches of the beta ketoadipate pathway for phenol and 2,4-DCP removal. Moreover, under high pollutant stress, the bacterium survived through differential gene expression in ribosome biogenesis, chemotaxis, membrane transport, and other pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author, Suchithra Tharamel Vasu, upon reasonable request.
References
Abarian M, Hassanshahian M, Esbah A (2019) Degradation of phenol at high concentrations using immobilization of Pseudomonas putida P53 into sawdust entrapped in sodium-alginate beads. Water Sci Technol 79:1387–1396. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.134
Aisami A, Yasid N, Shukor Y (2020) Effect of temperature and ph on phenol biodegradation by a newly identified Serratia sp. AQ5–03. Open J Educ Res 1:28–43. https://doi.org/10.52417/ojbr.v1i1.57
Asimakoula S, Marinakos O, Tsagogiannis E, Koukkou A-I (2023) Phenol degradation by pseudarthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Sphe3. Microorganisms 11:524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020524
Barik M, Das CP, Kumar Verma A et al (2021) Metabolic profiling of phenol biodegradation by an indigenous Rhodococcus pyridinivorans strain PDB9T N-1 isolated from paper pulp wastewater. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 158:105168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.105168
Cafaro V, Izzo V, Scognamiglio R et al (2004) Phenol hydroxylase and toluene/o-xylene monooxygenase from pseudomonas stutzeri OX1: interplay between two enzymes. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2211–2219. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.4.2211-2219.2004
Chen L, Li C, Xu B et al (2019) Microbial degradation of organic pollutants in groundwater related to underground coal gasification. Energy Sci Eng 7:2098–2111. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.415
Chris Felshia S, AshwinKarthick N, Thilagam R, Gnanamani A (2020) Elucidation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol degradation by Bacillus licheniformis strain SL10. Environ Technol 41:366–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1498923
Colin R, Ni B, Laganenka L, Sourjik V (2021) Multiple functions of flagellar motility and chemotaxis in bacterial physiology. FEMS Microbiol Rev 45:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuab038
Daisuke K, Toshihiro F, Tomokuni A et al (2009) Uncovering the protocatechuate 2,3-cleavage pathway genes. J Bacteriol 191:6758–6768. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00840-09
Dankaka SM, Muhammad JB, Usman S et al (2023) Phenol biodegradation by Acinetobacter baumanii and Citrobacter sedlakii isolated from petroleum products contaminated environment. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 8:100468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2023.100468
Eaton RW (1997) p-Cymene catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas putida F1: cloning and characterization of DNA encoding conversion of p-cymene to p-cumate. J Bacteriol 179:3171–3180. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.10.3171-3180.1997
Farag AM, Fawzy A, El-Naggar MY, Ghanem KM (2021) Biodegradation and enhancement of 2,4-dichlorophenol by marine halophilic Bacillus subtilis AAK. Egypt J Aquat Res 47:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2021.04.005
Favier L, Ungureanu CV, Simion AI et al (2021) Enhancing the biodegradation efficiency of a emergent refractory water pollutant by a bacterial isolate through a statistical process optimization approach. Process Saf Environ Prot 148:1133–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.02.012
Gerischer U (2002) Specific and global regulation of genes associated with the degradation of aromatic compounds in bacteria. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 4:111–121
Gu Q, Wu Q, Zhang J et al (2017) Acinetobacter sp. DW-1 immobilized on polyhedron hollow polypropylene balls and analysis of transcriptome and proteome of the bacterium during phenol biodegradation process. Sci Rep 7:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04187-6
Gu Q, Wu Q, Zhang J et al (2018) Isolation and transcriptome analysis of phenol-degrading bacterium from carbon–sand filters in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant. Front Microbiol 9:21–62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02162
Gu Q, Chen M, Zhang J et al (2021) Genomic analysis and stability evaluation of the phenol-degrading bacterium Acinetobacter sp. DW-1 during water treatment. Front Microbiol 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.687511
Hasan SA, Jabeen S (2015) Degradation kinetics and pathway of phenol by Pseudomonas and Bacillus species. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 29:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2014.991638
Hirakawa H, Kurushima J, Hashimoto Y, Tomita H (2020) Progress overview of bacterial two-component regulatory systems as potential targets for antimicrobial chemotherapy. Antibiotics 9:635. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100635
Hossain MF, Akter MA, Sohan MSR et al (2022) Bioremediation potential of hydrocarbon degrading bacteria: isolation, characterization, and assessment. Saudi J Biol Sci 29:211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.08.069
Kargi F, Eker S (2005) Kinetics of 2,4-dichlorophenol degradation by Pseudomonas putida CP1 in batch culture. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 55:25–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2004.06.010
Krastanov A, Alexieva Z, Yemendzhiev H (2013) Microbial degradation of phenol and phenolic derivatives. Eng Life Sci 13:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201100227
Lee GLY, Zakaria NN, Convey P et al (2020) Statistical optimisation of phenol degradation and pathway identification through whole genome sequencing of the cold-adapted Antarctic bacterium, Rhodococcus Sp. Strain AQ5-07. Int J Mol Sci 21:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249363
