Abstract
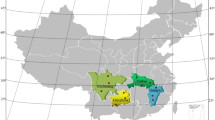
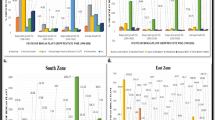
To address the adjustment of the Chinese agricultural industry and to better promote the development of Chinese household biogas, this article summarizes and analyzes the spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of the type and number of biogas digesters, biogas production, biogas fermentation materials, and methods of fermentation residue utilization and ecological agriculture with household biogas by compiling a dataset covering 31 provincial administrative regions in China. The results show that hydraulic biogas digesters are distributed mainly in northwestern and northeastern China; in addition, continuously stirred biogas digesters and bottom-discharging biogas digesters are distributed mainly in southern and northern China, respectively. Because of temperature and population, the Sichuan and Henan Provinces have the highest number of biogas digesters and biogas production. The type of biogas fermentation materials depends on the local raw materials. Biogas slurry and residue are widely used as fertilizers; furthermore, biogas slurry is used for seed soaking in northeastern and southern China, and biogas residue is used as feed in central southern and northern China. The “Three-in-one” and “Four-in-one” biogas ecological models are used mostly in southern and northern China, respectively, and both are mainly affected by temperature. Finally, we propose various problems and countermeasures to enhance the development of the household biogas industry in China. Our findings are critical for China’s policymakers to adopt effective measures for promoting the development of cleaner energy and the layout of the agricultural industry.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Abd Allah WE, Tawfik MA, Sagade AA, Gorjian S, Metwally KA, El-Shal HN (2021) Methane production enhancement of a family-scale biogas digester using cattle manure and corn stover under cold climates. Sustain Energy Techn 45:101163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101163
Ali S, Yan Q, Irfan M, Fahad S (2023) Relating biogas technology and environmental impact assessment: a roadmap towards clean energy for environmental sustainability. Environ Sci Pollut R 30:72832–72853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27553-6
Barua VB, Goud VV, Kalamdhad AS (2018) Microbial pretreatment of water hyacinth for enhanced hydrolysis followed by biogas production. Renew Energy 126:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.03.028
Chang IS, Zhao J, Yin XF, Wu J, Jia ZB, Wang LX (2011) Comprehensive utilizations of biogas in Inner Mongolia. China Renew Sust Energ Rev 15:1442–1453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2010.11.013
Chen L, Zhao LX, Ren CS, Wang F (2012b) The progress and prospects of rural biogas production in China. Energy Pol 51:8–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.05.052
Chen Q, Liu TB (2017) Biogas system in rural China: upgrading from decentralized to centralized? Renew Sustain Energy Rev 78:933–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.113
Chen QH, Zhang K (2020) Evolution of resource utilization of livestock and poultry waste in 70 years of new China. China Popul Resour Environ 30(06):166–176 (in Chinese) https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=ZGRZ202006017&DbName=CJFQ2020
Chen R (1997) Livestock-biogas-fruit systems in South China. Ecol Eng 8:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8574(96)00250-9
Chen SQ, Chen B, Song D (2012a) Life-cycle energy production and emissions mitigation by comprehensive biogas–digestate utilization. Bioresource Technol 114:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.084
Chen Y, Hu W, Feng YZ, Sandra S (2014) Status and prospects of rural biogas development in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 39:679–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.119
Chen Y, Yang G, Sweeney S, Feng Y (2010) Household biogas use in rural China: a study of opportunities and constraints. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14(1):545–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.019
Chen Y, Yang GH, Feng YZ, Ren GX (2009) Regional suitability evaluation index system of ‘three-in-one’ biogas ecological model. T Chin Soc Agr Eng 25(03):174–178 (in Chinese) https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=NYGU200903038&DbName=CJFQ2009
Chung C, Liu L, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wei Z (2022) Evolution of biogas policies in China (2001-2019): dynamics of policy instruments towards energy transitions. J Clean Prod 379:134642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134642
