Abstract
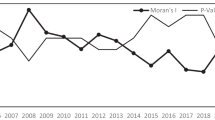
ICT has significantly transformed the traditional energy production and service methods, changed the correlation characteristics of energy consumption network, and contributed to the establishment of cross-regional, open, and synergistic energy ecological networks. In this paper, social network analysis (SNA), dynamic SYS-GMM model, and mediating effects model are employed to deliberate on the mechanism of ICT capital’s influence on the spatial correlation of energy consumption from 2000 to 2019. Firstly, this study employs an enhanced gravity model to precisely delineate the spatial correlation network of energy consumption in China, further applies the SNA to analyze the network structural characteristics, and then uses the econometric model to investigate the influence mechanism and heterogeneity of ICT capital on the spatial correlation of energy consumption. The study demonstrates a progressive spatial correlation in energy consumption in China, with eastern provinces emerge as the center of the network, assuming the position of the “dominant player.” Conversely, the central provinces act as the “bridge,” and western provinces are positioned at the periphery, referred to as the “edge” of the network. ICT capital contributes to improving the energy consumption spatial correlation, mainly by stimulating green technology innovation, promoting industrial structure optimization, accelerating human capital accumulation, and reducing income inequality. As ICT capital expands, the eastern region becomes more preeminent as a network hub for energy consumption, the central region increases its dominance slightly, and the western region’s marginal position does not change significantly. Furthermore, the presence of ICT capital significantly enhances the intensity of energy consumption spatial correlation more prominently for low-carbon pilot areas and high Internet level areas. This study guides provinces to fully utilize ICT capital to reach collaborative energy-saving goals, and promotes the breaking down of regional competitive barriers in energy systems to build cooperative energy conservation ecological networks.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the research results are primarily obtained from “China Statistical Yearbook (2000–2019),” “Provincial Statistical Yearbook (2000–2019),” “China Information Technology Statistical Yearbook (2000–2019),” “China Energy Statistical Yearbook (2000–2019),” and input–output tables in China.
References
Acheampong AO, Dzator J, Shahbaz M (2021) Empowering the powerless: does access to energy improve income inequality? Energy Econ 99:105288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105288
Ahn SJ (2020) Three characteristics of technology competition by IoT-driven digitization. Technol Forecast Soc 157:120062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120062
Albiman MM, Sulong Z (2017) The linear and non-linear impacts of ICT on economic growth, of disaggregate income groups within SSA region. Telecommun Policy 41(7–8):555–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2017.07.007
Asongu S, Amari M, Jarboui A, Mouakhar K (2021) ICT dynamics for gender inclusive intermediary education: minimum poverty and inequality thresholds in developing countries. Telecommun Policy 45(5):102125. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3794050
Asongu SA, Odhiambo NM (2019) How enhancing information and communication technology has affected inequality in Africa for Sustain Dev: an empirical investigation. Sustain Dev 27(4):647–656. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.1929
Ceccobelli M, Gitto S, Mancuso P (2012) ICT capital and labour productivity growth: a non-parametric analysis of 14 OECD countries. Telecommun Policy 36(4):282–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2011.12.012
Charfeddine L, Umlai M (2023) ICT sector, digitization and environmental sustainability: a systematic review of the literature from 2000 to 2022. Renew Sust Energ Rev 184:113482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2023.113482
Cheng YL, Lim MH, Hui KH (2021) Impact of internet of things paradigm towards energy consumption prediction: a systematic literature review. Sustain Cities Soc 78:103624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103624
Consoli D, Castellacci F, Santoalha A (2023) E-skills and income inequality within European regions. Ind Innov 30(7):919–946. https://doi.org/10.1080/13662716.2023.2230222
Djeunankan R, Njangang H, Tékam H (2023) How does economic complexity improve energy efficiency? Mechanism discussion and empirical test. Environ Sci Pollut R 30:96906–96925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28920-z
Du KR, Li JL (2019) Towards a green world: how do green technology innovations affect total-factor carbon productivity. Energy Pol 131:240–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.04.033
Du LZ, Wei MJ, Wu KY (2023) Information technology and firm’s green innovation: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollitt r 30:97601–97615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29320-z
Fang X, Cao Y (2023) Spatial Association Network Evolution and Variance Decomposition of Economic Sustainability Development Efficiency in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 20(4):2966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20042966
Fromhold-Eisebith M, Marschall P, Peters R, Thomes P (2021) Torn between digitized future and context dependent past–How implementing ‘Industry 4.0’production technologies could transform the German textile industry. Technol Forecast Soc. 166:120620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120620
