Abstract
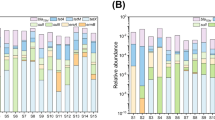
Engine oil spills have been associated with a wide range of human health problems. However, little is known about the effects of petroleum hydrocarbon pollution on soil microbial communities. In this study, three samples were collected from oil-polluted soils (OPS), and one control soil (CS) from Taolin town, China, near the old engine’s scrapes was used. The aims of this study were to conduct metagenomic sequencing and subsequently perform resistome and virulome analysis. We also aimed to validate anti-microbial resistance and virulence genes and anti-bacterial sensitivity profiles among the isolates from oil-polluted soils. The OPS microbial community was dominated by bacterial species compared to the control samples which were dominated by metazoans and other organisms. Secondly, the resistosome and virulome analysis showed that ARGs and virulence factors were higher among OPS microbial communities. Antibiotic susceptibility assay and qPCR analysis for ARGs and virulence factors showed that the oil-polluted soil samples had remarkably enhanced expression of these ARGs and some virulence genes. Our study suggests that oil pollution contributes to shifting microbial communities to more resilient types that could survive the toxicity of oil pollution and subsequently become more resilient in terms of higher resistance and virulence potential.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Alcock BP, Huynh W, Chalil R, Smith KW, Raphenya AR, Wlodarski MA, Edalatmand A, Petkau A, Syed SA, Tsang KK (2023) CARD 2023: expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res 51:D690–D699
Ataikiru T, Okorhi-Damisa F, Onyegbunwa A (2020) Hydrocarbon biodegradation and antibiotic sensitivity of microorganisms isolated from an oil polluted site in Kokori, Delta State, Nigeria. Issues in Biological Sciences and Pharmaceutical Research 8(2):43–50
Bao Y-J, Xu Z, Li Y, Yao Z, Sun J, Song H (2017) High-throughput metagenomic analysis of petroleum-contaminated soil microbiome reveals the versatility in xenobiotic aromatics metabolism. J Environ Sci 56:25–35
Bik HM, Halanych KM, Sharma J, Thomas WK (2012) Dramatic shifts in benthic microbial eukaryote communities following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. PLoS One 7:e38550
Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH (2015) Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12:59–60
Chen B, He R, Yuan K, Chen E, Lin L, Chen X, Sha S, Zhong J, Lin L, Yang L (2017) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) enriching antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the soils. Environ Pollut 220:1005–1013
Chen L, Yang J, Yu J, Yao Z, Sun L, Shen Y, Jin Q (2005) VFDB: a reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D325–D328
Chunyan X, Qaria MA, Qi X, Daochen Z (2023) The role of microorganisms in petroleum degradation: current development and prospects. Sci Total Environ 865:61112
Cirstea MD, Neagu S, Stefănescu M (2021) Antibioresistance and virulence factors spectrum in several bacterial strains isolated from polluted environments. available at Research Square
Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z, Wu S, Li W (2012) CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 28:3150–3152
Gao H, Wu M, Liu H, Xu Y, Liu Z (2022) Effect of petroleum hydrocarbon pollution levels on the soil microecosystem and ecological function. Environ Pollut 293:118511
Gorovtsov AV, Sazykin IS, Sazykina MA (2018) The influence of heavy metals, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and polychlorinated biphenyls pollution on the development of antibiotic resistance in soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:9283–9292
Gothwal R, Shashidhar T (2015) Antibiotic pollution in the environment: a review. Clean–Soil, Air, Water 43:479–489
Hewelke E, Gozdowski D (2020) Hydrophysical properties of sandy clay contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9697–9706
Hussain A, Mazumder R, Asadulghani M, Clark TG, Mondal D (2023): Chapter 8 - combination of virulence and antibiotic resistance: a successful bacterial strategy to survive under hostile environments. In: Kumar A, Tenguria S, Bacterial survival in the hostile environment. Academic Press, pp. 101-117
Hyatt D, Chen GL, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ (2010) Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics 11:119
Kashif S-u-R, Zaheer A, Arooj F, Farooq Z (2018) Comparison of heavy metals in fresh and used engine oil. Pet Sci Technol 36:1478–1481
Knapp CW, Callan AC, Aitken B, Shearn R, Koenders A, Hinwood A (2017) Relationship between antibiotic resistance genes and metals in residential soil samples from Western Australia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2484–2494
Lin X, Ma J, Zhou Z, Qiao B, Li Y, Zheng W, Tian Y (2023) Oil-contaminated sites act as high-risk pathogen reservoirs previously overlooked in coastal zones. Water Res 242:120225
