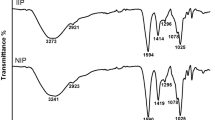
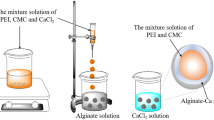
Abstract
A novel epichlorohydrin and thiourea grafted porous alginate adsorbent (UA-Ca/IIP) was synthesized using ion-imprinting and direct templating to remove copper ions (Cu(II)) and tetracycline (TC) in aqueous solution. UA-Ca/IIP demonstrated great selectivity for Cu(II) and TC among different coexisting anions (CO32−, PO43− and SO42−), cations (Ca2+, Mg2+ and NH4+), and antibiotics (oxytetracycline and sulfamethoxazole). The adsorption of TC and Cu(II) by UA-Ca/IIP was significantly affected by the pH of the solution, and the quantity of TC and Cu(II) adsorbed reached a maximum at pH 5. A pseudo-second-order model better fitted the kinetic data; the Langmuir model predicted the maximum adsorption quantities 3.527 mmol TC g−1 and 4.478 mmol Cu(II) g−1 at 298 K. Thermodynamic studies indicated that the TC and Cu(II) adsorption was more rapid at a higher temperature. Antagonistic and synergistic adsorption experiments showed that the adsorption capacity of TC would increase significantly with the increase of Cu(II) concentration. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated that along with the influence of pH, electrostatic interaction and complexation were the main mechanisms of TC and Cu(II) adsorption. Regeneration experiments revealed that TC and Cu(II) were removed efficiently and that UA-Ca/IIP was recyclable over the long term. These results show that the modified porous alginate microsphere is a green and recyclable adsorbent, which has good selectivity and high adsorption performance for the removal of TC and Cu(II).












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Benettayeb A, Guibal E, Morsli A, Kessas R (2017) Chemical modification of alginate for enhanced sorption of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II). Chem Eng J 316:704–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.131
Chen AH, Liu SC, Chen CY, Chen CY (2008) Comparative adsorption of Cu(II), Zn(II), and Pb(II) ions in aqueous solution on the crosslinked chitosan with epichlorohydrin. J Hazard Mater 154:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.009
Chen JH, Lin H, Luo ZH, He YS, Li GP (2011) Cu(II)-imprinted porous film adsorbent Cu–PVA–SA has high uptake capacity for removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution. Desalination 277:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.040
Dai J, Meng X, Zhang Y, Huang Y (2020) Effects of modification and magnetization of rice straw derived biochar on adsorption of tetracycline from water. Bioresour Technol 311:123455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123455
Dai C, Zhang M, Guo X, Ma X (2021) Mesoporous composite Ni-C-N/SA for selective adsorption of methylene blue from water. Chem Eng J 407:127181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127181
Dao X, Hao H, Bi J, Sun S, Huang X (2022) Surface complexation enhanced adsorption of tetracycline by ALK-MXene. Ind Eng Chem Res 61:6028–6036. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.2c00037
Deng J, Li X, Wei X, Liu Y, Liang J, Song B, Shao Y, Huang W (2020) Hybrid silicate-hydrochar composite for highly efficient removal of heavy metal and antibiotics: coadsorption and mechanism. Chem Eng J 387:124097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124097
Dong KQ, Xu KJ, Wei NS, Fang YY, Qin ZY (2022) Three-dimensional porous sodium alginate/gellan gum environmentally friendly aerogel: preparation, characterization, adsorption, and kinetics studies. Chem Eng Res Des 179:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2022.01.027
Dos Reis GS, Guy M, Mathieu M, Jebrane M, Lima EC, Thyrel M, Dotto GL, Larsson SH (2022) A comparative study of chemical treatment by MgCl2, ZnSO4, ZnCl2, and KOH on physicochemical properties and acetaminophen adsorption performance of biobased porous materials from tree bark residues. Colloids Surf A 642:128626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128626
Eltaweil AS, Mamdouh IM, Abd El-Monaem EM, El-Subruiti GM (2021) Highly efficient removal for methylene blue and Cu2+ onto UiO-66 metal-organic framework/carboxylated graphene oxide-incorporated sodium alginate beads. ACS Omega 6:23528–23541. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c03479
Eltaweil AS, Abd El-Monaem EM, Elshishini HM, El-Aqapa HG, Hosny M, Abdelfatah AM, Ahmed MS, Hammad EN, El-Subruiti GM, Fawzy M, Omer AM (2022) Recent developments in alginate-based adsorbents for removing phosphate ions from wastewater: a review. RSC Adv 12:8228–8248. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA09193J
