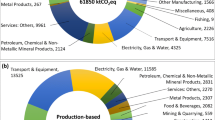
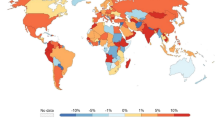
Abstract
Several emerging economies, including economies in belt and road initiative (BRI), are experiencing difficulty attaining sustainable development goals. The efficient utilization of biomass energy sources plays an essential role in attaining sustainable development goals, especially among developing economies. This study empirically investigates the ecological footprints, biomass energy demand, and per capita income association for 30 BRI economies from 1995 to 2021. The study incorporates cointegration and panel quantile regression (PQR) to identify the relationship among discussed variables. Empirical outcomes indicate a negative significant biomass energy demand and ecological footprints relationship, especially among the economies with high traits of ecological footprints. Moreover, the empirical findings also confirm the negative significant per capita income and ecological footprints relationship, while the square of per capita income approves a significant positive association with ecological footprints. These estimates confirm the EKC hypothesis among per capita income and ecological footprints. The findings of the current study help to determine the optimum level of modern biomass energy consumption, which helps to attain economic growth without compromising ecological sustainability.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sources of variables are mentioned in the “Literature review” section.
References
Abdo A, Li B, Qahtan A, Abdulsalam A, Aloqab A, Obadi W (2022) The influence of FDI on GHG emissions in BRI countries using spatial econometric analysis strategy: the significance of biomass energy consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:54571–54595
Ahmed A, Gazi S, Sohag K (2016) Biomass energy, technological progress and the environmental Kuznets curve: evidence from selected European countries. Biomass Bioenergy 90:202–208
Ahmed Z, Asghar M, Malik M, Nawaz K (2020) Moving towards a sustainable environment: the dynamic linkage between natural resources, human capital, urbanization, economic growth, and ecological footprint in China. Res Policy 67:101677
Akella A, Saini R, Sharma M (2009) Social, economical and environmental impacts of renewable energy systems. Renew Energy 34(2):390–396
Arshed N, Nasir S, Saeed MI (2022) Impact of the external debt on standard of living: a case of Asian countries. Soc Indic Res 163(1):321–340
Asici A, Acar S (2015) Does income growth relocate ecological footprint? Ecol Indic 61:707–717
Aydin M (2019) The effect of economic growth on obesity for the most obese countries: new evidence from the obesity Kuznets curve. Eur J Health Econ 20:1349–1358
Bai Y, He H, Ning Q (2019) Progress, problems and prospects of the “Delt and Road” research in the past five years. J Northwest Univ 49:149–162
Balezentis T, Streimikiene D, Zhang T, Liobikiene G (2019) The role of bioenergy in greenhouse gas emission reduction in EU countries: an Environmental Kuznets Curve modelling. Resour Conserv Recycl 142:225–231
Bekun F, Alola A, Sarkodie S (2019) Toward a sustainable environment: nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Sci Total Environ 657:1023–1029
Bilgili F, Koçak E, Bulut U, Kuşkaya S (2017) Can biomass energy be an efficient policy tool for sustainable development? Renew Sust Energ Rev 71:830–845
Capellan-Perez I, De-Castro C, Arto I (2017) Assessing vulnerabilities and limits in the transition to renewable energies: land requirements under 100% solar energy scenarios. Renew Sust Energ Rev 77:760–782
Cho J, Sohn S (2018) A novel decomposition analysis of green patent applications for the evaluation of R&D efforts to reduce CO2 emissions from fossil fuel energy consumption. J Clean Prod 193:290–299
Čuček L, Klemeš J, Kravanja Z (2012) A Review of Footprint analysis tools for monitoring impacts on sustainability. J Clean Prod 34:9–20
Danish, Ulucak R (2020) Linking biomass energy and CO2 in china using dynamic autoregressive-distributed lag simulations. J Clean Prod:1–9
Danish, Wang Z (2019) Does biomass energy consumption help to control environmental pollution? Evidence from BRICS countries. Sci Total Environ 670(20):1075–1083
Demirbas M, Balat M, Balat H (2009) Potential contribution of biomass to the sustainable energy development. Energy Convers Manag 50(7):1746–1760
Destek M, Sarkodie S (2019) Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of energy and financial development. Sci Total Environ 650:2483–2489
Destek M, Sinha A (2020) Renewable, non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and ecological footprint: evidence from organization for economic Co-operation and development countries. J Clean Prod 242(1):118537
Deutsch L, Jansson A, Troell M, R€onnb€ack P, Folke C, Kautsky N (2000) The ‘ecological footprint’: communicating human dependence on nature’s work. Ecol Econ 32:351–355
Dogan E, Inglesi L (2020) The impact of economic structure to the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis: evidence from European countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–8
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) The influence of real output, renewable and non-renewable energy, trade and financial development on carbon emissions in the top renewable energy countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 60:1074–1085
