Abstract
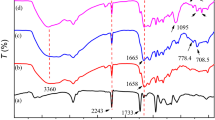
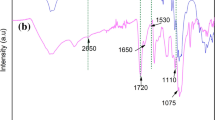
Heavy metals (e.g., Cu) in wastewater are attractive resources for diverse applications, and adsorption is a promising route to recovery of heavy metals from wastewater. However, high-performance adsorbents with high adsorption capacity, speed, and stability remain challenging. Herein, chelating fibers were prepared by chemically grafting amine and carboxyl groups onto the polyacrylonitrile fiber surface and used in the wastewater’s adsorption of Cu2+. The adsorption behavior of Cu2+ on the fibers was systematically investigated, and the post-adsorption fibers were comprehensively characterized to uncover the adsorption mechanism. The results show that chelated fiber has a 136.3 mg/g maximum capacity for Cu2+ adsorption at pH = 5, and the whole adsorption process could reach equilibrium in about 60 min. The adsorption process corresponds to the quasi-secondary kinetic and Langmuir models. The results of adsorption, FTIR, and XPS tests indicate that the synergistic coordination of -COOH and -NH2 plays a leading role in the rapid capture of Cu2+. In addition, introducing hydrophilic groups facilitates the rapid contact and interaction of the fibers with Cu2+ in the solution. After being used five times, the fiber’s adsorption capacity remains at over 90% of its original level.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chen C, Li F, Guo Z, Qu X, Wang J, Zhang J (2019) Preparation and performance of aminated polyacrylonitrile nanofibers for highly efficient copper ion removal. Colloid Surface A 568:334–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.02.020
Chen H, Zhou Y, Wang J, Lu J, Zhou Y (2020) Polydopamine modified cyclodextrin polymer as efficient adsorbent for removing cationic dyes and Cu2+. J Hazard Mater 389:121897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121897
Chen ZJ, Fang J, Wei W, Ngo HH, Guo W, Ni BJ (2022a) Emerging adsorbents for micro/nanoplastics removal from contaminated water: advances and perspectives. J Clean Prod 371:133676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133676
Chen ZJ, Zheng R, Wei W, Wei W, Zou W, Li J, Ni BJ, Chen H (2022b) Recycling spent water treatment adsorbents for efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation reaction. Resour Conserv Recy 178:106037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.106037
Cheng S, Meng M, Xing B et al (2022a) Preparation of valuable pyrolysis products from poplar waste under different temperatures by pyrolysis: evaluation of pyrolysis products. Biores Technol 364:128011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128011
Cheng S, Zhao S, Xing B et al (2022b) Facile one-pot green synthesis of magnetic separation photocatalyst-adsorbent and its application. J Water Process Eng 47:102802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102802
Cheng S, Meng W, Xing B et al (2023) Efficient removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by Mg/Fe bimetallic oxide-modified biochar: experiments and DFT investigations. J Clean Prod 403:136821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136821
Cho DW, Jeon BH, Chon CM, Kim Y, Schwartz FW, Lee ES, Song HA (2012) Novel chitosan/clay/magnetite composite for adsorption of Cu(II) and As(V). Chem Eng J 200:654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.126
Cho S, Kim JH, Yang KS, Chang M (2021) Facile preparation of amino-functionalized polymeric microcapsules as efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions removal. Chem Eng J 425:130645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130645
Deng S, Chen JP (2023) Aminated polyacrylonitrile fibers for lead and copper removal. Langmuir 19:5058–5064. https://doi.org/10.1021/la034061x
Deng SB, Bai R, Chen JP (2003) Behaviors and mechanisms of copper adsorption on hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile fibers. J Colloid Interf Sci 260:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(02)00243-6
Du M, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Lv M, Xu Q, Chen Z, Wen Q, Li A (2022) La-doped activated carbon as high-efficiency phosphorus adsorbent: DFT exploration of the adsorption mechanism. Sep Purif 298:121585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121585
Fang Y, Yu XY, Lou XWD (2018) Formation of hierarchical Cu-doped CoSe2 microboxes via sequential ion exchange for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 30:1706668. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706668
Gao J, Lei H, Han Z, Shi Q, Chen Y, Jiang Y (2017) Dopamine functionalized tannic-acid-templated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a new sorbent for the efficient removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Sci Rep 7:45215. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45215
He W, Cao J, Guo F, Guo Z (2023) Nanostructured carboxylated-wood aerogel membrane for high-efficiency removal of Cu (II) ions from wastewater. Chem Eng J 468:143747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.143747
Huang B, Liu Y, Li B, Liu S, Zeng G, Zeng Z, Wang X, Ning Q, Zheng B, Yang C (2017) Effect of Cu(II) ions on the enhancement of tetracycline adsorption by Fe3O4@SiO2-chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite. Carbohydr Polym 157:576–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.025
Irfai RA, Roto R, Aplrilita NH (2020) Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for adsorption of waste containing Cu2+ ions. KEM 840:43–47. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.840.43
