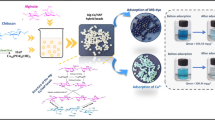
Abstract
The main aim of this research is focused on the synthesis of schist/alginate composite (SC/AL) adsorbent and its utilization for the removal of Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from waste streams using batch and column processes. The characterization of developed adsorbent was performed by X-ray fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, FTIR, and BET analyses. The most influential operating parameters (pH, contact time, temperature and initial adsorbate concentration) on the adsorption capacity of pollutants were examined to evaluate the performance of developed adsorbent. The kinetic and equilibrium adsorption results at pH 5.0 indicated that SC/AL composite had good adsorption capacity (qmax) for Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) estimated at 124.79 mg/g, 111.78 mg/g, and 119.78 mg/g, respectively. From the kinetic viewpoint, the good fit of pseudo-first-order kinetic model to the kinetic adsorption data indicated that dominant interaction of heavy metals with SC/AL composite was physisorption. The results of thermodynamic studies indicated that the adsorption of heavy metals onto SC/AL composite was endothermic and spontaneous in nature. The adsorption capacity of developed adsorbent could still reach relatively 85% of the original one after completing fifth cycle. Therefore, the reusability results of SC/AL composite were quite satisfied, making the developed adsorbent a commercially attractive and green method. Finally, in column studies, the effect of initial concentration of pollutants at pH 5.0 on the removal of heavy metal ions was investigated. The Thomas and Yoon-Nelson models provided a satisfactory explanation for the results of column data.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Allahkarami E, Azadmehr A, Noroozi F, Farrokhi S, Sillanpää M (2022a) Nitrate adsorption onto surface-modified red mud in batch and fixed-bed column systems: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:48438–48452
Allahkarami E, Dehghan Monfared A, Silva LFO, Dotto GL (2022c) Lead ferrite-activated carbon magnetic composite for efficient removal of phenol from aqueous solutions: synthesis, characterization, and adsorption studies. Sci Rep 12:1–16
Allahkarami E, Dehghan Monfared A, Silva LFO, Dotto GL (2023) Toward a mechanistic understanding of adsorption behavior of phenol onto a novel activated carbon composite. Sci Rep 13:1–16
Allahkarami E, Soleimanpour Moghadam N, Jamrotbe B, Azadmehr A (2023) Competitive adsorption of Ni (II) and Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by vermiculite-alginate composite: batch and fixed-bed column studies. J Dispers Sci Technol 44:1402–1412
Allahkarami E, Dehghan Monfared A, Silva LFO, Dotto GL (2023) Application of Pb–Fe spinel-activated carbon for phenol removal from aqueous solutions: fixed-bed adsorption studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:23870–23886
Bakr A-SA, Moustafa YM, Khalil MMH, Yehia MM, Motawea EA (2015) Magnetic nanocomposite beads: synthesis and uptake of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solutions. Can J Chem 93:289–296
Bankole MT, Abdulkareem AS, Mohammed IA, Ochigbo SS, Tijani JO, Abubakre OK, Roos WD (2019) Selected heavy metals removal from electroplating wastewater by purified and polyhydroxylbutyrate functionalized carbon nanotubes adsorbents. Sci Rep 9:4475
Bishop A, Woolley A, Hamilton W (1999) Cambridge guide to minerals, rocks and fossils. Cambridge University Press, China
Carotenuto G, Camerlingo C (2020) Kinetic investigation of water physisorption on natural clinoptilolite at room temperature. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 302:110238
Chiew CSC, Yeoh HK, Pasbakhsh P, Krishnaiah K, Poh PE, Tey BT, Chan ES (2016) Halloysite/alginate nanocomposite beads: kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism for lead adsorption. Appl Clay Sci 119:301–310
Dolatyari L, Yaftian MR, Rostamnia S (2016) Removal of uranium(VI) ions from aqueous solutions using Schiff base functionalized SBA-15 mesoporous silica materials. J Environ Manag 169:8–17
Dong Y, Sang D, He C, Sheng X, Lei L (2019) Mxene/alginate composites for lead and copper ion removal from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 9:29015–29022
Dubey R, Bajpai J, Bajpai AK (2016) Chitosan-alginate nanoparticles (CANPs) as potential nanosorbent for removal of Hg (II) ions. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 6:32–44
Ehsani A, Aghdasinia H, Farshchi ME, Rostamnia S, Khataee A (2023) Synthesis of sodium alginate/carboxy-methyl cellulose/Cu-based metal-organic framework composite for adsorption of tetracycline from aqueous solution: isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic approach. Surfaces and Interfaces 36:102506
