Abstract
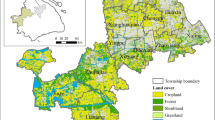
The ecological security (ES) of urban agglomeration and surrounding environmental system is related to the sustainable development of cities, which is a hot spot that we must pay attention to. In this study, four subsystems composed of natural base, landscape structure, ecosystem stability, and anthropogenic interference were used to evaluate the comprehensive ecological security (CES) of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GHMGBA) in 2000, 2010 and 2020. The results show that CES of the region was generally well. The central urban region of GHMGBA was unsafety with an area proportion of about 24.5%, the periphery was safety with an area proportion of about 43.5%, and the others are transitional zone. From 2000 to 2020, the CES change first slightly decreases and then relatively stable, and the transfer of different safety levels mainly occurs in the transitional zone. In 2010-2020 the transfer of different levels of CES is more frequent than in 2000-2010, indicating that the spatial-temporal pattern of CES fluctuated sharply during 2010-2020. The urban-rural gradient showed that with the increase of distance, CES fluctuations increase, but decreases at about 20-40km, 60-80km and 120-140km away from the city center, which may be sub-urban regions. The overall CES change range gradually decreases with increasing distance from urban centers. This study helps to understand the temporal and spatial distribution of ecological environment and urban-rural gradient in typical urban regions, and provides a reference for the collaborative planning of urban agglomeration.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are included within the article. Data will be made available from authors on reasonable request.
References
Abbaszadeh Tehrani N, Mohd Shafri HZ, Salehi S, Chanussot J, Janalipour M (2022) Remotely-Sensed Ecosystem Health Assessment (RSEHA) model for assessing the changes of ecosystem health of Lake Urmia Basin. Int J Image Data Fusion 13(2):180–205. https://doi.org/10.1080/19479832.2021.1924880
Bi M, Xie G, Yao C (2020) Ecological security assessment based on the renewable ecological footprint in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Ecol Indic 116:106432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106432
Cen X, Wu C, Xing X, Fang M, Garang Z, Wu Y (2015) Coupling intensive land use and landscape ecological security for urban sustainability: An integrated socioeconomic data and spatial metrics analysis in Hangzhou city. Sustainability 7(2):1459–1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7021459
Chen Y, Wang J (2020) Ecological security early-warning in central Yunnan Province, China, based on the gray model. Ecol Indic 111:106000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.106000
Cheng H, Zhu L, Meng J (2021) Fuzzy evaluation of the ecological security of land resources in mainland China based on the Pressure-State-Response framework. Sci Total Environ 150053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150053
Chu X, Deng X, Jin G, Wang Z, Li Z (2017) Ecological security assessment based on ecological footprint approach in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Phys Chem Earth 101:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2017.05.001
Dai E, Wu Z, Du X (2018) A gradient analysis on urban sprawl and urban landscape pattern between 1985 and 2000 in the Pearl River Delta, China. Front Earth Sci 12:791–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-017-0637-0
Dai L, Liu Y, Luo X (2021) Integrating the MCR and DOI models to construct an ecological security network for the urban agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 754:141868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141868
Dong R, Zhang X, Li H (2019) Constructing the ecological security pattern for sponge city: a case study in Zhengzhou, China. Water 11(2):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020284
Du P, Xia J, Du Q, Luo Y, Tan K (2013) Evaluation of the spatio-temporal pattern of urban ecological security using remote sensing and GIS. Int J Remote Sens 34(3):848–863. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2012.714503
Fan F, Liu Y, Chen J, Dong J (2021) Scenario-based ecological security patterns to indicate landscape sustainability: A case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Landsc Ecol 36(7):2175–2188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-020-01044-2
Feng Y, Yang Q, Tong X, Chen L (2018) Evaluating land ecological security and examining its relationships with driving factors using GIS and generalized additive model. Sci Total Environ 633:1469–1479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.272
Fu Y, Shi X, He J, Yuan Y, Qu L (2020) Identification and optimization strategy of county ecological security pattern: A case study in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol Indic 112:106030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.106030