Fan L, Lu Y, Yang LY, Huang F, Ouyang XK (2019) Fabrication of polyethylenimine-functionalized sodium alginate/cellulose nanocrystal/polyvinyl alcohol core-shell microspheres ((PVA/SA/CNC)@PEI) for diclofenac sodium adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 554:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.06.099
Feng X, Li X, Luo H, Su B, Ma J (2022) Facile synthesis of Ni-based layered double hydroxides with superior photocatalytic performance for tetracycline antibiotic degradation. J Solid State Chem 307:122827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2021.122827
Feng Y, Chen G, Zhang Y, Li DG, Ling C, Wang QY, Liu GG (2022) Superhigh co-adsorption of tetracycline and copper by the ultrathin g-C3N4 modified graphene oxide hydrogels. J Hazard Mater 424:127362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127362
Fotsing PN, Woumfo ED, Mezghich S, Mignot M, Mofaddel N, Le Derf F, Vieillard J (2020) Surface modification of biomaterials based on cocoa shell with improved nitrate and Cr(VI) removal. RSC Adv 10:20009–20019. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra03027a
Gaballah MS, Guo J, Sun H, Aboagye D, Sobhi M, Muhmood A, Dong R (2021) A review targeting veterinary antibiotics removal from livestock manure management systems and future outlook. Bioresour Technol 333:125069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125069
Gao X, Zhang Y, Zhao Y (2017) Biosorption and reduction of Au (III) to gold nanoparticles by thiourea modified alginate. Carbohydr Polym 159:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.11.095
Gao X, Liu J, Li M, Guo C, Long H, Zhang Y, Xin L (2020) Mechanistic study of selective adsorption and reduction of Au (III) to gold nanoparticles by ion-imprinted porous alginate microspheres. Chem Eng J 385:123389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123897
Gao M, Liang H, Bao S, Xu T, Zhang Y, Bai J, Li C (2022) Bifunctional BiOCl/TiO2 decorated membrane for antibiotic photodegradation and oil-water emulsion separation. Appl Surf Sci 578:151960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151960
Gomaa H, Shenashen MA, Elbaz A, Kawada S, El-Nasr TAS, Cheira MF, Eid AI, El-Safty SA (2021) Inorganic-organic mesoporous hybrid segregators for selective and sensitive extraction of precious elements from urban mining. J Colloid Interface Sci 604:61–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.07.002
Gomaa H, Shenashen MA, Elbaz A, Yamaguchi H, Abdelmottaleb M, El-Safty SA (2021) Mesoscopic engineering materials for visual detection and selective removal of copper ions from drinking and waste water sources. J Hazard Mater 406:124314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124314
Gong Y, Wang Y, Tang M, Zhang H, Wu P, Liu CJ, He J, Jiang W (2022) A two-step process coupling photocatalysis with adsorption to treat tetracycline-copper(II) hybrid wastewaters. J Water Process Eng 47:102710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102710
Guy M, Mathieu M, Anastopoulos IP, Martínez MG, Rousseau F, Dotto GL, de Oliveira HP, Lima EC, Thyrel M, Larsson SH, dos Reis GS (2022) Process parameters optimization, characterization, and application of KOH-activated Norway spruce bark graphitic biochars for efficient azo dye adsorption. Molecules 27:456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020456
Hajri AK, Jamoussi B, Albalawi AE, Alhawiti OHN, Alsharif AA (2022) Designing of modified ion-imprinted chitosan particles for selective removal of mercury(II) ions. Carbohydr Polym 286:119207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119207
Jiang B, Lin Y, Mbog JC (2018) Biochar derived from swine manure digestate and applied on the removals of heavy metals and antibiotics. Bioresour Technol 270:603–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.022
Laus R, Favere BT (2011) Competitive adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions by chitosan crosslinked with epichlorohydrin–triphosphate. Bioresource Technol 102:8769–8776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.057
Li YX, Li W, Wu J, Xu LC, Su QH, Xiong X (2007) Contribution of additives Cu to its accumulation in pig feces: study in Beijing and Fuxin of China. J Environ Sci 19:610–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(07)60101-6
Li J, Li Y, Cui K, Li H, Feng J, Pu X, Xiong W, Liu N, Yuan G (2022) Novel MOFs-based ion-imprinted polymer for selective separation of cobalt ions from waste battery leaching solution. Inorg Chim Acta 536:120922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2022.120922
Ma S, Jing J, Liu P, Li Z, Jin W, Xie B, Zhao Y (2020) High selectivity and effectiveness for removal of tetracycline and its related drug resistance in food wastewater through schwertmannite/graphene oxide catalyzed photo-Fenton-like oxidation. J Hazard Mater 392:122437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122437