Frondel M, Sommer S, Vance C (2019) Heterogeneity in German residential electricity consumption: a quantile regression approach. Energy Pol 131:370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.03.045
Gao CX, Su B, Sun M, Zhang XL, Zhang ZH (2018) Interprovincial transfer of embodied primary energy in China: a complex network approach. Appl Energy 215:792–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.02.075
Gao D, Li G, Yu JY (2022) Does digitization improve green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from Chinese 213 cities. Energ 247:123395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.123395
Giampietro M (2019) On the circular bioeconomy and decoupling: implications for sustainable growth. Ecol Econ 162:143–156
Haini H (2019) Internet penetration, human capital and economic growth in the ASEAN economies: evidence from a translog production function. Appl Econ Lett 26(21):1774–1778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.05.001
Haini H (2021) Examining the impact of ICT, human capital and carbon emissions: evidence from the ASEAN economies. Int Econ 166:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inteco.2021.03.003
Hao Y, Li Y, Guo YX, Chai JX, Yang CX, Wu HT (2022) Digitalization and electricity consumption: does internet development contribute to the reduction in electricity intensity in China? Energy Pol 164:112912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112912
Hong JK, Gu JP, He RX, Wang XZ, Shen QP (2020) Unfolding the spatial spillover effects of urbanization on interregional energy connectivity: evidence from province-level data. Energ 196:116990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.116990
Hou ZZ, Jin M, Kumbhakar SC (2020) Productivity spillovers and human capital: a semiparametric varying coefficient approach. Eur J Oper Res 287(1):317–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2020.04.039
Huang JB, Xiang SQ, Wu PL, Chen X (2022) How to control China’s energy consumption through technological progress: a spatial heterogeneous investigation. Energ 238:121965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121965
Huang YD, Li M, Yu FR, Si PB, Zhang YH (2023) Performance optimization for energy-efficient industrial internet of things based on ambient backscatter communication: an A3C-FL approach. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking 7(3):1121–1134. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGCN.2023.3260199
Iqbal J, Khan M, Talha M, Farman H, Jan B, Muhammad A, Khattak HA (2018) A generic internet of things architecture for controlling electrical energy consumption in smart homes. Sustain Cities Soc 43:443–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.09.020
Jiang QC, Ma XJ (2021) Spillovers of environmental regulation on carbon emissions network. Technol Forecast Soc 169:120825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120825
Jin G, Lei W, Zhou WZ, Wei C (2022) Powering green digitalization: evidence from 5G network infrastructure in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 182:106286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106286
Jin HL, Zhao J (2021) Real-time energy consumption detection simulation of network node in internet of things based on artificial intelligence. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 44:101004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101004
Kallal R, Haddaji A, Ftiti Z (2021) ICT diffusion and economic growth: evidence from the sectorial analysis of a periphery country. Technol Forecast Soc 162:120403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120403
Lee CC, Yuan ZH, Wang QR (2022) How does information and communication technology affect energy security? International evidence. Energy Econ 109:105969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.105969
Lin BQ, Sai R (2022) Sustainable transitioning in Africa: a historical evaluation of energy productivity changes and determinants. Energ 250:123833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.123833
Liu JB, Peng XB, Zhao J (2023) Analyzing the spatial association of household consumption carbon emission structure based on social network. J Comb Optim 45(2):79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-023-01004-x
Lv ZK, Liu WX, Xu T (2022) Evaluating the impact of information and communication technology on Renew Energy consumption: a spatial econometric approach. Renew Energ 189:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.005
Ma SY, Zhang YF, Lv JX, Ge YT, Yang HD, Li L (2020) Big data driven predictive production planning for energy-intensive manufacturing industries. Energ 211:118320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118320
Maroufkhani P, Desouza KC, Perrons RK, Iranmanesh M (2022) Digital transformation in the resource and energy sectors: a systematic review. Resour Policy 76:102622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102622
Mei BJ, Khan AA, Khan SU, Ali MBU, Luo JC (2023) Variation of digital economy’s effect on carbon emissions: improving energy efficiency and structure for energy conservation and emission reduction. Environ Sci Pollut R 30(37):87300–87313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28010-0
Murshed M (2020) An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-trade openness on renew energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36254–36281. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-020-09497-3
Mushtaq R, Bruneau C (2019) Microfinance, financial inclusion and ICT: implications for poverty and inequality. Technol Soc 59:101154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.101154
