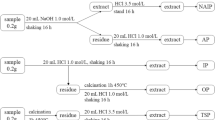
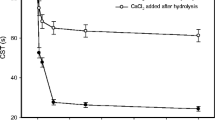
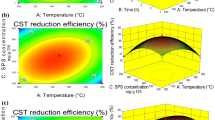
Abstract
Acid treatment can increase the sludge calorific value to some extent by separating inorganic elements. In order to determine the mechanism by which acidification affects the sludge calorific value from an organic perspective, we investigated the changes in organic matter and dewaterability under different pH conditions. The results of this study showed that acidification conditioning retained organic matter while removing a greater amount of inorganic elements. Furthermore, acid treatment significantly increased the zeta potential and particle size of sludge particles and facilitated the precipitation of biological organic components from the supernatant to the surface of sludge particles. Acid-treated sludge exhibited a lower moisture content and a higher proportion of organic matter, and sludge treated with H2SO4, HCl, and HNO3 exhibited respective increases in calorific values of 12.14%, 7.92%, and 8.01% under pH 2. The calorific value of the acid-treated sludge was higher, making it more suitable for subsequent incineration. The findings of this study serve as a reference and foundation for efficient sludge incineration.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the fndings of this study are openly available on request.
References
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2005) Standard Methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. In: American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Baker A (2001) Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix characterization of some sewage-impacted rivers. Environ Sci Technol 35:948–953. https://doi.org/10.1021/es000177t
Cai MQ, Hu JQ, Wells G, Seo Y, Spinney R, Ho SH, Dionysiou DD, Su J, Xiao RY, Wei ZS (2018) Understanding mechanisms of synergy between acidification and ultrasound treatments for activated sludge dewatering: from bench to pilot-scale investigation (vol 52, pg 4313, 2018). Environ Sci Technol 52:6077–6177. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02098
Chen YG, Yang HZ, Gu GW (2001) Effect of acid and surfactant treatment on activated sludge dewatering and settling. Water Res 35:2615–2620. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00565-0
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation–emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37:5701–5710. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034354c
Dai QX, Ma LP, Ren NQ, Ning P, Guo ZY, Xie LG (2019) Research on the variations of organics and heavy metals in municipal sludge with additive acetic acid and modified phosphogypsum. Water Res 155:42–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.015
Djandja OS, Yin LX, Wang ZC, Duan PG (2021) From wastewater treatment to resources recovery through hydrothermal treatments of municipal sewage sludge: a critical review. Process Saf Environ 151:101–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.05.006
Domínguez L, Rodríguez M, Prats D (2010) Effect of different extraction methods on bound EPS from MBR sludges. Part I: Influence of extraction methods over three-dimensional EEM fluorescence spectroscopy fingerprint. Desalination 261:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.05.054
Fan HJ, Zhou H, Wang J (2014) Pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludges in a slowly heating and gas sweeping fixed-bed reactor. Energ Convers Manag 88:1151–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.05.043
Fan SS, Wang Y, Wang Z, Tang J, Tang J, Li XD (2017) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by sewage sludge-derived biochar: adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism. J Environ Chem Eng 5:601–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.019
Guo SH, Li G, Qu JH, Liu XL (2011) Improvement of acidification on dewaterability of oily sludge from flotation. Chem Eng J 168:746–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.070
Guo L, Lu MM, Li QQ, Zhang JW, Zong Y, She ZL (2014) Three-dimensional fluorescence excitation-emission matrix (EEM) spectroscopy with regional integration analysis for assessing waste sludge hydrolysis treated with multi-enzyme and thermophilic bacteria. Bioresour Technol 171:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.025
Guo S, Yu S-X, Che D-Y, Liu H-P, Sun B-Z (2022) Migration characteristics of heavy metals during co-combustion of dehydrated sludge with straw. J Fuel Chem Technol 50:283–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60168-8
Herbert D, Phipps PJ, Strange RE (1971) Chapter III chemical analysis of microbial cells. Methods Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70641-X
Higgins MJ, Novak JT (1997) The effect of cations on the settling and dewatering of activated sludges: laboratory results. Water Environ Res 69:215–224. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143097X125371
