Abstract
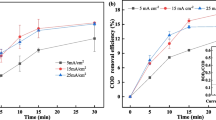
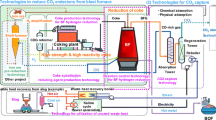
Coolant oil from auto part manufacturing contains additives resulting in high chemical oxygen demand (COD) in wastewater. In this study, COD treatment of coolant oil was investigated in a metal–organic framework (MOF) with MIL-88A by a modified air-Fenton (MAF) process by varying synthetic coolant oil concentrations (1–5%), pH (3–9), air-flow rate (1–2 L/min), amount of MIL-88A (0.2–1.0 g), and reaction time (30–180 min). The results were analyzed using central composite design (CCD) and response surface methodology (RSM) using Minitab ver. 19. The characteristic MIL-88A was characterized by XRD that showed a spindle-like shape with 2θ at 10.2° and 13.0°. The FTIR spectrum revealed the vibrational frequencies at Fe–O (564 cm−1), C–O (1391 and 1600 cm−1), and C = O (1216 and 1710 cm−1). The optimum treatment efficiency was studied from 30 CCD conditions in the presence of coolant oil (5%, COD ~ 132,000 mg/L), pH (9), air flow rate (2 L/min), and MIL-88A (1 g) within 177 min. The results obtained from the experiment and the COD prediction were found to be 92.64% and 93.45%, respectively. The main mechanism of iron(III) in MIL-88A is proposed to be the production of hydroxyl radical (·OH) that oxidizes the organic matter in the coolant oil. Moreover, the MAF process was applied to the used industrial coolant oil and was found to be 62.59% efficient.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available on request.
References
Alipanah N, Yari H, Mahdavian M, Ramezanzadeh B, Bahlakeh G (2021) MIL- 88A (Fe) filler with duplicate corrosion inhibitive/barrier effect for epoxy coatings: electrochemical, molecular simulation, and cathodic delamination studies. J Ind Eng Chem 97:200–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.01.035
Amaro-Gahete J, Klee R, Esquivel D, Ruiz JR, Jimenez-Sanchidrian C, Romero-Salguero FJ (2019) Fast ultrasound-assisted synthesis of highly crystalline MIL-88A particles and their application as ethylene adsorbents. Ultrason Sonochem 50:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.08.027
Amin MM, Golbini Mofrad MM, Pourzamani H, Sebaradar SM, Ebrahim K (2017) Treatment of industrial wastewater contaminated with recalcitrant metal working fluids by the photo-Fenton process as post-treatment for DAF. J Ind Eng Chem 45:412–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.10.010
Bagherzadeh E, Zebarjad SM, Hosseini HRM, Chagnon P (2019) Preparation, optimization and evolution of the kinetic mechanism of an Fe-MIL-88A metal–organic framework. CrystEngComm 21(3):544–553. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CE01876F
Bai S, Liu X, Zhu K, Wu S, Zhou H (2016) Metal–organic framework-based separator for lithium–sulfur batteries. Nat Energy 1(7):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/NENERGY.2016.94
Cheng M, Lai C, Liu Y, Zeng G, Huang D, Zhang C, Qin L, Hu L, Zhou C, Xiong W (2018) Metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient heterogeneous Fenton-like catalysis. Coord Chem Rev 368:80–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2018.04.012
Corlett EK, Blade H, Hughes LP, Sidebottom PJ, Walker D, Walton RI, Brown SP (2019) An XRD and NMR crystallographic investigation of the structure of 2, 6-lutidinium hydrogen fumarate. CrystEngComm 21(22):3502–3516. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CE00633H
Cui Z, Kerekes JP (2018) Potential of red edge spectral bands in future landsat satellites on agroecosystem canopy green leaf area index retrieval. MDPI 10:1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091458
Cui Z, Kerekes JP (2018) Impact of wavelength shift in relative spectral response at high angles of incidence in landsat-8 operational land imager and future landset design concept. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(10):5873–5883. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2827394
Daligaux V, Richard R, Manero M-H (2021) Deactivation and regeneration of zeolite catalysts used in pyrolysis of plastic wastes—a process and analytical review. Catalysts 11(7):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070770
Du Y, Zhou M, Lei L (2007) Kinetic model of 4-CP degradation by Fenton/O2 system. Water Res 41(5):1121–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.11.038
Fu H, Song XX, Wu L, Zhao C, Wang P, Wang CC (2020) Room-temperature preparation of MIL-88A as a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst for degradation of rhodamine B and bisphenol a under visible light. Mater Res Bull 125:110806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.110806
Gao Y, Li S, Li Y, Yao L, Zhang H (2017) Accelerated photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant over metal-organic framework MIL-53(Fe) under visible LED light mediated by persulfate. Appl Catal B 202:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.09.005