Jia X, Zhao J, Wang J, Ren H, Hong Z, Wu K (2021) Amine functionalized polyacrylonitrile fibers for the selective preconcentration of trace metals prior to their on-line determination by ICP-MS. Anal Methods 13:2504–2511. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY00511A
Jiang W, Chen X, Pan B, Zhang Q, Teng L, Chen Y, Liu L (2014) Spherical polystyrene-supported chitosan thin film of fast kinetics and high capacity for copper removal. J Hazard Mater 276:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.032
Jiang C, Wang X, Wang G, Hao C, Li X, Li T (2019) Adsorption performance of a polysaccharide composite hydrogel based on crosslinked glucan/chitosan for heavy metal ions. Compos B Eng 169:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.03.082
Ju P, Liu Q, Zhang H, Chen R, Liu J, Yu J, Liu P, Zhang M, Wang J (2019) Hyperbranched topological swollen-layer constructs of multi-active sites polyacrylonitrile (PAN) adsorbent for uranium(VI) extraction from seawater. Chem Eng J 374:1204–1213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.222
Kadirvelu K, Faur Brasquet C, Cloirec PL (2000) Removal of Cu(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II) by adsorption onto activated carbon cloths. Langmuir 16:8404–8409. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0004810
Krstić V, Urošević T, Pešovski BA (2018) Review on adsorbents for treatment of water and wastewaters containing copper ions. chem. Eng Sci 192:273–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2018.07.022
Li M, Liu Y, Liu S, Shu D, Zeng G, Hu X, Tan X, Jiang L, Yan Z, Cai X (2017) Cu(II)-influenced adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by magnetic graphene oxide/nitrilotriacetic acid nanocomposite: competition and enhancement mechanisms. Chem Eng J 319:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.016
Li J, Zheng L, Wang SL, Wu Z, Wu W, Niazi NK, Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J, Bolan N, Ok YS, Wang H (2019a) Sorption mechanisms of lead on silicon-rich biochar in aqueous solution: spectroscopic investigation. Sci Total Environ 672:572–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.003
Li M, Meng X, Huang K, Feng J, Jiang S (2019b) A novel composite adsorbent for the separation and recovery of indium from aqueous solutions. Hydrometallurgy 186:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.04.003
Li F, Fei P, Dong Y, Zhang M, Feng Y, Liu S, Jia L (2022) Competitive coordination of iron(III) and copper(II) ions with amidoximated polyacrylonitrile nanofiber and the catalytic performance of the complex. J Ind Text 51:1456S-1475S. https://doi.org/10.1177/15280837211063905
Liu Z, Qiu K, Dong Y, Jin Z, Liu L, Wu J (2022) Sb-Fe bimetallic non-aqueous phase desulfurizer for efficient absorption of hydrogen sulfide: a combined experimental and DFT study. Korean J Chem Eng 39:3305–3314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-022-1253-6
Liu Z, Chen Z, Chen Q, Liu L, Wang Y, Shu P, Zhong Y, Sun Z, Qiu K (2023a) Heterogeneous catalytic oxidation regeneration of desulfurization-rich liquor with Fe3+ modified chitosan. Front Environ Sci Eng 2:1167552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenve.2023.1167552
Liu Z, Qiu K, Sun G (2023b) A minated polyacrylonitrile fibers for the removal of hydrogen sulfide from natural gas at room temperature. RES CHEM INTERMEDIAT 49:701–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-022-04897-1
Liu Z, Sun G, Chen Z, Qiu K (2023c) Anchoring Cu-N active sites on functionalized polyacrylonitrile fibers for highly selective H2S/CO2 separation. J Hazard Mater 450:131084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131084
Natrayan L, Arul Kumar PV, Dhanraj JA, Kaliappan S, Sivakumar NS, Patil PP, Sekar S, Paramasivam P (2022) Synthesis and analysis of impregnation on activated carbon in multiwalled carbon nanotube for Cu adsorption from wastewater. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2022:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7470263
Qi J, He X, Lu Q (2022) Novel chelating polyacrylonitrile membrane for efficient capture of Cu2+, Pb2+ and Fe3+. Chem Eng J 450:138203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138203
Qin X, Zeng X, Cheng S et al (2023) Preparation of double functional carbon-based ZnO derived from rape straw for dye wastewater treatment. J Water Process Eng 52:103588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.103588
Qiu L, Phule AD, Wen S, Zhang X, Chen Q, Zhang ZX (2021) Multifunctional adsorbent: oleophobic latex sponge for removing dyes and Cu2+ from sewage waste. Macromol Mater Eng 306:2100096. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.202100096
Qiu K, Liu ZH, Dong Y, Liu LW, Li W, Niu SH, Jin ZB (2022) [Bmim]FeCl4 efficient catalytic oxidative removal of H2S by Cu2+ synergistic reinforcement. Chem Eng Technol 45:1867–1875. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.202200235
Shao J, Shao P, Peng M, Li M, Yao Z, Xiong X, Qiu C, Zheng Y, Yang L, Luo X (2023) A pyrazine based metal-organic framework for selective removal of copper from strongly acidic solutions. Front Environ Sci Eng 17:33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-023-1633-0
Shen SS, Yang JJ, Liu CX, Bai RB (2017) Immobilization of copper ions on chitosan/cellulose acetate blend hollow fiber membrane for protein adsorption. RSC Adv 7:10424–10431. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA00148G
