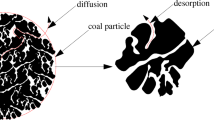
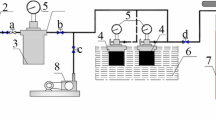
Abstract
An in-depth understanding of gas diffusion characteristics in coal is of great value to coalbed methane (CBM) production planning and coal mine safety management. However, the mechanism and model of gas diffusion is still unclear, and some methods for determining diffusion coefficients are not accurate enough. Accordingly, a free gas density gradient (FGDG)–driven coal particle gas desorption and diffusion model was established in this work, and numerical solutions were performed via finite difference method (FDM) and dimensionless method. The variation rules of dimensionless gas pressure, gas content, desorption capacity, and desorption rate were obtained. Finally, the application of the dimensionless method in diffusion modeling and diffusion coefficient inversion was discussed. The results show that the dimensionless method can simplify mathematical equation processing and analyze the common phenomena of desorption and diffusion under different parameters. The gas desorption diffusion in coal particles is from the surface to the inside, and there is obvious desorption hysteresis effect. The larger the dimensionless radius or dimensionless time, the smaller the dimensionless gas pressure, gas content, and dimensionless desorption rate. The dimensionless cumulative gas desorption amount increased rapidly first and then tended to flat with dimensionless time. The simulated curve can be easily converted into the variation curves of several different measured parameters, and the diffusion coefficient can be calculated accurately. The prediction curve of the FGDG diffusion model is in good agreement with the experimentally measured data, which verifies its reasonableness. The research content aims to provide some ideas for modeling gas desorption and diffusion behavior.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Airey EM (1968) Gas emission from broken coal. An experimental and theoretical investigation. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 5(6):475–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(68)90036-3
Bitsanis I, Vanderlick TK, Tirrell M, Davis HT (1988) A tractable molecular theory of flow in strongly inhomogeneous fluids. J Chem Phys 89:3152. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.454972
Busch A, Gensterblum Y, Krooss BM, Littke R (2004) Methane and carbon dioxide adsorption-diffusion experiments on coal: upscaling and modeling. Int J Coal Geol 60(2):151–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2004.05.002
Chen M, Chen Y, Yun X, Wang L et al (2022) Water adsorption characteristic and its impact on pore structure and methane adsorption of various rank coals. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17802-x
Crank J (1975) The mathematics of diffusion(second edition). Oxford Univ Press
Fan C, Li S, Luo M et al (2017) Coal and gas outburst dynamic system. Int J Min Sci Technol 27(1):49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2016.11.003
Hou X, Liu S, Zhu Y, Yang Y (2020) Experimental and theoretical investigation on sorption kinetics and hysteresis of nitrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide in coals. Fuel 268:117349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117349
Huang Q, Wu B, Liu Y et al (2022) Experimental and simulation investigations of the impact of polyacrylamide on CBM ad-/desorption. J Pet Sci Eng 208:109300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109300
Jin K, Cheng Y, Ren T et al (2018) Experimental investigation on the formation and transport mechanism of outburst coal-gas flow: implications for the role of gas desorption in the development stage of outburst. Int J Coal Geol 194:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2018.05.012
Kang J, Zhou F, Xia T, Ye G (2016) Numerical modeling and experimental validation of anomalous time and space subdiffusion for gas transport in porous coal matrix. Int J Heat Mass Transf 100:747–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.04.110
Lau HC, Li H, Huang S (2017) Challenges and opportunities of coalbed methane development in China. Energy and Fuels 31(5):4588–4602. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b00656
Li Z, Liu Y, Xu Y, Song D (2016) Gas diffusion mechanism in multi-scale pores of coal particles and new diffusion model of dynamic diffusion coefficient. J China Coal Soc 41(03):633–643. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.0208
Liu A, Liu P, Liu S (2020) Gas diffusion coefficient estimation of coal: a dimensionless numerical method and its experimental validation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 162:120336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120336
Liu J, Qin Y, Zhang S, He C (2019) Numerical solution for borehole methane flow in coal seam based on a new dual-porosity model. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 68:102916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2019.102916
Liu P, Liu A, Zhong F et al (2021) Pore/fracture structure and gas permeability alterations induced by ultrasound treatment in coal and its application to enhanced coalbed methane recovery. J Pet Sci Eng 205:108862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108862
Liu P, Qin Y, Liu S, Hao Y (2018) Non-linear gas desorption and transport behavior in coal matrix: Experiments and numerical modeling. Fuel 214:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.10.120