Peng BH, Wang YY, Wei G (2020) Energy eco-efficiency: is there any spatial correlation between different regions? Energy Pol 140:111404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111404
Ren SY, Hao Y, Xu L, Wu HT, Ba N (2021) Digitalization and energy: how does internet development affect China’s energy consumption? Energy Econ 98:105220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105220
Saldivia M, Kristjanpoller W, Olson JE (2020) Energy consumption and GDP revisited: a new panel data approach with wavelet decomposition. Appl Energy 272:115207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115207
Secundo G, Ndou V, Del VP, De PG (2020) Sustain Dev, intellectual capital and technology policies: a structured literature review and future research agenda. Technol Forecast Soc 153:119917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.119917
Shabani ZD, Shahnazi R (2019) Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, information and communications technology, and gross domestic product in Iranian economic sectors: a panel causality analysis. Energ 169:1064–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.11.062
Shen XB, Lin BQ (2021) Does industrial structure distortion impact the energy intensity in China? Sustain Prod Consump 25:551–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2020.12.012
Shi XH, Chu JH, Zhao CY (2021) Exploring the spatiotemporal evolution of energy intensity in China by visual technology of the GIS. Energ 228:120650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120650
Sun HY (2022) What are the roles of green technology innovation and ICT employment in lowering carbon intensity in China? A city-level analysis of the spatial effects. Resour Conserv Recycl 186:106550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106550
Sun WQ, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Wu JZ (2020) Material and energy flows of the iron and steel industry: status quo, challenges and perspectives. Appl Energy 268:114946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114946
Topcu E, Altinoz B, Aslan A (2020) Global evidence from the link between economic growth, natural resources, energy consumption, and gross capital formation. Resour Policy 66:101622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101622
Trahan RT, Hess DJ (2021) Who controls electricity transitions? Digitization, decarbonization, and local power organizations. Energy Res Soc Sci 80:102219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2021.102219
Wang HP, Liu PL (2023) Spatial correlation network of renewable energy consumption and its influencing factors: evidence from 31 Chinese provinces. Renew Energ 217:119173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.119173
Wang J, Sun FR, Lv KJ, Wang LS (2022a) Industrial agglomeration and firm energy intensity: how important is spatial proximity? Energy Econ 112:106155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106155
Wang M, Xu M, Ma SJ (2021a) The effect of the spatial heterogeneity of human capital structure on regional green total factor productivity. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 59:427–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2021.09.018
Wang N, Fu XD, Wang SB (2022b) Spatial-temporal variation and coupling analysis of residential energy consumption and economic growth in China. Appl Energy 309:118504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.118504
Wang Q, Zhang FY, Li RR, Li LJ (2022c) Forecasting China’s energy demand post-COVID-19 pandemic: insights from energy type differences and regional differences. Energy Strategy Rev 42:100881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2022.100881
Wang SB, Liu HM, Pu HX, Yang H (2020) Spatial disparity and hierarchical cluster analysis of final energy consumption in China. Energ 197:117195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.117195
Wang SB, Zhao C, Liu HB, Tian XL (2021b) Exploring the spatial spillover effects of low-grade coal consumption and influencing factors in China. Resour Policy 70:101906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101906
Wang XJ, Han RQ, Zhao MH (2023a) Evaluation and impact mechanism of high-quality development in China’s coastal provinces. Int J Environ Res Public Health 20(2):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021336
Wang Y, Gong X (2022) Analyzing the difference evolution of provincial energy consumption in China using the functional data analysis method. Energy Econ 105:105753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105753
Wang YH, He YG (2023) Does information and communication technology trade openness matter for China’s energy transformation and environmental quality? Energ 16(4):2016. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042016
Wang ZS, Xie WC, Zhang CY (2023b) Towards COP26 targets: characteristics and influencing factors of spatial correlation network structure on US carbon emission. Resour Policy 81:103285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.103285
Wu HT, Hao Y, Ren SY, Yang XD, Xie G (2021a) Does internet development improve green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from China Energy Pol 153:112247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112247
Wu Y, Wu YP, Guerrero JM, Vasquez JC (2021b) A comprehensive overview of framework for developing sustainable energy internet: from things-based energy network to services-based management system. Renew Sust Energ Rev 150:111409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111409
Wu Y, Wu YP, Guerrero JM, Vasquez JC (2021c) Digitalization and decentralization driving transactive energy Internet: key technologies and infrastructures. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 126:106593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2020.106593