Ekwueme D, Zoaka J, Alola A (2021) Carbon emission effect of renewable energy utilization, fiscal development, and foreign direct investment in South Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:41821–41833
Fisher R (1932) Inverse probability and the use of likelihood. Math Proc Camb Philos Soc 28:257–261
Frees E (1995) Assessing cross-sectional correlation in panel data. J Econ 69:393–414
Frees E (2004) Longitudinal and panel data: analysis and applications in the social sciences. Cambridge University Press
Friedman M (1937) The use of ranks to avoid the assumption of normality implicit in the analysis of variance. J Am Stat Assoc 32:675–701
Friedman N, Linial M, Peer D (2000) Using Bayesian networks to analyze expression data. J Comput Biol. https://doi.org/10.1089/106652700750050961
Galli A (2015) On the rationale and policy usefulness of ecological footprint accounting:the case of Morocco. Environ Sci Pol 48:210–224
Gao J, Zhang L (2021) Does biomass energy consumption mitigate CO2 emissions? The role of economic growth and urbanization: evidence from developing Asia. J Asia Pac Econ 26(1):96–115
GML (2019) Global monitoring laboratory database, greenhouse gases category. accessed from https://gml.noaa.gov/dv/data/
Grossman G, Krueger A (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement. National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, MA. https://doi.org/10.3386/w3914
Grossman G, Krueger A (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110:353–377
Guney T, Kantar K (2020) Biomass energy consumption and sustainable development. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 21:1–6
Hafeez M, Yuan C, Khelfaoui I, Musaad A, Akbar M, Jie L (2019) Evaluating the energy consumption inequalities in the one belt and one road region: implications for the environment. Energies 12(7):1–15
Hassan S, Xia E, Khan N, Shah S (2019) Economic growth, natural resources, and ecological footprints: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:2929–2938
Hettige H, Mani M, Wheeler D (2000) Industrial pollution in economic development: the curve revisited. J Dev Econ 62:445–476
Huber J (2000) Towards industrial ecology: sustainable development as a concept of ecological modernization. J Environ Policy Plan 2:269–285
Hunag Y (2016) Understanding China’s belt & road initiative: motivation, framework and assessment. China Econ Rev 40:314–321
IEA (2018) International Energy Agency. Accessed from https://www.iea.org/:WorldEnergyOutlook
Im K, Pesaran M, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econ 115:53–74
Jean B, Gagnon B and Klain A (2021) Biomass supply and the sustainable development goals, International case studies. IEA Bioenergy, Technology Collaboration Programme
Khan A, Hussain J, Bano S, Chenggang Y (2019) The repercussions of foreign direct investment, renewable energy and health expenditure on environmental decay? J Environ Plan Manag 63(11):1–22
Kihombo S, Ahmed Z, Chen S, Adebayo T, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Linking financial development, economic growth, and ecological footprint: what is the role of technological innovation? Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11
Kihombo S, Vaseer A, Ahmed Z, Chen S, Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo T (2021b) Is there a tradeoff between financial globalization, economic growth, and environmental sustainability? An advanced panel analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11
Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo T, Khan Z, Ali S (2021) Does globalization matter for ecological footprint in Turkey? Evidence from dual adjustment approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(11):14009–14017
Kissinger M, Haim A (2008) Urban hinterlands: the case of an Israeli town ecological footprint. Environ Dev Sustain 10(4):391–405
Kongbuamai N, Bui Q, Yousaf H, Liu Y (2020) The impact of tourism and natural resources on the ecological footprint: a case study of ASEAN countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(16):19251–19264
Lam J, Cullinane K, Lee P (2018) The 21st-century maritime silk road:challenges and opportunities for transport management and practice. Transp Rev 38(4):413–415
Le Blanc D (2015) Towards integration at last? The sustainable development goals as a network of targets. Sustain Dev 23(3):176–187
Li J, Chen Y, Xu C, Li Z (2019) Evaluation and analysis of ecological security in arid areas of Central Asia based on the emergy ecological footprint (EEF) model. J Clean Prod 235:667–677
Liu J, Hull V, Godfray H, Tilman D, Gleick P, Hoff H et al (2018) Nexus approaches to global sustainable development. Nat Sustain 1:466–476
Lozano F, Lozano R, Freire P, Jimenez C, Sakao T, Ortiz M (2018) New perspectives for green and sustainable chemistry and engineering: approaches from sustainable resource and energy use, management, and transformation. J Clean Prod 172:227–232
Lu W (2020) The interplay among ecological footprint, real income, energy consumption, and trade openness in 13 Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(36):45148–45160
Maddala G, Wu S (1999) A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 61:631–652