Shi XL, Chen Y, Hu Q, Zhang W, Luo C, Duan P (2017) A potential industrialized fiber-supported copper catalyst for one-pot multicomponent CuAAC reactions in water. J Ind Eng Chem 53:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.04.014
Shin DH, Ko YG, Choi US, Kim WN (2004) Design of high efficiency chelate fibers with an amine group to remove heavy metal ions and pH-related FT-IR analysis. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:2060–2066. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie030696f
Soltanzadeh M, Kiani G, Khataee A (2013) Adsorptive capacity of polyacrylonitrile modified with triethylenetetramine for removal of copper and cadmium ions from aqueous solutions. Environ Prog Sustain Energy https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.11895
Tong X, Li J, Yuan J, Xu R (2011) Adsorption of Cu(II) by biochars generated from three crop straws. Chem Eng J 172:828–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.06.069
Tu Y, Ren LF, Lin Y, Shao J, He Y, Gao X, Shen Z (2020) Adsorption of antimonite and antimonate from aqueous solution using modified polyacrylonitrile with an ultrahigh percentage of amidoxime groups. J Hazard Mater 388:121997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121997
Wang D, Hu J, Liu D, Chen Q, Li J (2017) Selective transport and simultaneous separation of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Mg(II) using a dual polymer inclusion membrane system. J Membrane Sci 524:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.11.027
Wang T, Wang Q, Soklun H, Qu G, Xia T, Guo X, Jia H, Zhu L (2019a) A green strategy for simultaneous Cu(II)-EDTA decomplexation and Cu precipitation from water by bicarbonate-activated hydrogen peroxide/chemical precipitation. Chem Eng J 370:1298–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.005
Wang X, Lou Y, Ye X, Chen X, Fang L, Zhai Y, Zheng Y, Xiong C (2019b) Green chemical method for the synthesis of chromogenic fiber and its application for the detection and extraction of Hg2+ and Cu2+ in environmental medium. J Hazard Mater 364:339–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.051
Wang J, Ren J, Tang Q, Wang X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Du Z, Wang W, Huang L, Belfiore LA, Tang J (2022) An efficient cyan emission from copper (II) complexes with mixed organic conjugate ligands. Materials 15:1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051719
Wei W, Li J, Han X, Yao Y, Zhao W, Han R, Li S, Zhang Y, Zheng C (2021) Insights into the adsorption mechanism of tannic acid by a green synthesized nano-hydroxyapatite and its effect on aqueous Cu(II) removal. Sci Total Environ 778:146189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146189
Xavier ALP, Adarme OFH, Furtado LM, Ferreira GMD, Silva LHM, Gil LF, Gurgel LVA (2018) Modeling adsorption of copper(II), cobalt(II) and nickel(II) metal ions from aqueous solution onto a new carboxylated sugarcane bagasse. Part II: optimization of monocomponent fixed-bed column adsorption. J Colloid Interf Sci 516:431–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.01.068
Xu G, Xu W, Tian S, Zheng W, Yang T, Wu Y, Xiong Q, Kianpoor Kalkhajeh Y, Gao H (2021a) Enhanced phosphate removal from wastewater by recyclable fiber supported quaternary ammonium salts: highlighting the role of surface polarity. Chem Eng J 416:127889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127889
Xu W, Zheng W, Wang F, Xiong Q, Shi XL, Kalkhajeh YK, Xu G, Gao H (2021b) Using iron ion-loaded aminated polyacrylonitrile fiber to efficiently remove wastewater phosphate. Chem Eng J 403:126349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126349
Xu X, Zhang M, Lv H, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Yu DG (2022) Electrospun polyacrylonitrile-based lace nanostructures and their Cu(II) adsorption. Sep Purif 288:120643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120643
Zheng W, Wu Q, Xu W, Xiong Q, Kianpoor Kalkhajeh Y, Zhang C, Xu G, Zhang W, Ye X, Gao H (2022) Efficient capture of phosphate from wastewater by a recyclable ionic liquid functionalized polyacrylonitrile fiber: a typical “release and catch” mechanism. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 8:607–618. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00737H
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 51974039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, validation. ZC: supervision, writing—review and editing. DZ: supervision, writing—review and editing. BJN: supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This manuscript was only submitted on Environmental Science and Pollution Research. The authors ensure they have permission to use software, questionnaires/(webs) surveys and scales in their studies (if appropriate). This research may not be misapplied to threaten public health or national security. The manuscript does not involve relevant ethical research.
Consent to participate
Results in this manuscript were presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation (including image-based manipulation).
Consent for publication
All co-authors have seen and approved the manuscript and agreed to its publication submissions.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Chen, Z., Zhang, D. et al. Carboxyl and polyamine groups functionalized polyacrylonitrile fibers for efficient recovery of copper ions from solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 2243–2257 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31227-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31227-8