Abstract
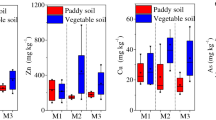
Cadmium (Cd) pollution induced by smelting process is of great concern worldwide. However, the comprehensive risk assessment of Cd exposures in smelting areas with farming coexist is lacking. In this study, atmospheric deposition, soil, surface and drinking water, rice, wheat, vegetable, fish, pork, and human hair samples were collected in rice–wheat rotation area near nonferrous smelter to investigate smelting effect on environmental Cd pollution and human health. Results showed high Cd deposition (0.88–2.61 mg m−2 year−1) combined with high bioavailability (37–42% totality) in study area. Moreover, 90%, 83%, 57%, and 3% of sampled soil, wheat, rice, and vegetable of Cd were higher than national allowable limits of China, respectively, indicating smelting induced serious environmental Cd pollution. Especially, higher Cd accumulation occurred in wheat compared to rice by factors of 1.5–2.0. However, as for Cd exposure to local residents, due to rice as staple food, rice intake ranked as main route and accounted for 49–53% of total intake, followed by wheat and vegetable. Cd exposure showed high potential noncarcinogenic risks with hazard quotient (HQ) of 0.63–4.99 using Monte Carlo probabilistic simulation, mainly from crop food consumption (mean 94% totality). Further, residents’ hair Cd was significant correlated with HQ of wheat and rice ingestion, highlighting negative impact of cereal pollution to resident health. Therefore, smelting process should not coexist with cereal cultivating.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abubakar A, Zangina AS, Maigari AI, Badamasi MM, Ishak MY, Abdullahi AS, Haruna JA (2022) Pollution of heavy metal threat posed by e-waste burning and its assessment of human health risk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(40):61065–61079
Alvarenga P, Palma P, Goncalves AP, Fernandes RM, Cunha-Queda AC, Duarte E, Vallini G (2007) Evaluation of chemical and ecotoxicological characteristics of biodegradable organic residues for application to agricultural land. Environ Int 33(4):505–513
Chang H, Yang P, Lin H, Yeh K, Chen M, Wang S (2020) Indium uptake and accumulation by rice and wheat and health risk associated with their consumption. Environ Sci Technol 54(23):14946–14954
Chen H, Yang X, Wang P, Wang Z, Li M, Zhao F (2018) Dietary cadmium intake from rice and vegetables and potential health risk: a case study in Xiangtan, southern China. Sci Total Environ 639:271–277
CNEMC (1990) Background values of soil elements in China. China Environmental Press, Beijing
CNMEE (2018) Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land, GB15618–2018. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China, Beijing, China.
Cupara N, Nikolic I, Durovic D, Milasevic I, Medin D, Krivokapic S (2022) Heavy metal assessment in agricultural soils and vegetables in the vicinity of industrial pollutants in the Pljevlja municipality (Montenegro): ecological and health risk approach. Environ Monit Assess 194(11):819
De Temmerman L, Waegeneers N, Ruttens A, Vandermeiren K (2015) Accumulation of atmospheric deposition of As, Cd and Pb by bush bean plants. Environ Pollut 199:83–88
Dutta D, Goel S, Kumar S (2022) Health risk assessment for exposure to heavy metals in soils in and around E-waste dumping site. J Environ Chem Eng 10(2):107269
Fan T, Long T, Lu Y, Yang L, Mi N, Xia F, Wang X, Deng S, Hu Q, Zhang F (2022) Meta-analysis of Cd input-output fluxes in agricultural soil. Chemosphere 303:134974
Feng W, Guo Z, Xiao X, Peng C, Shi L, Ran H, Xu W (2019) Atmospheric deposition as a source of cadmium and lead to soil-rice system and associated risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:160–167
Fu Y, Li F, Guo S, Zhao M (2021) Cadmium concentration and its typical input and output fluxes in agricultural soil downstream of a heavy metal sewage irrigation area. J Hazard Mater 412:125203
Gil F, Hernández AF, Márquez C, Femia P, Olmedo P, López-Guarnido O, Pla A (2011) Biomonitorization of cadmium, chromium, manganese, nickel and lead in whole blood, urine, axillary hair and saliva in an occupationally exposed population. Sci Total Environ 409(6):1172–1180
Guleria A, Singh R, Chakma S, Birke V (2022) Ecological and human health risk assessment of chromite ore processing residue (COPR) dumpsites in Northern India: a multi-pathways based probabilistic risk approach. Process Saf Environ Prot 163:405–420
Jia X, Zhang L, Zhao J, Ren M, Li Z, Wang J, Wang S, Liu Y, An H, Li Y, Yan L, Li Z, Liu X, Pan B, Ye R (2021) Associations between endocrine-disrupting heavy metals in maternal hair and gestational diabetes mellitus: a nested case-control study in China. Environ Int 157:106770