Lee GL, Zakaria NN, Futamata H et al (2022) Metabolic pathway of phenol degradation of a cold-adapted Antarctic bacteria. Arthrobacter Sp Catalysts 12:1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12111422
Li Y, Orlando BJ, Liao M (2019) Structural basis of lipopolysaccharide extraction by the LptB2FGC complex. Nature 567:486–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1025-6
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr AL, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
Lucchini JJ, Corre J, Cremieux A (1990) Antibacterial activity of phenolic compounds and aromatic alcohols. Res Microbiol 141:499–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/0923-2508(90)90075-2
Ma Y, Li L, Awasthi MK et al (2020) Time-course transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanisms of Burkholderia sp. adaptation to high phenol concentrations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:5873–5887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10672-2
Mahgoub SA, Qattan SYA, Salem SS et al (2023) Characterization and biodegradation of phenol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella variicola strains isolated from sewage sludge and their effect on soybean seeds germination. Molecules 28:1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031203
Mahon CR, Lehman DC (2019) Textbook of diagnostic microbiology. Elsevier Health Sciences, Saunders
Mohd Ariff MA, Abdullah N (2019) Optimization of reflux extraction for cat’s whiskers leaves extract using response surface methodology. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 26:24. https://doi.org/10.2298/CICEQ190228024A
Mohn WW, Kennedy KJ (1992) Reductive dehalogenation of chlorophenols by Desulfomonile tiedjei DCB-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1367–1370. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.58.4.1367-1370.1992
Morawski B, Segura A, Ornston LN (2000) Repression of Acinetobacter vanillate demethylase synthesis by VanR, a member of the GntR family of transcriptional regulators. FEMS Microbiol Lett 187:65–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09138.x
Nor Suhaila Y, Ramanan RN, Rosfarizan M et al (2013) Optimization of parameters for improvement of phenol degradation by Rhodococcus UKMP-5M using response surface methodology. Ann Microbiol 63:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0496-6
Oluwasanu AA (2018) Fate and Toxicity of chlorinated phenols of environmental implications: a review. Med Anal Chem Int J 2:000126. https://doi.org/10.23880/macij-16000126
Panigrahy N, Barik M, Sahoo RK, Sahoo NK (2020) Metabolic profile analysis and kinetics of p-cresol biodegradation by an indigenous Pseudomonas citronellolis NS1 isolated from coke oven wastewater. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 147:104837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.104837
Pinheiro PF, Menini LAP, Bernardes PC et al (2018) Semisynthetic phenol derivatives obtained from natural phenols: antimicrobial activity and molecular properties. J Agric Food Chem 66:323–330. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04418
Prochownik EV, Wang H (2021) The metabolic fates of pyruvate in normal and neoplastic cells. Cells 10:762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040762
Sasi R, Suchithra TV (2023) Transcriptome analysis of a novel and highly resistant hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria during the removal of phenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 11:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04509-x
Shakya M, Lo C-C, Chain PSG (2019) Advances and challenges in metatranscriptomic analysis. Front Genet 10:453–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-9758-9_21
Singh P, Gupta S (2016) Optimization of biodegradation process of river water containing phenol using response surface methodology by Psuedomonas putida (P. putida ). Int J Curr Res 8:44217–44222
Subramaniam K, Shaharuddin NA, Tengku-Mazuki TA et al (2020) Statistical optimisation for enhancement of phenol biodegradation by the Antarctic soil bacterium Arthrobacter sp. strain AQ5–15 using response surface methodology py. J Environ Biol 41:1560–1569. https://doi.org/10.22438/JEB/41/6/MRN-1496
Subramaniam K, Athirrah T, Mazuki T et al (2019) Isolation and optimisation of phenol degradation by antarctic isolate using one factor at time. Malaysian J Biochem Mol Biol 1:79–86
van Schie PM, Young LY (2000) Biodegradation of phenol: mechanisms and applications. Bioremediat J 4:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/10588330008951128
Xu N, Qiu C, Yang Q et al (2021) Analysis of phenol biodegradation in antibiotic and heavy metal resistant Acinetobacter lwoffii NL1. Front Microbiol 12:725–755. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.725755
Zhou J, Yu X, Ding C et al (2011) Optimization of phenol degradation by Candida tropicalis Z-04 using Plackett-Burman design and response surface methodology. J Environ Sci 23:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60369-5
Zhu M, Dai X (2020) Bacterial stress defense: the crucial role of ribosome speed. Cell Mol Life Sci 77:853–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03304-0
Funding
Kerala State Council for Science Technology and Environment (Sasthra Bhavan, Pattom, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India-695004) (Research Fellowship-Sanction order No.29/FSHP/2016/KSCSTE dated 24.03.2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors, RS and STV, contributed to the study's conception and design. RS performed material preparation, data collection, and experimental analyses. RS wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors commented on previous versions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sasi, R., Tharamel Vasu, S. Revealing the degradation mechanisms of the hyper-tolerant bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa STV1713 under high phenol and 2,4-DCP-induced stress conditions through RNA-seq analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 5625–5640 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31500-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31500-w