Feng Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang X-F, Yao J (2018) In-situ gelation of sodium alginate supported on melamine sponge for efficient removal of copper ions. J Colloid Interface Sci 512:7–13
Gao X, Guo C, Hao J, Zhao Z, Long H, Li M (2020) Adsorption of heavy metal ions by sodium alginate based adsorbent-a review and new perspectives. Int J Biol Macromol 164:4423–4434
Gao J, Li Z, Wang Z, Chen T, Hu G, Zhao Y, Han X (2022) Facile synthesis of sustainable tannin/sodium alginate composite hydrogel beads for efficient removal of methylene blue. Gels 8:486–499
Gong X-L, Lu H-Q, Li K, Li W (2022) Effective adsorption of crystal violet dye on sugarcane bagasse–bentonite/sodium alginate composite aerogel: characterisation, experiments, and advanced modelling. Sep Purif Technol 286:120478
Googerdchian F, Moheb A, Emadi R (2012) Lead sorption properties of nanohydroxyapatite–alginate composite adsorbents. Chem Eng J 200:471–479
Gotoh T, Matsushima K, Kikuchi K-I (2004) Preparation of alginate–chitosan hybrid gel beads and adsorption of divalent metal ions. Chemosphere 55:135–140
Guibal E (2004) Interactions of metal ions with chitosan-based sorbents: a review. Sep Purif Technol 38:43–74
Guo J, Han Y, Mao Y, Wickramaratne MN (2017) Influence of alginate fixation on the adsorption capacity of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals to Cu2+ ions. Colloids Surf, A 529:801–807
Gürel A (2006) Adsorption characteristics of heavy metals in soil zones developed on spilite. Environ Geol 51:333–340
Hameed BH, Chin LH, Rengaraj S (2008) Adsorption of 4-chlorophenol onto activated carbon prepared from rattan sawdust. Desalination 225:185–198
Ho YS, Porter JF, McKay G (2002) Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of divalent metal ions onto peat: copper, nickel and lead single component systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 141:1–33
Isawi H (2020) Using zeolite/polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate nanocomposite beads for removal of some heavy metals from wastewater. Arab J Chem 13:5691–5716
Jiang H, Yang Y, Lin Z, Zhao B, Wang J, Xie J, Zhang A (2020) Preparation of a novel bio-adsorbent of sodium alginate grafted polyacrylamide/graphene oxide hydrogel for the adsorption of heavy metal ion. Sci Total Environ 744:140653
Jiao C, Xiong J, Tao J, Xu S, Zhang D, Lin H, Chen Y (2016) Sodium alginate/graphene oxide aerogel with enhanced strength–toughness and its heavy metal adsorption study. Int J Biol Macromol 83:133–141
Karimi-Maleh H, Darabi R, Karimi F, Karaman C, Shahidi SA, Zare N, Baghayeri M, Fu L, Rostamnia S, Rouhi J, Rajendran S (2023) State-of-art advances on removal, degradation and electrochemical monitoring of 4-aminophenol pollutants in real samples: a review. Environ Res 222:115338
Kołodyńska D, Gęca M, Skwarek E, Goncharuk O (2018) Titania-coated silica alone and modified by sodium alginate as sorbents for heavy metal ions. Nanoscale Res Lett 13:1–12
Kudełko J (2018) Effectiveness of mineral waste management. Int J Min Reclam Environ 32:440–448
Kudełko J, Wirth H, Kaczan W, Bagiński L (2021) Characteristics of clay raw materials from the Turów Lignite Mine Waste, Poland: potential for industrial applications. Sustainability 13:6513
Li Y, Liu F, Xia B, Du Q, Zhang P, Wang D, Wang Z, Xia Y (2010) Removal of copper from aqueous solution by carbon nanotube/calcium alginate composites. J Hazard Mater 177:876–880
Li Y, Du Q, Liu T, Sun J, Wang Y, Wu S, Wang Z, Xia Y, Xia L (2013) Methylene blue adsorption on graphene oxide/calcium alginate composites. Carbohyd Polym 95:501–507
Lottermoser B, Lottermoser BG (2010) Mine wastes: Characterization, treatment and environmental impacts 43–117
Marzban N, Moheb A, Filonenko S, Hosseini SH, Nouri MJ, Libra JA, Farru G (2021) Intelligent modeling and experimental study on methylene blue adsorption by sodium alginate-kaolin beads. Int J Biol Macromol 186:79–91
Milojković JV, Lopičić ZR, Anastopoulos IP, Petrović JT, Milićević SZ, Petrović MS, Stojanović MD (2019) Performance of aquatic weed - waste Myriophyllum spicatum immobilized in alginate beads for the removal of Pb(II). J Environ Manag 232:97–109
Mohammadi R, Azadmehr A, Maghsoudi A (2019) Fabrication of the alginate-combusted coal gangue composite for simultaneous and effective adsorption of Zn (II) and Mn (II). J Environ Chem Eng 7:103494
Pan L, Wang Z, Yang Q, Huang R (2018) Efficient removal of lead, copper and cadmium ions from water by a porous calcium alginate/graphene oxide composite aerogel. Nanomaterials 8:957
Papageorgiou SK, Katsaros FK, Kouvelos EP, Kanellopoulos NK (2009) Prediction of binary adsorption isotherms of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ on calcium alginate beads from single adsorption data. J Hazard Mater 162:1347–1354