Curry N, Pillay P (2015) Integrating solar energy into an urban small-scale anaerobic digester for improved performance. Renew Energy 83:280–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.03.073
Deng LW, Liu Y, Zheng D, Wang L, Pu XD, Song L, Wang ZY, Lei YH, Chen ZA, Long Y (2017) Application and development of biogas technology for the treatment of waste in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:845–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.265
DPES (2018) China population and employment statistical yearbook Department of Population and Employment Statistics. National Bureau of Statistics China Agriculture Press, Beijing China (in Chinese) https://navi.cnki.net/KNavi/YearbookDetail?pcode=CYFD&pykm=YZGRL&bh= (Accessed 21 September 2019)
Feng YZ, Guo Y, Yang GH, Qin XW, Song ZL (2012) Household biogas development in rural China: on policy support and other macro sustainable conditions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:5617–5624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.06.019
Han I (2021) Socio-economic characteristics influencing farmers’ willingness-to-adopt domestic biogas technology in rural Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut R 28:20690–20699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12042-x
Haque S, Singh R, Pal DB, Harakeh S, Alghanmi M, Teklemariam AD, Abujamel TS, Srivastava N, Gupta VK (2022) Recent update on anaerobic digestion of paddy straw for biogas production: advancement, limitation and recommendations. Environ Res 215:114292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114292
Hu W, Chen Y (2016) Regional suitability evaluation of the ‘five-in-one’ ecological orchard model in Northwest China. J Ningxia U (Natural Science Edition) 37(02):237–241 (in Chinese). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=NXDZ201602023&DbName=CJFQ2016
Huang HX, Zhang LX, Luo HJ (2007) Development status and countermeasures of rural biogas in Guangdong Province. Guangdong Agr Sci 10:101–102 (in Chinese). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=GDNY200710039&DbName=CJFQ2007
Jiang XY, Sommer SG, Christensen KV (2011) A review of the biogas industry in China. Energ Policy 39(10):6073–6081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.07.007
Jung SY, Lee JC, Moon DH, Kim KH, Kwon EE (2021) Upgrading biogas into syngas through dry reforming. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 143:110949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110949
Kończak M, Siatecka A, Nazarkovsky MA, Czech B, Oleszczuk P (2021) Sewage sludge and solid residues from biogas production derived biochar as an effective bio-waste adsorbent of fulvic acids from water or wastewater. Chemosphere 278:130447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130447
Li CJ, Liao YC, Wen XX, Wang YF, Yang F (2015) The development and countermeasures of household biogas in northwest grain for green project areas of China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 44:835–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.01.027
Li F, Cheng S, Yu H, Yang D (2016) Waste from livestock and poultry breeding and its potential assessment of biogas energy in rural China. J Clean Prod 126:451–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.104
Li JS, Duan N, Guo S, Shao L, Lin C, Wang JH, Hou J, Hou Y, Meng J, Han MY (2012a) Renewable resource for agricultural ecosystem in China: ecological benefit for biogas by-product for planting. Ecol Inform 12:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2012.05.004
Li Y, Liu Y, Hu Y, Li J, Ao Y, Liu Q (2012b) Study on the heat preservation effect of “four-in-one” rural energy ecological model in the north of China. Renew Energy Resour 30(1):55–57. https://doi.org/10.13941/j.cnki.21-1469/tk.2012.01.009
Liang FH, Xu L, Ji L, He QY, Wu LL, Yan SP (2021) A new approach for biogas slurry disposal by adopting CO2-rich biogas slurry as the flower fertilizer of Spathiphyllum: feasibility, cost and environmental pollution potential. Sci Total Environ 770:145333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145333
Luo T, Benyamin K, Huang RY, Chen Q, Mei ZL, Pan JT, Liu HB (2020) Analysis of revolution in decentralized biogas facilities caused by transition in Chinese rural areas. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 133:110133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110133
Maksud B, Md Alam HM, Ajith DA, Alisher M (2019) Why adoption is slow despite promising potential of biogas technology for improving energy security and mitigating climate change in Sri Lanka? Renew Sustain Energy Rev 105:378–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.02.010
MOA (2011) Implementing rural biogas construction policy. ministry of agriculture of China (in Chinese). http://www.moa.gov.cn/ztzl/lszczc/201103/t20110325_1955104.htm. (Accessed 14 October 2020)