Mao W, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wen N, Guan Y (2022) Adsorption and photocatalysis removal of arsenite, arsenate, and hexavalent chromium in water by the carbonized composite of manganese-crosslinked sodium alginate. Chemosphere 292:133391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133391
Mckinney CW, Loftin KA, Meyer MT, Davis JG, Pruden A (2010) tet and sul antibiotic resistance genes in livestock lagoons of various operation type, configuration, and antibiotic occurrence. Environ Sci Technol 44:6102–6109. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9038165
Meouche W, Margaillan A (2013) Recent advances on ion-imprinted polymers. React Funct Polym 73:859–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2013.03.021
Qing Z, Wang L, Liu X, Song Z, Qian F, Song Y (2022) Simply synthesized sodium alginate/zirconium hydrogel as adsorbent for phosphate adsorption from aqueous solution: performance and mechanisms. Chemosphere 291:133103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133103
Sheng X, Wang J, Cui Q, Zhang W, Zhu X (2021) A feasible biochar derived from biogas residue and its application in the efficient adsorption of tetracycline from an aqueous solution. Environ Res 112:175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112175
Wang B, Lv XL, Feng D, Xie LH, Zhang J, Li M, Xie Y, Li JR, Zhou HC (2016) Highly stable Zr(IV)-based metal-organic frameworks for the detection and removal of antibiotics and organic explosives in water. J Am Chem Soc 138:6204–6216. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b01663
Wang Y, Wang X, Li J, Li Y, Xia S, Zhao J, Minale TM, Gu Z (2019) Coadsorption of tetracycline and copper(II) onto struvite loaded zeolite–an environmentally friendly product recovered from swine biogas slurry. Chem Eng J 371:366–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.058
Wang W, Zhu Z, Zhang M, Wang S, Qu C (2020) Synthesis of a novel magnetic multi-amine decorated resin for the adsorption of tetracycline and copper. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 106:130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.10.017
Wu H, Liu Y, Chen B, Yang F, Wang L, Kong Q, Ye T, Lian J (2021) Enhanced adsorption of molybdenum(VI) from aquatic solutions by chitosan-coated zirconium–iron sulfide composite. Sep Purif Technol 279:119736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119736
Yang Y, Song W, Lin H, Wang W, Du L, Xing W (2018) Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in global lakes: a review and meta-analysis. Environ Int 116:60–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.04.011
Yang X, Chen L, Ren D, Wang S, Ren Z (2022) Adsorption of Pb (II) from water by treatment with an O-hydroxyphenyl thiourea-modified chitosan. Int J Biol Macromol 220:280–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.08.090
Zhang W, Ou J, Wang B, Wang H, He Q, Song J, Zhang H, Tang M, Zhou L, Gao Y, Sun S (2021) Efficient heavy metal removal from water by alginate-based porous nanocomposite hydrogels: the enhanced removal mechanism and influencing factor insight. J Hazard Mater 418:126358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126358
Zhang H, Ma R, Yang Y, Huang L, Chen N, Xie Q (2022) Study of ion-imprinted adsorbent materials on diatom-based Cr(VI) surfaces. Mater Lett 308:131149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131149
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers, as well as the editor for their editorial comments and suggestions, which improved the manuscript considerably.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province of China (2208085ME154), the Open Project of Engineering Research Center of Biofilm Water Purification and Utilization Technology of Ministry of Education (BWPU2021KF08), the open fund of State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse (PCRRF210010), and the key projects of Anhui Provincial Department of Education of China (KJ2020A0266).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wenkai Wu: methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing — original draft; Xiangpeng Gao: data curation, writing — original draft. Bo Chen and Guanhua Meng: writing — review and editing. Feng Xue: validation, visualization, writing — review and editing. Qiaoping Kong and Jianhua Yang: resources, methodology. Jianjun Lian: conceptualization, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing, project administration, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Gao, X., Chen, B. et al. Selective adsorption of tetracycline and copper(II) on ion-imprinted porous alginate microspheres: performance and potential mechanisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 105538–105555 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29810-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29810-0