Garcia-Costa AL, Luengo A, Zazo JA, Casas JA (2021) Cutting oil-water emulsion wastewater treatment by microwave assisted catalytic wet peroxide oxidation. Sep Purif Technol 257:117940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117940
Gu Y, Cui Z, Yu X, Wang L, Xiu C (2011) A novel algorithm for modifying echocardiographic particle image velocimetry flow field. 4th Int Conf Biomed Eng Inform (BMEI). https://doi.org/10.1109/BMEI.2011.6098258
Gu Y, Cui Z, Xiu C, Wang L (2014) Ultrasound echocardiography deskpeckling with non-local means time series filter. Nerocomputing 124:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.07.022
Guy OJ, Walker KAD (2016) Chapter 4- Graphene functionalization for biosensor applications. Silicon Carbide Biotechnology (2nd edn), pp 85–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802993-0.00004-6
Hayati P, Mehrabadi Z, Karimi M, Janczak J, Mohammadi K, Mahmoudi G, Dadi F, Fard MJS, Hasanzadeh A, Rostamnia S (2021) Photocatalytic activity of new nanostructures of an Ag(I) metal-organic framework (Ag-MOF) for the efficient degradation of MCPA and 2,4-D herbicide under sunlight irradiation. New J Chem 45:3408. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj02460k
Hu M, Wang Y, Yang J, Sun Y, Xing G, Deng R, Hu X, Zhang G (2019) Competitive electrochemical immunosensor for maduramicin detection by multiple signal amplification strategy via hemin@Fe-MIL-88NH2/AuPt. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111554
Karimi-Maleh H, Darabi R, Karimi F, Karaman C, Shahidi SA, Zare N, Baghayeri M, Fu L, Rostamnia S, Jalal Rouhi, Rajendran S (2023) State-of-art advances on removal, degradation and electrochemical monitoring of 4-aminophenol pollutants in real samples: A review. Environ Res 222:115338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115338
Liang R, Luo S, Jing F, Shen L, Qin N, Wu L (2015) A simple strategy for fabrication of Pd@ MIL-100 (Fe) nanocomposite as a visible-light-driven photocatalyst for the treatment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs). Appl Catal B 176:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.009
Liao X, Wang F, Wang F, Cai Y, Yao Y, Teng BT, Hao Q, Shuxiang L (2019) Synthesis of (100) surface oriented MIL-88A-Fe with rod-like structure and its enhanced Fenton-like performance for phenol removal. Appl Catal B Environ 259:118064–118075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118064
Lin KYA, Chang HA, Hsu CJ (2015) Iron-based metal organic framework, MIL-88A, as a heterogeneous persulfate catalyst for decolorization of Rhodamine B in water. RSC Adv 5(41):32520–32530. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA01447F
Liu W, Hsieh S, Chen W, Lee J (2007) Study of nanosized zinc oxide on Cu–Zn alloy substrate using Taguchi method. Surf Coat Technol 201(22–23):9238–9242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2007.04.064
Matavos-Aramyan S, Moussavi M (2017) Advances in Fenton and Fenton based oxidation processes for industrial effluent contaminants control-a review. Int J Environ Sci Nat Resour 2(4):1–18. https://doi.org/10.19080/IJESNR.2017.02.555594
Mellot-Draznieks C, Serre C, Surblé S, Audebrand N, Férey G (2005) Very large swelling in hybrid frameworks: a combined computational and powder diffraction study. J Am Chem Soc 127(46):16273–16278. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja054900x
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003) A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J Hazard Mater 98(1–3):33–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3894(02)00282-0
Pera-Titus M, Garcı́aMolina V, Baños MA, Giménez J, Esplugas S (2004) Degradation of chlorophenols by means of advanced oxidation processes: a general review. Appl Catal B: Environ 47(4):219–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.09.010
Phaniendra A, Jestadi DB, Periyasamy L (2015) Free radicals: properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem 30(1):11–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-014-0446-0
Roustamnia S, Alamgholiloo H, Jafari M, Rookhosh R, Abbasi AR (2016) Synthesis and catalytic study of open metal site metal-organic frameworks of Cu3(BTC)2 microbelts in selective organic sulfide oxidation. Appl Organometal Chem 30:954–958. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3528
Seo DC, Lee HJ, Hwang HN, Park MR, Kwak NW, Cho IJ, Cho JS, Seo JY, Joo WH, Park KH, Heo JS (2007) Treatment of non-biodegradable cutting oil wastewater by ultrasonication-Fenton oxidation process. Water Sci Technol 55:251–259. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2007.009