Houghton JI, Stephenson T (2002) Effect of influent organic content on digested sludge extracellular polymer content and dewaterability. Water Res 36:3620–3628. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00055-6
Huber F, Blasenbauer D, Mallow O, Lederer J, Winter F, Fellner J (2016) Thermal co-treatment of combustible hazardous waste and waste incineration fly ash in a rotary kiln. Waste Manag 58:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.09.013
Jin Bo, Wilén B-M, Lant P (2004) Impacts of morphological, physical and chemical properties of sludge flocs on dewaterability of activated sludge. Chem Eng J 98:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2003.05.002
Keeley J, Smith AD, Judd SJ, Jarvis P (2016) Acidified and ultrafiltered recovered coagulants from water treatment works sludge for removal of phosphorus from wastewater. Water Res 88:380–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.039
Keiding K, Wybrandt L, Nielsen PH (2001) Remember the water—a comment on EPS colligative properties. Water Sci Technol 43:17–23. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2001.0330
Kim MS, Lee KM, Kim HE, Lee HJ, Lee C, Lee C (2016) Disintegration of waste activated sludge by thermally-activated persulfates for enhanced dewaterability. Environ Sci Technol 50:7106–7115. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00019
Kuo NW, Ma HW, Yang YM, Hsiao TY, Huang CM (2007) An investigation on the potential of metal recovery from the municipal waste incinerator in Taiwan. Waste Manag 27:1673–1679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.11.009
Laspidou CS, Rittmann BE (2002) A unified theory for extracellular polymeric substances, soluble microbial products, and active and inert biomass. Water Res 36:2711–2720. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00413-4
Li XY, Yang SF (2007) Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res 41:1022–1030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.037
Li M, Tang YY, Ren NN, Zhang ZT, Cao YM (2018) Effect of mineral constituents on temperature-dependent structural characterization of carbon fractions in sewage sludge-derived biochar. J Clean Prod 172:3342–3350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.090
Liang HL, Yin SZ, Yang YF, Sun LP, Li RH (2023) The effect of hydrochloric acidification conditioning on calorific value of sludge. J Sun Yat-sen University (Natural Science Edition) 62:93–101. https://doi.org/10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2022c018. (in Chinese)
Liao BQ, Allen DG, Droppo IG, Leppard GG, Liss SN (2001) Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability. Water Res 35:339–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00277-3
Liu Y, Fang HHP (2003) Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on flocculation, settling, and dewatering of activated sludge. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 33:237–273. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380390814479
Liu JB, Yu DW, Zhang J, Yang M, Wang YW, Wei YS, Tong J (2016) Rheological properties of sewage sludge during enhanced anaerobic digestion with microwave-H2O2 pretreatment. Water Res 98:98–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.073
Liu He, Shi J, Xu X, Zhan X, Fu Bo, Li Y (2017) Enhancement of sludge dewaterability with filamentous fungi Talaromyces flavus S1 by depletion of extracellular polymeric substances or mycelium entrapment. Bioresour Technol 245:977–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.185
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
Lu HL, Zhang WH, Wang SZ, Zhuang LW, Yang YX, Qiu RL (2013) Characterization of sewage sludge-derived biochars from different feedstocks and pyrolysis temperatures. J Anal Appl Pyrol 102:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2013.03.004
Mahmoud A, Hoadley AFA, Citeau M, Sorbet JM, Olivier G, Vaxelaire J, Olivier J (2018) A comparative study of electro-dewatering process performance for activated and digested wastewater sludge. Water Res 129:66–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.10.063
Mikkelsen LH, Keiding K (2002) Physico-chemical characteristics of full scale sewage sludges with implications to dewatering. Water Res 36:2451–2462. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00477-8
Mobaraki M, Semken RS, Mikkola A, Pyrhonen J (2018) Enhanced sludge dewatering based on the application of high-power ultrasonic vibration. Ultrasonics 84:438–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2017.12.002
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003) A review of thermal sludge pre-treatment processes to improve dewaterability. J Hazard Mater 98:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00320-5