Jiang Z, Guo Z, Peng C, Liu X, Zhou Z, Xiao X (2021) Heavy metals in soils around non-ferrous smelteries in China: status, health risks and control measures. Environ Pollut 282:117038
Kumar M, Rahman MM, Ramanathan AL, Naidu R (2016) Arsenic and other elements in drinking water and dietary components from the middle Gangetic plain of Bihar, India: health risk index. Sci Total Environ 539:125–134
Li X, Li Z, Lin C, Bi X, Liu J, Feng X, Zhang H, Chen J, Wu T (2018) Health risks of heavy metal exposure through vegetable consumption near a large-scale Pb/Zn smelter in central China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:99–110
Liang Y, Wang R, Sheng GD, Pan L, Lian E, Su N, Tang X, Yang S, Yin D (2023) Geochemical controls on the distribution and bioavailability of heavy metals in sediments from Yangtze River to the East China Sea: assessed by sequential extraction versus diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) technique. J Hazard Mater 452:131253
Liu H, Zhou J, Li M, Hu Y, Liu X, Zhou J (2019) Study of the bioavailability of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition on the soil-pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) system. J Hazard Mater 362:9–16
Liu H, Zhou J, Li M, Xia R, Wang X, Zhou J (2022) Dynamic behaviors of newly deposited atmospheric heavy metals in the soil-pak choi system. Environ Sci Technol 56(17):12734–12744
Liu Y, Cui J, Peng Y, Lu Y, Yao D, Yang J, He Y (2020) Atmospheric deposition of hazardous elements and its accumulation in both soil and grain of winter wheat in a lead-zinc smelter contaminated area Central China. Sci Total Environ 707:135789
Liu Y, Xiao T, Baveye PC, Zhu J, Ning Z, Li H (2015) Potential health risk in areas with high naturally-occurring cadmium background in southwestern China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:122–131
Meng Z, Huang S, Xu T, Deng Y, Lin Z, Wang X (2020) Transport and transformation of Cd between biochar and soil under combined dry-wet and freeze-thaw aging. Environ Pollut 263:114449
Pan YP, Wang YS (2015) Atmospheric wet and dry deposition of trace elements at 10 sites in Northern China. Atmos Chem Phys 15(2):951–972
Park J-H, Choi K-K (2013) Risk assessment of soil, water and crops in abandoned Geumryeong mine in South Korea. J Geochem Explor 128:117–123
Petit JCJ, Maggi P, Pirard C, Charlier C, Ruttens A, Lienard A, Colinet G, Remy S (2022) Human biomonitoring survey (Pb, Cd, As, Cu, Zn, Mo) for urban gardeners exposed to metal contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 312:120028
Qiao Y, Hou H, Chen L, Wang H, Jeyakumar P, Lu Y, Cao L, Zhao L, Han D (2022) Comparison of Pb and Cd in wheat grains under air-soil-wheat system near lead-zinc smelters and total suspended particulate introduced modeling attempt. Sci Total Environ 839:156290
Qing Y, Yang J, Zhu Y, Li Y, Ma W, Zhang C, Li X, Wu M, Wang H, Kauffman AE, Xiao S, Zheng W, He G (2020) Cancer risk and disease burden of dietary cadmium exposure changes in Shanghai residents from 1988 to 2018. Sci Total Environ 734:139411
Qu M, Chen J, Huang B, Zhao Y (2020) Exploring the spatially varying relationships between cadmium accumulations and the main influential factors in the rice-wheat rotation system in a large-scale area. Sci Total Environ 736:139565
Shi J, Shi Y, Feng Y, Li Q, Chen W, Zhang W, Li H (2019a) Anthropogenic cadmium cycles and emissions in Mainland China 1990–2015. J Clean Prod 230:1256–1265
Shi T, Ma J, Wu F, Ju T, Gong Y, Zhang Y, Wu X, Hou H, Zhao L, Shi H (2019b) Mass balance-based inventory of heavy metals inputs to and outputs from agricultural soils in Zhejiang Province, China. Sci Total Environ 649:1269–1280
Skalny AV, Zhukovskaya EV, Kireeva GN, Skalnaya MG, Grabeklis AR, Radysh IV, Shakieva RA, Nikonorov AA, Tinkov AA (2018) Whole blood and hair trace elements and minerals in children living in metal-polluted area near copper smelter in Karabash, Chelyabinsk region Russia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(3):2014–2020
Sun S, Zhang H, Luo Y, Guo C, Ma X, Fan J, Chen J, Geng N (2022) Occurrence, accumulation, and health risks of heavy metals in Chinese market baskets. Sci Total Environ 829:154597
USEPA (2011) Exposure factors handbook. U.S. Environment Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
Wang F, Peng L, Zhou X, Zeng Q, Luo S (2021a) Typical sources of Cd to paddy fields in different contaminated areas and their impacts on Cd accumulation in topsoil and rice in Changzhutan. China Environ Res 193:110523