Mafakheri F, Nasiri F (2014) Modeling of biomass-to-energy supply chain operations: applications, challenges and research directions. Energy Policy 67:116–126
Maji L, Sulaiman C (2019) Renewable energy consumption and economic growth. Renewable energy consumption and economic growth. Energy Rep 5:384–392
Meadows D, Meadows D, Randers J, Behrens W (1972) The limits to growth: a report for the Club of Rome’s project on the predicament of ma universe books, New York
Mensah C, Long X, Boamah K, Bediako I, Dauda L, Salman M (2018) The effect of innovation on CO2 emissions of OCED countries from 1990 to 2014. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:29678–29698
Owusu A, Sarkodie S (2016) A review of renewable energy sources, sustainability issues and climate change mitigation. Cogent Eng 3(1):1167990
Ozcan B, Apergis N, Shahbaz M (2018) A revisit of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Turkey: new evidence from bootstrap rolling window causality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:32381–32394
Ozturk I, Bilgili F (2015) Economic growth and biomass consumption nexus: dynamic panel analysis for Sub-Sahara African countries. Appl Energy 137:110–116
Pan H, Zhuang M, Geng Y, Wu F, Dong H (2019) Emergy-based ecological footprint analysis for a mega-city: the dynamic changes of Shanghai. J Clean Prod 210:552–562
Pata U (2018) Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J Clean Prod 187:770–779
Pesaran H (2004a) General diagnostic tests for cross-sectional dependence in panels. Cambridge Working Papers in Economics. Accessed from https://econpapers.repec.org/paper/camcamdae/0435.htm
Pesaran M (2004b) General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. University of Cambridge Cambridge Working Papers in Economics No. 0435
Pesaran M (2006) Estimation and inference in large heterogeneous panels with a multifactor error structure. Econometrica 74(4):967–1012
Pesaran M (2015) Time series and panel data econometrics. Oxford University Press
Powell D (2022) Quantile regression with nonadditive fixed effects. Empir Econ:1–17
Rashid A, Irum A, Malik I, Ashraf A, Rongqiong L, Liu G (2018) Ecological footprint of Rawalpindi; Pakistan’s first footprint analysis from urbanization perspective. J Clean Prod 170:362–368
Ripple W, Wolf C, Newsome T, Galetti M, Alamgir M, Crist E et al (2017) World scientists’ warning to humanity: a second notice. Bioscience 67(12):1026–1028
Sarkodie S (2020) Causal effect of environmental factors, economic indicators and domestic material consumption using frequency domain causality test. Sci Total Environ 736:139602
Schnaiberg A, Gould K (2000) Environment and society: the enduring conflict. St.Martin’s Press, New York, NY, USA
Selden T, Song D (1994) Environmental quality and development is there a Kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? J Environ Econ Manag 27:147–162
Shafik N, Bandyopadhyay S (1992) Economic growth and environmental quality: time series and cross-country evidence. The World Bank: Background paper for the world development report, Washington, DC
Shah S, Naqvi S, Riaz S, Anwar S, Abbas N (2020) Nexus of biomass energy, key determinants of economic development and environment: a fresh evidence from Asia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 133:11024
Shahbaz M, Nasir M, Roubaud D (2018) Environmental degradation in France: the effects of FDI, financial development, and energy innovations. Energy Econ 74:843–857
Sharif A, Afshan S, Qureshi M (2019) Idolization and ramification between globalization and ecological footprints: evidence from quantile-on-quantile approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:11191–11211
Shittu W, Adedoyin FF, Shah MI, Musibau HO (2021) An investigation of the nexus between natural resources, environmental performance, energy security and environmental degradation: evidence from Asia. Res Policy 73:102227
Sikka M, Thornton T, Worl R (2013) Sustainable biomass energy and indigenous cultural models of well-being in an Alaska forest ecosystem. Ecol Soc 18(3)
Sinha A (2017) Inequality of renewable energy generation across OECD countries: a note. Renew Sust Energ Rev 79:9–14
Sinha A, Sengupta T, Alvarado R (2020) Interplay between technological innovation and environmental quality: formulating the SDG policies for next 11 economies. J Clean Prod:118549
Smith K, Frumkin H, Balakrishnan K, Butler C, Chafe Z, Fairlie I et al (2013) Energy and human health. Annu Rev Public Health 34:159–188
Sohail H, Arshed N (2022) Contribution of Islamic debt financing in entrepreneurship promoting financial sector transformation. Int J Manag Res Emerg Sci 12(2)
Solarin S, Al-Mulali U, Gan G, Shahbaz M (2018) The impact of biomass energy consumption on pollution: evidence from 80 developed and developing countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(23):22641–22657
Su L, Hong N, Zhou X, He J, Ma Y, Jiang H et al (2020) Evaluation of the secondary transmission pattern and epidemic prediction of COVID-19 in the four metropolitan areas of China. Front Med. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00171
Sulaiman C, Abdul-Rahim A, Ofozor C (2020) Does wood biomass energy use reduce CO2 emissions in European Union member countries? Evidence from 27 members. J Clean Prod 253:119996