Máthé I, Benedek T, Táncsics A, Palatinszky M, Lányi S, Márialigeti K (2012) Diversity, activity, antibiotic and heavy metal resistance of bacteria from petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soils located in Harghita County (Romania). Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 73:41–49
Maurya AP, Rajkumari J, Pandey P (2021) Enrichment of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in polyaromatic hydrocarbon–contaminated soils: a major challenge for environmental health. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:12178–12189
Noman SM, Shafiq M, Bibi S, Mittal B, Yuan Y, Zeng M, Li X, Olawale OA, Jiao X, Irshad M (2023) Exploring antibiotic resistance genes, mobile gene elements, and virulence gene factors in an urban freshwater samples using metagenomic analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:2977–2990
Obini U, Okafor C, Afiukwa J (2013) Determination of levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil contaminated with spent motor engine oil in Abakaliki Auto-Mechanic Village. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 17:169–175
Qaria MA, Kumar N, Hussain A, Qumar S, Doddam SN, Sepe LP, Ahmed N (2018) Roles of cholesteryl-α-glucoside transferase and cholesteryl glucosides in maintenance of Helicobacter pylori morphology, cell wall integrity, and resistance to antibiotics. mBio 9(6):10–1128. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01523-18
Quillaguaman J, Guzman D, Campero M, Hoepfner C, Relos L, Mendieta D, Higdon SM, Eid D, Fernandez CE (2021) The microbiome of a polluted urban lake harbors pathogens with diverse antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes. Environ Pollut 273:116488
Ranjan A, Shaik S, Mondal A, Nandanwar N, Hussain A, Semmler T, Kumar N, Tiwari SK, Jadhav S, Wieler LH (2016) Molecular epidemiology and genome dynamics of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-producing extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli strains from India. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:6795–6805
Salam LB, Obayori OS, Ilori MO, Amund OO (2021) Impact of spent engine oil contamination on the antibiotic resistome of a tropical agricultural soil. Ecotoxicology 30:1251–1271
Sazykin I, Minkina T, Khmelevtsova L, Antonenko E, Azhogina T, Dudnikova T, Sushkova S, Klimova M, Karchava SK, Seliverstova EY (2021) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, antibiotic resistance genes, toxicity in the exposed to anthropogenic pressure soils of the Southern Russia. Environ Res 194:110715
Shi H, Hu X, Li W, Zhang J, Hu B, Lou L (2023) Soil component: a potential factor affecting the occurrence and spread of antibiotic resistance genes. Antibiotics 12:333
Su Q, Yu J, Fang K, Dong P, Li Z, Zhang W, Liu M, Xiang L, Cai J (2023) Microbial removal of petroleum hydrocarbons from contaminated soil under arsenic stress. Toxics 11:143
Suhadolnik MLS, Costa PS, Paiva MC, de Matos Salim AC, Barbosa FAR, Lobo FP, Nascimento AMA (2022) Spatiotemporal dynamics of the resistome and virulome of riverine microbiomes disturbed by a mining mud tsunami. Sci Total Environ 806:150936
Szyszlak-Bargłowicz J, Zając G, Wolak A (2021) Heavy metal content in used engine oils depending on engine type and oil change interval. Arch Environ Protection 47(2):1–94
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Zhang Z, Wang Y, Chen B, Lei C, Yu Y, Xu N, Zhang Q, Wang T, Gao W, Lu T (2022) Xenobiotic pollution affects transcription of antibiotic resistance and virulence factors in aquatic microcosms. Environ Pollut 306:119396
Zhu D, Qaria MA, Zhu B, Sun J, Yang B (2022) Extremophiles and extremozymes in lignin bioprocessing. Renew Sust Energ Rev 157:112069
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BE2021691), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (carbon neutralization, BK20220003) and the Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Technology and Material of Water Treatment, Suzhou University of Science and Technology, Suzhou 215009, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Majjid A. Qaria conceptualized the idea, performed the experiments, wrote, and prepared the figures and tables. Chunyan Xu cured the data, performed the experiment, and analyzed the data. Arif Hussain improved the manuscript contents, wrote, edited, discussed, and reviewed the manuscript. Muhammad Zohaib Nawaz edited, discussed, and reviewed the manuscript. Daochen Zhu supervised, edited, and improved the idea of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors agreed with the content and that all gave explicit consent to submit and that they obtained consent from the responsible authorities at the institute/organization where the work has been carried out, before the work is submitted. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qaria, M.A., Xu, C., Hussain, A. et al. Metagenomic investigations on antibiotic resistance and microbial virulence in oil-polluted soils from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 110590–110599 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30137-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30137-z