MOA (2017) China agriculture statistical report. Ministry of Agriculture of China China Agricultural Press, Beijing China (in Chinese) https://navi.cnki.net/KNavi/YearbookDetail?pcode=CYFD&pykm=YZGNT&b=. (Accessed 9 August 2020)
Nafees M, Ali S, Naveed M, Rizwan M (2018) Efficiency of biogas slurry and Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN to improve growth, physiology, and antioxidant activity of Brassicanapus L. in chromium-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:6387–6397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0924-z
NBS (2008) China statistical yearbook. National Bureau of Statistics China Statistics Press, Beijing China (in Chinese) https://navi.cnki.net/KNavi/YearbookDetail?pcode=CYFD&pykm=YINFN&bh=. (Accessed 21 July 2020)
NBS (2018) China statistical yearbook. National Bureau of Statistics China Statistics Press, Beijing China (in Chinese). https://navi.cnki.net/KNavi/YearbookDetail?pcode=CYFD&pykm=YINFN&bh=. (Accessed 30 July 2020)
Niyungeko C, Liang X, Liu C, Liu Z, Sheteiwy M, Zhang H, Zhou J, Tian G (2018) Effect of biogas slurry application rate on colloidal phosphorus leaching in paddy soil: a column study. Geoderma 325:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.147
Qi XS, Zhang SP, Wang YZ, Wang RQ (2005) Advantages of the integrated pig-biogas-vegetable greenhouse system in North China. Ecol Eng 24:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2004.11.001
Rajendran K, Aslanzadeh S, Taherzadeh MJ (2012) Household biogas digesters-a review. Energies 5(8):2911–2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5082911
Rao JT, Kong DM, Wang TJ (2011) Practice and exploration of separating floating cover type biogas digester in Chebaling National Nature Reserve. J Agr Resour Environ 28(05):51–53 (in Chinese) https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=NHFZ201105012&DbName=CJFQ2011
Santosh Y, Sreekrishnan TR, Kohli S, Rana V (2004) Enhancement of biogas production from solid substrates using different techniques-a review. Bioresource Technol 95:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.02.010
Shi W, Fang Y, Chang Y, Xie G (2023) Toward sustainable utilization of crop straw: greenhouse gas emissions and their reduction potential from 1950 to 2021 in China. Resour Conserv Recy 190:106824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106824
Singh KJ, Sooch SS (2004) Comparative study of economics of different models of family size biogas plants for state of Punjab, India. Energy Convers Manag 45:1329–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2003.09.018
Singh SP, Vatsa DK, Verma HN (1997) Problems with biogas plants in Himachal Pradesh. Bioresour Technol 59:69–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00123-X
Song ZL, Zhang C, Yang GH, Feng YZ, Ren GX, Han XH (2014) Comparison of biogas development from households and medium and large-scale biogas plants in rural China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 33:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.01.084
Trang T, Nhu JD, Pieterjan S, Sophie H, Cong VN, Patrick S, Thomas S (2015) Resource usage of integrated Pig-Biogas-Fish system: partitioning and substitution within attributional life cycle assessment. Resour Conserv Recy 102:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.06.011
Wang C, Yang Y, Zhang Y (2012b) Rural household livelihood change, fuelwood substitution, and hilly ecosystem restoration: evidence from China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:2475–2482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.01.070
Wang C, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Pang M (2016a) Alternative policies to subsidize rural household biogas digesters. Energ Policy 93:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.03.007
Wang F, Cai YQ, Qiu HG (2012a) Analysis on the current situation, driving and restricting factors of biogas development in China. T Chin Soc Agr Eng 28(01):184–189 (in Chinese). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2012
Wang H, Tu M, Liu W (2019) Household biogas digesters or medium-large-scale biogas plants: a conflicting issue in rural China. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:32919–32927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06426-x
Wang H, Xu J, Sheng L, Liu X (2018) Effect of addition of biogas slurry for anaerobic fermentation of deer manure on biogas production. Energy 165:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.09.196
Wang XJ, Lu XG, Yang GH, Feng YZ, Ren GX, Han XH (2016b) Development process and probable future transformations of rural biogas in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:703–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.09.097