Sun Y, Lu Y, Wang T, Ma H, He G (2008) Pattern of patent-based environmental technology innovation in China. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 75(7):1032–1042
Tugcu C, Ozturk I, Aslan A (2012) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and economic growth relationship revisited: Evidence from G7 countries. Energy Econ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2012.08.021
Ulucak R (2020) Linking biomass energy and CO2 emissions in China using dynamic autoregressive-distributed lag simulations. J Clean Prod 250:119533
Van Fan Y, Varbanov PS, Klemeš JJ, Nemet A (2018) Process efficiency optimization and integration for cleaner production. J Clean Prod 174:177–183
Wackernagel M, Monfreda C (2004) Ecological footprints and energy. In: Encyclopedia of Energy, pp 1–11
Wackernagel M, Onisto L, Bello P, Linares A, Falfan I, Garcıa J (1999) National natural capital accounting with the ecological footprint concept. Ecol Econ 29(3):375–390
Wackernagel M, Rees W (1996) Our ecological footprint: reducing human impact on the earth. New Society Publisher, London
Wackernagel M, Rees W (1997) Perceptual and structural barriers to investing in natural capital: economics from an ecological footprint perspective. Ecol Econ 20(1):3–24
Wang S, Zeng J, Liu X (2019) Examining the multiple impacts of technological progress on CO2 emissions in China: a panel quantile regression approach. Renew Sust Energ Rev 103:140–150
Wang Z, Bui Q, Zhang B (2020) The relationship between biomass energy consumption and human development: empirical evidence from BRICS countries. Energy:116906
WDI. (2021). DataBank World development indicators. accessed from https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-developmentindic.
Westerlund J, Edgerton D (2008) A simple test for cointegration in dependent panels with structural breaks. Oxf Bull Econ Stat. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0084.2008.00513.x
Wiedmann T, Barret J (2010) A review of the ecological footprint indicator perceptions and method. Sustainability 2(6):1645–1693
Wiedmann T, Schandl H, Lenzen M, Moran D, Suh S, West J et al (2015) The material footprint of nations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:6271–6276
Yang B, Jahanger A, Ali M (2021) Remittance inflows affect the ecological footprint in BICS countries: do technological innovation and financial development matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(18):23482–23500
Yasmeen R, Zhaohui C, Shah W, Kamal M, Khan A (2022) Exploring the role of biomass energy consumption, ecological footprint through FDI and technological innovation in B&R economies: a simultaneous equation approach. Energy 244:122703
Zafar M, Zaidi S, Khan N, Mirza F, Hou F, Kirmani S (2019) The impact of natural resources, human capital, and foreign direct investment on the ecological footprint: the case of the United States. Res Policy 63:101428
Zia S, Rahman MU, Noor MH, Khan MK, Bibi M, Godil DI et al (2021) Striving towards environmental sustainability: how natural resources, human capital, financial development, and economic growth interact with ecological footprint in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(37):52499–52513
Zoaka J, Ekwueme D, Güngör H (2022) Will financial development and clean energy utilization rejuvenate the environment in BRICS economies? Bus Strateg Environ 31(5):2156–2170
Zoaka J, Güngör H (2023) Effects of financial development and capital accumulation on labor productivity in sub-Saharan Africa: new insight from cross sectional autoregressive lag approach. Financial Innov. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40854-022-00397-8
Zuo S, Zhu M, Xu Z, Oláh J, Lakner Z (2022) The dynamic impact of natural resource rents, financial development, and technological innovations on environmental quality: empirical evidence from BRI economies. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(1):130
Acknowledgements
Thank all the supervisors and respective affiliations for their kind support.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, literature review, and original draft preparation, [Muhammad Awais Anwar], methodology and data duration, [Noman Arshed], writing, review, and editing [Aviral Kumar Tiwari]. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication and ethical approval
All the authors agree to publish this study. There is no need for ethical approval because this study does not use patient and animal data. Further, this material is the author's original work, which has yet to be previously published elsewhere. The paper is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The paper reflects the author’s own research and analysis truthfully and completely.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Conflicts of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anwar, M.A., Arshed, N. & Tiwari, A.K. Nexus between biomass energy, economic growth, and ecological footprints: empirical investigation from belt and road initiative economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 115527–115542 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30481-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30481-0
Keywords
- One Belt One Road (OBOR)
- Biomass energy consumption
- Ecological footprints
- Per capita income Technological innovation
- Panel quantile regression