Gao Y, Huang H, Wu Z (2010) Landscape ecological security assessment based on projection pursuit:a case study of nine cities in the Pearl River Delta. Acta Ecol Sin 30(21):5894–5903 https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/stxb201021020 (In Chinese)
Gao Y, Wu Z, Lou Q, Huang H, Cheng J, Chen Z (2012) Landscape ecological security assessment based on projection pursuit in Pearl River Delta. Environ Monit Assess 184(4):2307–2319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2119-2
Gao Y, Zhang C, He Q, Liu Y (2017) Urban ecological security simulation and prediction using an improved cellular automata (CA) approach—a case study for the city of Wuhan in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(6):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14060643
Gao Y, Jia J, Lu Y, Sun X, Wen X, He N, Yang T (2020) Progress in watershed geography in the Yangtze River Basin and the affiliated ecological security perspective in the past 20 years, China. J Geogr Sci 30:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-020-1759-y
Ghosh S, Chatterjee ND, Dinda S (2021) Urban ecological security assessment and forecasting using integrated DEMATEL-ANP and CA-Markov models: A case study on Kolkata Metropolitan Area, India. Sustain Cities Soc 68:102773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.102773
Guo A, Yue W, Yang J, He T, Zhang M, Li M (2022) Divergent impact of urban 2D/3D morphology on thermal environment along urban gradients. Urban Clim 45:101278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2022.101278
Guo C, Zhu Y, Sun W, Song J (2017) Dataset of biological abundance index of China in 1985 and 2005 at 1 km resolution. J Global Change Data Discov 1(1):60–65. https://doi.org/10.3974/geodp.2017.01.09
Guo Y (2016) Analysis of landscape ecological security in a fast growing urban district: the case of Shenzhen City. Geomatics Spatial Inform Technol 39(12):127–131. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2016.12.039 (In Chinese)
Gong JZ, Liu YS, Xia BC, Zhao GW (2009) Urban ecological security assessment and forecasting, based on a cellular automata model: A case study of Guangzhou, China. Ecol Modell 220(24):3612–3620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.10.018
Han S, Xiong J, Li D (2016) Evaluation index system of land ecological security in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. Guangdong Agric Sci 43(2):83–88. https://doi.org/10.16768/j.issn.1004-874x.2016.02.016 (In Chinese)
Hu Z, Gong J, Li T, Sun J (2018) Ecological security assessment and situation analysis of Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. Ecol Environ Sci 27(2):304–312. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2018.02.015 (In Chinese)
Huang J, Yu H, Han D, Zhang G, Wei Y, Huang J, An L, Liu X, Ren Y (2020a) Declines in global ecological security under climate change. Ecol Indic 117:106651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106651
Huang J, Hu Y, Zheng F (2020b) Research on recognition and protection of ecological security patterns based on circuit theory: a case study of Jinan City. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(11):12414–12427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07764-x
Huang Q, Peng B, Elahi E, Wan A (2021) Evolution and driving mechanism of ecological security pattern: a case study of Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration. Integr Environ Assess Manag 17(3):573–583. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.4358
Jiang X (2011) Urban ecological security evaluation and analysis based on fuzzy mathematics. Procedia Eng 15:4451–4455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.08.836
Jiao M, Wang Y, Hu M, Xia B (2021) Spatial deconstruction and differentiation analysis of early warning for ecological security in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustain Cities Soc 64:102557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102557
Jin G, Deng X, Zhao X, Guo B, Yang J (2018) Spatiotemporal patterns in urbanization efficiency within the Yangtze River Economic Belt between 2005 and 2014. J Geogr Sci 28:1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-018-1545-2
Jin X, Wei L, Wang Y, Lu Y (2021) Construction of ecological security pattern based on the importance of ecosystem service functions and ecological sensitivity assessment: a case study in Fengxian County of Jiangsu Province, China. Environ Dev Sustain 23(1):563–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00596-2
Kang X, Liu X, Zhang S, Ma X (2007) Regional eco-security assessment of southwest Beijing. Chin J Appl Ecol 18(12):2846–2852. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.2007.0463 (In Chinese)