Wang J, Wang L, Wang Y, Tsang DCW, Yang X, Beiyuan J, Yin M, Xiao T, Jiang Y, Lin W, Zhou Y, Liu J, Wang L, Zhao M (2021b) Emerging risks of toxic metal(loid)s in soil-vegetables influenced by steel-making activities and isotopic source apportionment. Environ Int 146:106207
Wang L, Jin Y, Weiss DJ, Schleicher NJ, Hou D (2021c) Possible application of stable isotope compositions for the identification of metal sources in soil. J Hazard Mater 407:1–17
Wang W, Chen M, Guo L, Wang WX (2017) Size partitioning and mixing behavior of trace metals and dissolved organic matter in a South China estuary. Sci Total Environ 603–604:434–444
Wang Y, Liu C, Zhou D, Chen H (2016) A new approach for evaluating soil heavy metal impact: a comprehensive index combined soil environmental quality and agricultural products quality. J of Agro-Environ Sci 35(7):1225–1232
Xu J, Li Y, Wang S, Long S, Wu Y, Chen Z (2023) Sources, transfers and the fate of heavy metals in soil-wheat systems: the case of lead (Pb)/zinc (Zn) smelting region. J Hazard Mater 441:129863
Yang J, Cang L, Wang X, Xu H, Zhou D (2020) Field survey study on the difference in Cd accumulation capacity of rice and wheat in rice-wheat rotation area. J Soils Sed 20(4):2082–2092
Yang Q, Zhang L, Wang H, Martin JD (2022) Bioavailability and health risk of toxic heavy metals (As, Hg, Pb and Cd) in urban soils: a Monte Carlo simulation approach. Environ Res 214:113772
Yang X, Liu J, McGrouther K, Huang H, Lu K, Guo X, He L, Lin X, Che L, Ye Z, Wang H (2016) Effect of biochar on the extractability of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) and enzyme activity in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):974–984
Zhang L, Gao C, Chen C, Zhang W, Huang X-Y, Zhao F-J (2020a) Overexpression of rice OsHMA3 in wheat greatly decreases cadmium accumulation in wheat grains. Environ Sci Technol 54(16):10100–10108
Zhang S, Gu Y, Zhu Z, Hu S, Kopittke PM, Zhao F, Wang P (2021) Stable isotope fractionation of cadmium in the soil-rice-human continuum. Sci Total Environ 761:1–8
Zhang X, Yan Y, Wadood SA, Sun Q, Guo B (2020b) Source apportionment of cadmium pollution in agricultural soil based on cadmium isotope ratio analysis. Appl Geochem 123:104776
Zheng J, Li M, Tang B, Luo W, Ma Y, Ren M, Yu Y, Luo X, Mai B (2021) Levels, spatial distribution, and impact factors of heavy metals in the hair of metropolitan residents in China and human health implications. Environ Sci Technol 55(15):10578–10588
Zhong S, Li X, Li F, Liu T, Huang F, Yin H, Chen G, Cui J (2021) Water management alters cadmium Isotope fractionation between shoots and nodes/leaves in a soil-rice system. Environ Sci Technol 55(19):12902–12913
Zhou J, Liang J, Hu Y, Zhang W, Liu H, You L, Zhang W, Gao M, Zhou J (2018) Exposure risk of local residents to copper near the largest flash copper smelter in China. Sci Total Environ 630:453–461
Zhou J, Zhang C, Du B, Cui H, Fan X, Zhou D, Zhou J (2021) Soil and foliar applications of silicon and selenium effects on cadmium accumulation and plant growth by modulation of antioxidant system and Cd translocation: comparison of soft vs. durum wheat varieties. J Hazard Mater 402:123546–123546
Zhou Y, Jiang D, Ding D, Wu Y, Wei J, Kong L, Long T, Fan T, Deng S (2022) Ecological-health risks assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around a super-sized lead-zinc smelter with a long production history, in China. Environ Pollut 307:119487
Zhu Z, Xu Z, Peng J, Fei J, Yu P, Wang M, Tan Y, Huang Y, Zhran M, Fahmy A (2022) The contribution of atmospheric deposition of cadmium and lead to their accumulation in rice grains. Plant Soil 477:373–387
Zou M, Zhou S, Zhou Y, Jia Z, Guo T, Wang J (2021) Cadmium pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: a review. Environ Pollut 280:116965
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2020QD129), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20220599), and the Jiangsu Provincial Double-Innovation Doctor Program (JSSCBS20211033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.L. and M.L. designed this investigation. H.W., H.W., and M.L. were responsible for preparing and collecting the samples, experiment instrument operation, and data analysis. H.L. was responsible for writing paper. J.Z., Y.Z., and X.W. were responsible for modifying and editing of this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Wang, H., Zhou, J. et al. Environmental cadmium pollution and health risk assessment in rice–wheat rotation area around a smelter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 433–444 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31215-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31215-y