Qin H, Hu T, Zhai Y, Lu N, Aliyeva J (2020) The improved methods of heavy metals removal by biosorbents: a review. Environ Pollut 258:113777
Rezai B, Allahkarami E (2021a) Wastewater treatment processes—techniques, technologies, challenges faced, and alternative solutions. In: Karri RR, Ravindran G, Dehghani MH (eds) Soft computing techniques in solid waste and wastewater management, 1st edn. Elsevier, Netherland, pp 35–53
Rezai B, Allahkarami E (2021b) Application of neural networks in wastewater degradation process for the prediction of removal efficiency of pollutants. In: Karri RR, Ravindran G, Dehghani MH (eds) Soft computing techniques in solid waste and wastewater management, 1st edn. Elsevier, Netherland, pp 75–93
Roh H, Yu M-R, Yakkala K, Koduru JR, Yang J-K, Chang Y-Y (2015) Removal studies of Cd (II) and explosive compounds using buffalo weed biochar-alginate beads. J Ind Eng Chem 26:226–233
Rostamnia S, Mohsenzad F (2018) Nanoarchitecturing of open metal site Cr-MOFs for oxodiperoxo molybdenum complexes [MoO(O2)2@En/MIL-100(Cr)] as promising and bifunctional catalyst for selective thioether oxidation. Molecular Catalysis 445:12–20
Sellaoui L, Soetaredjo FE, Ismadji S, Benguerba Y, Dotto GL, Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Rodrigues AE, Lamine AB, Erto A (2018) Equilibrium study of single and binary adsorption of lead and mercury on bentonite-alginate composite: experiments and application of two theoretical approaches. J Mol Liq 253:160–168
Sharif A, Khorasani M, Shemirani F (2018) Nanocomposite bead (NCB) based on bio-polymer alginate caged magnetic graphene oxide synthesized for adsorption and preconcentration of lead (II) and copper (II) ions from urine, saliva and water samples. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 28:2375–2387
Shawky HA (2011) Improvement of water quality using alginate/montmorillonite composite beads. J Appl Polym Sci 119:2371–2378
Shen W, An Q-D, Xiao Z-Y, Zhai S-R, Hao J-A, Tong Y (2020) Alginate modified graphitic carbon nitride composite hydrogels for efficient removal of Pb (II), Ni (II) and Cu (II) from water. Int J Biol Macromol 148:1298–1306
Simonin J-P (2016) On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 300:254–263
Taghavi R, Rostamnia S, Farajzadeh M, Karimi-Maleh H, Wang J, Kim D, Jang HW, Luque R, Varma RS, Shokouhimehr M (2022) Magnetite metal–organic frameworks: applications in environmental remediation of heavy metals, organic contaminants, and other pollutants. Inorg Chem 61:15747–15783
Vijayalakshmi K, Gomathi T, Latha S, Hajeeth T, Sudha PN (2016) Removal of copper (II) from aqueous solution using nanochitosan/sodium alginate/microcrystalline cellulose beads. Int J Biol Macromol 82:440–452
Wang Y-y, Yao W-b, Wang Q-w, Yang Z-h, Liang L-f, Chai L-y (2016) Synthesis of phosphate-embedded calcium alginate beads for Pb(II) and Cd(II) sorption and immobilization in aqueous solutions. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 26:2230–2237
Wang B, Gao B, Wan Y (2018) Entrapment of ball-milled biochar in Ca-alginate beads for the removal of aqueous Cd(II). J Ind Eng Chem 61:161–168
Wang B, Wan Y, Zheng Y, Lee X, Liu T, Yu Z, Huang J, Ok YS, Chen J, Gao B (2019) Alginate-based composites for environmental applications: a critical review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 49:318–356
Xie X, Ma X, Guo L, Fan Y, Zeng G, Zhang M, Li J (2019) Novel magnetic multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymer for selective and rapid removal and detection of alkylphenols in water. Chem Eng J 357:56–65
Zhuang Y, Yu F, Chen H, Zheng J, Ma J, Chen J (2016) Alginate/graphene double-network nanocomposite hydrogel beads with low-swelling, enhanced mechanical properties, and enhanced adsorption capacity. J Mater Chem A 4:10885–10892
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Esmaeil Allahkarami performed the experiments, prepared the original draft, and contributed in analysis, and interpretation. Ebrahim Allahkarami contributed in reviewing and editing the paper, validation, analysis and interpretation of the results. Amirreza Azadmehr supervised the project and contributed in writing and editing, data curation, and reviewing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Allahkarami, E., Allahkarami, E. & Azadmehr, A. Enhancing the efficiency of Ni(II), Cd(II), and Cu(II) adsorption from aqueous solution using schist/alginate composite: batch and continuous studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 105504–105521 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29808-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29808-8