Li X, Tian M, Wang H, Wang H, Yu J (2014) Development of an ecological security evaluation method based on the ecological footprint and application to a typical steppe region in China. Ecol Indic 39:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.12.014
Li JX, Chen YN, Xu CC, Li Z (2019) Evaluation and analysis of ecological security in arid areas of Central Asia based on the emergy ecological footprint (EEF) model. J Clean Prod 235:664–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.005
Li Z, Li M, Xia B (2020a) Spatio-temporal dynamics of ecological security pattern of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration based on LUCC simulation. Ecol Indic 114:106319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106319
Li M, Hu M, Xia B (2020b) Spatial differentiation and aggregation characteristics of ecological security of urban agglomeration in the Pearl River Delta. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni 59(1):96–104. https://doi.org/10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2020.01.012 (In Chinese)
Lin L, Chen W, Liu Y (2020) Analysis of landscape pattern change and ecological risk assessment in Sanming area. J Subtrop Resour Environ 15(3):83–90. https://doi.org/10.19687/j.cnki.1673-7105.2020.03.011 (In Chinese)
Liu Y, Cui N, Han R, Guo L (2020) Establishing ecological security patterns based on reconstructed ecosystem services value in rapidly urbanizing areas: A case study in Zhuhai City, China. Sustainability 12(16):6629. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166629
MEPPRC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China) (2015) National environmental protection standards of the People's Republic of China: Technical criterion for ecosysrem status evaluation (HJ192-2015). China Environmental Press, Beijing
Moarrab Y, Salehi E, Amiri MJ, Hovidi H (2021) Spatial–temporal assessment and modeling of ecological security based on land-use/cover changes (case study: Lavasanat watershed). Intl J Environ Sci Technol, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03534-5
Ou ZR, Zhu QK, Sun YY (2017) Regional ecological security and diagnosis of obstacle factors in underdeveloped regions: a case study in Yunnan Province, China. J Mountain Sci 14(5):870–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-4199-5
Peng J, Pan Y, Liu Y, Zhao H, Wang Y (2018) Linking ecological degradation risk to identify ecological security patterns in a rapidly urbanizing landscape. Habitat Intl 71:110–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.11.010
Peng C, Li B, Nan B (2021) An analysis framework for the ecological security of urban agglomeration: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J Clean Prod 315:128111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128111
Wen X, Zhu J, Gao W (2020) Empirical analysis on cooperative efficiency of ecological security in nine cities of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area under the heterogeneous system:based on PSR and GIS-DEA combined model. Ecol Econ 36(4):200–205 (In Chinese)
Wang S, Zhang X, Wu T, Yang Y (2019) The evolution of landscape ecological security in Beijing under the influence of different policies in recent decades. Sci Total Environ 646:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.146
Wang X, Zhong W, Li T, Quan M, Wang B, Wei Z (2021a) A 16.2-kyr lacustrine sediment record of mercury deposition in Dahu Swamp, eastern Nanling Mountains, southern China: Analysis of implications for climatic changes. Quat Int 592:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2021.04.013
Wang X, Zhang C, Liao Y, Liu G, Wang B, Yu J (2021b) Spatial and temporal characteristics of hemeroby degree in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area during 1980-2018. Bull Soil Water Conserv 41(3):333–341. https://doi.org/10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2021.03.043 (In Chinese)
Wang H, Ma X, Du Y (2021c) Constructing ecological security patterns based on ecological service importance and ecological sensitivity in Guangdong Province. Acta Ecol Sin 41(5):1705–1715. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb202001080068 (In Chinese)
Wang X, Liu G, Xiang A, Qureshi S, Li T, Song D, Zhang C (2022) Quantifying the human disturbance intensity of ecosystems and its natural and socioeconomic driving factors in urban agglomeration in southern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:11493–11509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16349-1
Weng H, Kou J, Shao Q (2020) Evaluation of urban comprehensive carrying capacity in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area based on regional collaboration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(16):20025–20036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08517-6
Wu J, Luo K, Ma H, Wang Z (2020) Ecological security and restoration pattern of Pearl River Delta, based on ecosystem service and gravity model. Acta Ecol Sin 40(23):8417–8429. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb202003150550 (In Chinese)