Liu Q, Cheng Y (2014) Measurement of pressure drop in drainage boreholes and its effects on the performance of coal seam gas extraction: a case study in the Jiulishan Mine with strong coal and gas outburst dangers. Nat Hazards 71(3):1475–1493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0957-7
Liu T, Lin B (2019) Time-dependent dynamic diffusion processes in coal: model development and analysis. Int J Heat Mass Transf 134:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.01.005
Lu S, Wang C, Li M et al (2021) Gas time-dependent diffusion in pores of deformed coal particles: model development and analysis. Fuel 295:120566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120566
Nandi SP, Walker PL (1970) Activated diffusion of methane in coal. Fuel 49(3):309–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(70)90023-2
Nie B, Guo Y, Wu S, Zhang L (2001) Theoretical model of gas diffusion through coal particles and its analytical solution. J China Univ Min Technol 30(1):21–24
Pillalamarry M, Harpalani S, Liu S (2011) Gas diffusion behavior of coal and its impact on production from coalbed methane reservoirs. Int J Coal Geol 86(4):342–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2011.03.007
Qin Y, Hao Y, Liu P, Wang J (2015) Coal particle gas desorption experiment and numerical simulation in enclosed space. Meitan Xuebao/Journal China Coal Soc 40(1):87–92. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.0346
Qin Y, Hao Y, Wang Y et al (2013) Numerical solution of gas emission in coal particle based on two kind of mathematical model. J China Univ Min Technol 42(6):923–928. https://doi.org/10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.2013.06.006
Qin Y, Moore TA, Shen J et al (2018) Resources and geology of coalbed methane in China: a review. Int Geol Rev 60(5–6):777–812. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2017.1408034
Qin Y, Wang J (2016) Dimensionless analysis of gas emission in coal particles based on finite volume method. J China Coal Soc 41(02):399–405. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.0371
Qin Y, Zhao Z, Xu H et al (2022) Numerical solution of three mathematical models of gas adsorption in coal particle based on finite difference method. Fuel 308:122036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122036
Ritter D, Vinson D, Barnhart E et al (2015) Enhanced microbial coalbed methane generation: a review of research, commercial activity, and remaining challenges. Int J Coal Geol 146:28–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2015.04.013
Ruckenstein E, Vaidyanathan AS, Youngquist GR (1971) Sorption by solids with bidisperse pore structures. Chem Eng Sci 26(9):1305–1318. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(71)80051-9
Tan Y, Pan Z, Liu J et al (2018) Experimental study of impact of anisotropy and heterogeneity on gas flow in coal. Part I: Diffusion and adsorption. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.05.173
Xu H, Qin Y, Wu F et al (2021) Mathematical model and numerical solution of constant pressure adsorption of gas in coal particles. J Min Sci Technol 6(4):445–452
Xu H, Qin Y, Wu F et al (2022) Numerical modeling of gas extraction from coal seam combined with a dual-porosity model: Finite difference solution and multi-factor analysis. Fuel 313:122687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122687
Xu H, Tang D, Zhao J et al (2015) A new laboratory method for accurate measurement of the methane diffusion coefficient and its influencing factors in the coal matrix. Fuel 158:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.05.046
Xue S, Tu Q, Hao Y et al (2023) Occurrence and development criteria of coal and gas outbursts based on energy conversion. Fuel 341:127781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127781
Yang Q, Wang Y (1986) Theory of methane diffusion from coal cuttings and its application. J China Coal Soc 03:87–94
Zhao W, Cheng Y, Jiang H et al (2017) Modeling and experiments for transient diffusion coefficients in the desorption of methane through coal powders. Int J Heat Mass Transf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.03.065
Zhao W, Cheng Y, Pan Z et al (2019) Gas diffusion in coal particles: a review of mathematical models and their applications. Fuel 252:77–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.065
Zhou A, Zhang M, Wang K et al (2020) Airflow disturbance induced by coal mine outburst shock waves: a case study of a gas outburst disaster in China. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 128:104262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104262
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project no.: 51874315; 52074303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hao Xu: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, supervision, writing—original draft. Gang Wang: visualization, supervision, writing—review and editing. Qiming Huang: visualization, writing—review and editing. Yueping Qin: resources, supervision. Fengjie Zhang: data curation, investigation. Fan Wu: investigation, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Wang, G., Huang, Q. et al. Nondimensional analysis and application of gas desorption and diffusion driven by density gradient in coal particles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 121881–121894 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30886-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30886-x