Shameer PM, Nishath PM (2019) Chapter 8 - Exploration and enhancement on fuel stability of biodiesel: a step forward in the track of global commercialization. Advanced Biofuels:181-213. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102791-2.00008-8
Taghavi R, Rostamnia S (2022) Schiff-base post-synthetic modification of IRMOF-3 to encapsulate Pd nanoparticles: it’s application in C-C bond formation cross-coupling Suzuki reaction. Chem Methodol 6:629–638. https://doi.org/10.22034/CHEMM.2022.339192.1496
Taghavi R, Rostamnia S, Farajzadeh M, Karimi-Maleh H, Wang J, Kim D, Jang WJ, Luque R, Varma RS, Shokouhimehr M (2022) Magnetite metal-organic frameworks: applications in environmental remediation of heavy metals, organic contaminants, and other pollutants. Inorg Chem 61:15747–15783. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c01939
Thorne PS, Sprince NL (2005) Metal working fluids. University of Iowa, In Textbook of clinical occupational and environmental medical, pp 1043–1054
Utset B, Garcia J, Casado J, Domènech X, Peral J (2000) Replacement of H2O2 by O2 in Fenton and photo-Fenton reactions. Chemosphere 41(8):1187–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(00)00011-4
Vahid A, Mojtaba F, Abbas S, Reza K (2013) Evaluation of the metalwork cutting fluid treatment performance using fenton oxidation process in comparison with coagulation-flocculation. Casp J Appl Sci Res 2(5):90-98. http://www.cjasr.com
Vidale M, Craig O, Desset F, Guida G, Bianchetti P, Sidoti G, Mariottini M, Battistella E (2012) A chlorite container found on the surface of shahdad (Kerman, Iran) and its cosmetic content. Iran 50(1):27–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/05786967.2012.11834711
Wang J, Wan J, Ma Y, Wang Y, Pu M, Guan Z (2016) Metal–organic frameworks MIL-88A with suitable synthesis conditions and optimal dosage for effective catalytic degradation of Orange G through persulfate activation. RSC Adv 6(113):112502–112511. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra24429g
Xiong Z, Lai B, Yang P, Zhou Y, Wang J, Fang S (2015) Comparative study on the reactivity of Fe/Cu bimetallic particles and zero valent iron (ZVI) under different conditions of N2, air or without aeration. J Hazard Mater 297:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.05.006
Xu WT, Ma L, Ke F, Peng FM, Xu GS, Shen YH, Zhu JF, Qiu LG, Yuan YP (2014) Metal-organic frameworks MIL-88A hexagonal microrods as a new photocatalyst for efficient decolorization of methylene blue dye. Dalton Trans 43(9):3792–3798. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt52574k
Ye Z, Padilla JA, Xuriguera E, Brillas E, Sirés I (2020) Magnetic MIL (Fe)-type MOF-derived N-doped nano-ZVI@ C rods as heterogeneous catalyst for the electro-Fenton degradation of gemfibrozil in a complex aqueous matrix. Appl Catal B: Environ 266:118604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118604
Yuan Y, Lai B, Tang YY (2016) Combined Fe0/air and Fenton process for the treatment of dinitrodiazophenol (DDNP) industry wastewater. Chem Eng J 283:1514–1521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.104
Zenkevich I, Ishchenko E, Makarov A, Sonchik O (2010) Air oxidation of organic compounds in aqueous solutions. Ecochemical and analytical aspects. Russ J General Chem 80(13):2671–2681
Zhang Y, Zhou J, Chen X, Wang L, Cai W (2019) Coupling of heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes and photocatalysis in efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by Fe-based MOFs: synergistic effect and degradation pathway. Chem Eng J 369:745–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.108
Zhu L, Zhou X, Liu W, Kong Z (2022) Total organic carbon content logging prediction based on machine learning: a brief review. Energy Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engeos.2022.03.001
Acknowledgements
The research project was supported by the Interdisciplinary Program in Environmental Science, Graduate School, Chulalongkorn University. The laboratory activities were supported by the Department of Environmental Science, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K. S. carried out the experiment and wrote the manuscript with input from all the authors. V. K. conceived of the presented idea and supervised the project. S. W. verified the analytical methods. All the authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All the authors contributed to the preparation of this research and co-participated in the article.
Consent for publication
All the authors have approved to submit the final draft for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Suwannasung, K., Kanokkantapong, V. & Wongkiew, S. Modified air-Fenton with MIL-88A for chemical oxygen demand treatment in used coolant oil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 105429–105439 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29685-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29685-1