Wu X, Liu S, Sun Y, An Y, Dong S, Liu G (2019) Ecological security evaluation based on entropy matter-element model: A case study of Kunming city, southwest China. Ecol Indic 102:469–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.02.057
Xu X, Lin H, Fu Z, Bu R (2001) Regional ecological risk assessment of wetland in the Huanghe River Delta. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekin 37(1):111–120. https://doi.org/10.13209/j.0479-8023.2001.020
Yang C, Liu H, Li Q, Cui A, Xia R, Shi T, Zhang J, Guo W, Zhou X, Wu G (2021) Rapid urbanization induced extensive forest loss to urban land in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Chin Geogr Sci 31(1):93–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1177-9
Yu G, Zhang S, Yu Q, Fan Y, Zeng Q, Wu L, Zhou R, Nan N, Zhao P (2014) Assessing ecological security at the watershed scale based on RS/GIS: a case study from the Hanjiang River Basin. Stoch Env Res Risk A 28(2):307–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-013-0750-x
Zhang H, Tang X, Wang S, Guo L, Yong Y, Wang X (2006) Regional ecological security of rapidly urbanizing Pearl River Delta, China: a case study of Foshan City. J Natl Resour 21(4):615–624. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2006.04.015 (In Chinese)
Zhang L, Peng J, Liu Y, Wu J (2017) Coupling ecosystem services supply and human ecological demand to identify landscape ecological security pattern: A case study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Urban Ecosyst 20(3):701–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-016-0629-y
Zhang D, Wang X, Qu L, Li S, Lin Y, Yao R, Zhou X, Li J (2020a) Land use/cover predictions incorporating ecological security for the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Ecol Indic 119:106841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106841
Zhang J, Yu L, Li X, Zhang C, Shi T, Wu X, Yang C, Gao W, Li Q, Wu G (2020b) Exploring annual urban expansions in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area: Spatiotemporal features and driving factors in 1986–2017. Remote Sens 12(16):2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162615
Zhang J, Ma L (2021) Urban ecological security dynamic analysis based on an innovative emergy ecological footprint method. Environ Dev Sustain 23:16163–16191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01341-z
Zhang S, Shao H, Li X, Xian W, Shao Q, Yin Z, Lai F, Qi J (2022b) Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecological Security Pattern of Urban Agglomerations in Yangtze River Delta Based on LUCC Simulation. Remote Sens 14(2):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020296
Zhang Y, Qiao Q, Liu J, Sang H, Yang D, Zhai L, Li N, Yuan X (2022a) Coastline changes in mainland China from 2000 to 2015. Int J Image Data Fusion 13(1):95–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/19479832.2021.1943011
Zhou D, Lin Z, Ma S, Qi J, Yan T (2021) Assessing an ecological security network for a rapid urbanization region in Eastern China. Land Degrad Dev 32(8):2642–2660. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3932
Zhou R, Lin M, Wu Z, Liu H, Zhong L (2020) Construction of ecological security in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from the perspective of importance of ecosystem services. Ecol Econ 36(7):189–196 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (No. GJJ201419), the Humanities and Social Science Research Planning Project for Universities of Jiangxi Province (No. GL20116), the University Students Innovation Practice Training Program of The Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Climbing Program Special Funds for Science and Technology Innovation Strategy of Guangdong Province (No. pdjh2020b0169), and the Challenge Cup Gold Seed Project of South China Normal University (No. 20DKKA01). The authors thank editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments, suggestions, and help in enhancing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaojun Wang: Data curation, Resources, Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing-original draft preparation, Writing-review and editing; Guangxu Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-review and editing, Supervision, Funding; Churan Zhang, and Yiling Liao: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Drawing, Writing-original draft preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics in publishing
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Liu, G., Zhang, C. et al. Spatial-temporal pattern and urban-rural gradient of comprehensive ecological security in urban agglomeration in South China from 2000 to 2020. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 102474–102489 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29460-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29460-2