Xu B, Sendra-García J, Gao Y, Chen XH (2020) Driving total factor productivity: capital and labor with tax allocation. Technol Forecast Soc 150:119782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.119782
Xu C, Zhao WQ, Li XF, Cheng BD, Zhang MZ (2023). Quality of life and carbon emissions reduction: does digital economy play an influential role?. Clim Policy. 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/14693062.2023.2197862
Xu Q, Zhong MR (2022) Shared prosperity, energy-saving, and emission-reduction: can ICT capital achieve a “win-win-win” situation? J Environ Manage 319:115710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115710
Xu Q, Zhong MR, Cao MY (2022a) Does digital investment affect carbon efficiency? Spatial effect and mechanism discussion. Sci Total Envir 827:154321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154321
Xu Q, Zhong MR, Li X (2022b) How does digitalization affect energy? Int Evid Energy Econ 107:105879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.105879
Xue Y, Tang C, Wu H, Liu JM, Hao Y (2022) The emerging driving force of energy consumption in China: does digital economy development matter? Energy Pol 165:112997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112997
Yan ZM, Sun Z, Shi R, Zhao MJ (2023) Smart city and green development: empirical evidence from the perspective of green technological innovation. Technol Forecast Soc 191:122507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122507
Yang B, Liu BZ, Peng JC, Liu XJ (2022) The impact of the embedded global value chain position on energy-biased technology progress: evidence from China’s manufacturing. Technol Soc 71:102065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.102065
Yasmeen R, Cui ZH, Shah WUH, Kamal MA, Khan A (2022) Exploring the role of biomass energy consumption, ecological footprint through FDI and technological innovation in B&R economies: a simultaneous equation approach. Energ 244:122703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.122703
Yin ZH, Zeng WP (2023) The effects of industrial intelligence on China’s energy intensity: the role of technology absorptive capacity. Technol Forecast Soc 191:122506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122506
Yuan SJ, Musibau HO, Genç SY, Shaheen R, Ameen A, Tan ZX (2021) Digitalization of economy is the key factor behind fourth industrial revolution: how G7 countries are overcoming with the financing issues? Technol Forecast Soc 165:120533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120533
Zhang Z, Chen H (2022) Dynamic interaction of renewable energy technological innovation, environmental regulation intensity and carbon pressure: evidence from China. Renew Energ 192:420–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.04.136
Zhao MX, Lv LH, Wu J, Wang S, Zhang N, Bai ZH, Luo H (2022) Total factor productivity of high coal-consuming industries and provincial coal consumption: based on the dynamic spatial Durbin model. Energ 251:123917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.123917
Zhao YM, Wang D (2023) Spatial connection network characteristics and development trend forecast of natural gas industry’s sustainable development resilience in China. Sci Progress 106(1):00368504221148352. https://doi.org/10.1177/00368504221148352
Zheng Y, Tang J, Huang FB (2023) The impact of industrial structure adjustment on the spatial industrial linkage of carbon emission: from the perspective of climate change mitigation[J]. J Environ Manage 345:118620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118620
Zhou CL, Lin XQ, Wang RH, Song BY (2023) Real-time carbon emissions monitoring of high-energy-consumption enterprises in Guangxi based on electricity big data. Energ 16(13):5124. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135124
Zhou L, Tang LZ (2021) Environmental regulation and the growth of the total-factor carbon productivity of China’s industries: evidence from the implementation of action plan of air pollution prevention and control. J Environ Manage 296:113078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113078
Zhou Q, Zhang XL, Shao QL, Wang XL (2019) The non-linear effect of environmental regulation on haze pollution: empirical evidence for 277 Chinese cities during 2002–2010. J Environ Manage 248:109274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109274
Acknowledgements
We also have an appreciation to the Editor and anonymous referees for the very useful comments and suggestions.
Funding
This study received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (72373165), the Late Subsidized Projects of the National Social Science Foundation of China “theoretical and empirical research on digital economy driving economic high-quality development and green and low-carbon transformation”, the High-end Think Tank Project of Central South University (2021znzk01), the Major Project of the National Social Science Foundation of China (21&ZD103), and the Graduate Innovation Program of Hunan Province (CX20230236).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Meirui Zhong, Jialu Xia, and Qiong Xu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jialu Xia, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All the co-authors agreed to participate in the research.
Consent for publication
All the co-authors agreed to publish the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, M., Xia, J. & Xu, Q. How ICT capital affects the spatial correlation of energy consumption—a new perspective based on spatially correlation network. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 121770–121793 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30867-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30867-0