Patel S, Kundu S, Halder P, Rickards L, Paz-Ferreiro J, Surapaneni A, Madapusi S, Shah K (2019) Thermogravimetric analysis of biosolids pyrolysis in the presence of mineral oxides. Renew Energ 141:707–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.04.047
Raheem A, Sikarwar VS, He J, Dastyar W, Dionysiou DD, Wang W, Zhao M (2018) Opportunities and challenges in sustainable treatment and resource reuse of sewage sludge: a review. Chem Eng J 337:616–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.149
Raynaud M, Vaxelaire J, Olivier J, Dieudé-Fauvel E, Baudez J-C (2012) Compression dewatering of municipal activated sludge: effects of salt and pH. Water Res 46:4448–4456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.05.047
Shao L, He P, Yu G, He P (2009) Effect of proteins, polysaccharides, and particle sizes on sludge dewaterability. J Environ Sci 21:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60015-2
Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2006) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic and anaerobic sludge using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res 40:1233–1239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.01.023
Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Li XY (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Biotechnol Adv 28:882–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.08.001
Silva JD, Rodrigues G, Meireles CD, Ribeiro SD, Vieira JG, da Silva CV, Cerqueira DA (2012) Thermal analysis and FTIR studies of sewage sludge produced in treatment plants. The case of sludge in the city of Uberlandia-MG, Brazil. Thermochim Acta 528:72–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2011.11.010
Wei H, Gao BQ, Ren J, Li AM, Yang H (2018) Coagulation/flocculation in dewatering of sludge: a review. Water Res 143:608–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.029
Wei H, Hu P, Li AM, Yang H (2019) Evaluation of acidification and oxidation of sludge to improve the effect of a starch-based flocculant on the dewaterability of sewage sludge. J Environ Manag 231:405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.058
Wong JWC, Zhou J, Kurade MB, Murugesan K (2015) Influence of ferrous ions on extracellular polymeric substances content and sludge dewaterability during bioleaching. Bioresour Technol 179:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.099
Xu GR, Yan ZC, Wang YC, Wang N (2009) Recycle of Alum recovered from water treatment sludge in chemically enhanced primary treatment. J Hazard Mater 161:663–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.008
Xu T, Wang CB, Hong DK, Li S, Yue S (2023) The synergistic effect during co-combustion of municipal sludge and coal: experimental and ReaxFF molecular dynamic study. Energy 262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.125553
Yu GH, He PJ, Shao LM, He PP (2008) Stratification structure of sludge flocs with implications to dewaterability. Environ Sci Technol 42:7944–7949. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8016717
Zhai YB, Peng WF, Zeng GM, Fu ZM, Lan YM, Chen HM, Wang C, Fan XP (2012) Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of sewage sludge for different sizes and heating rates. J Therm Anal Calorim 107:1015–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1644-0
Zhang BP, Xiong SJ, Xiao B, Yu DK, Jia XY (2011) Mechanism of wet sewage sludge pyrolysis in a tubular furnace. Int J Hydrogen Energ 36:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.05.100
Zhou L, Guo X, Xiao B, Liu J (2011) Research on the estimation method of calorific value of residual sludge in municipal sewage treatment plants. Water Supply Drainage 47:134–39. https://doi.org/10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2011.09.024. (in Chinese)
Funding
This study was financially supported by China Energy Engineering Group Guangdong Electric Power Design Institute Co., Ltd (CG-2021-K-016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lieyang Lv: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, investigation, methodology, visualization. Meiqi Yang: investigation, data curation, validation. Wei Liu: funding acquisition, conceptualization, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval, consent to participate, and consent for publication
Not applicable. The manuscript does not report on or involve any animals, humans, human data, human tissue, or plants, nor does it contain any individual personal data.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme Luiz Dotto
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
I have not submitted my manuscript to a preprint server before submitting it to Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, L., Yang, M. & Liu, W. Effects of organic matter and dewaterability changes on sludge calorific value during acid treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 2104–2116 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30957-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30957-z