Wang YM, Sun ZF, Zhang C (2013) Investigation and analysis on utilization rate of rural household biogas in Hebei Province. China Biogas 31(04):61–64 (in Chinese) https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbna me=CJFD2013
Xu ZM, Wang Z, Gao Q, Wang LL, Chen LL, Li QG, Jiang JJ, Ye HJ, Wang DS, Yang P (2019) Influence of irrigation with microalgae-treated biogas slurry on agronomic trait, nutritional quality, oxidation resistance, and nitrate and heavy metal residues in Chinese cabbage. J Environ Manage 244:453–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.058
Xue SR, Song JH, Wang XJ, Shang ZZ, Sheng CJ, Li CY, Zhu YF, Liu JY (2020) A systematic comparison of biogas development and related policies between China and Europe and corresponding insights. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 117:109474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109474
Yan B, Li Y, Qin Y, Shi W, Yan J (2022) Spatial-temporal distribution of biogas production from agricultural waste per capita in rural China and its correlation with ground temperature. Sci Total Environ 817:152987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.152987
Yan B, Yan J, Li Y, Qin Y, Yang L (2021) Spatial distribution of biogas potential, utilization ratio and development potential of biogas from agricultural waste in China. J Clean Prod 292:126077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126077
Yan L, Liu Q, Liu C, Liu Y, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gu W (2019) Effect of swine biogas slurry application on soil dissolved organic matter (DOM) content and fluorescence characteristics. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184:109616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109616
Yang Y, Bao WQ, Xie GH (2019) Estimate of restaurant food waste and its biogas production potential in China. J Clean Prod 211:309–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.160
Yin DX, Liu W, Zhai NN, Wang YD, Ren CJ, Yang GH (2017) Regional differentiation of rural household biogas development and related driving factors in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 67:1008–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.023
Yu Q, Liu RH, Li K, Ma RJ (2019) A review of crop straw pretreatment methods for biogas production by anaerobic digestion in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 107:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.02.020
Zhang C, Wu L (2023) Farm biogas project considering carbon trading indicates promising economic results-a case study. Environ Sci Pollut R 30:65865–65878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27016-y
Zheng Y, Wei J, Li J (2012) Anaerobic fermentation technology increases biomass energy use efficiency in crop residue utilization and biogas production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:4588–4596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.03.061
Zhou KX (1986) Study on the biogas fermentation process in North China through technical appraisal. China Biogas 1:31 (in Chinese) https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=ZGZQ198601013&DbName=CJFQ1986
Zhu R (2020) Causes and countermeasures of rural household biogas project idle. Mod Agr. Sci Technol 17:152–153 (in Chinese). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=ANHE202017095&DbName=CJFQ2020
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Scientific Research Funds for Hainan University (grant numbers: KYQD(ZR)1850, KYQD(ZR)1848).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL and CL contributed to the study conception, design, methodology, and project administration. ZL and CL analyzed the data and wrote the original draft. ZL, CL, XJ, SL, JC, SY, GH, WC, XS, RJ, JY, DS, CL, and CL performed the investigation and data collection and commented on previous versions of the manuscript. CL and CL provided a review and modification. ZL, CL, XJ, SL, JC, SY, GH, WC, XS, RJ, JY, DS, CL, and CL read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
We confirmed that this study did not use human subjects, and the results of all surveys are objective facts and do not have subjective opinions. It otherwise followed common ethical standards like anonymity and data security. Thus, ethical approval and informed consent are not applicable for this study.
Consent to participate
The participants not in the authors agreed to participate in this study.
Consent for publication
The participants not in the authors have given their consent to publish this work.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, ., Lan, C., Jin, X. et al. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of China’s household biogas: evidence from provincial-level data. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 110119–110132 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30069-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30069-8