Abstract
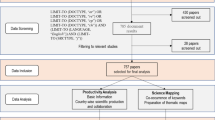
This paper aims at analyzing the research productivity and scientific knowledge discovery of the COVID-19 pandemic in agriculture using a bibliometric analysis approach. A total of 1514 research papers indexed in the Scopus database, covering a period of 2020 to 2022, are processed using VOSviewer and R-Studio software. The analysis of research productivity indicates that the number of research publications on COVID-19 and agriculture has exponentially increased globally, and about 80% of the research papers have been published in the top 10 countries led by the USA, India, and China. The countries are increasingly collaborating in undertaking research on COVID-19 and agriculture. Furthermore, major journals and articles with citations have been extracted to analyze the leading publication avenues and focused areas of research. The science mapping is done using co-occurrence and thematic map. With the help of co-occurrence analysis, six clusters are identified depicting major research themes, i.e., COVID-19 and agricultural supply chain disruption, COVID-19 and human health issues and coping strategies, COVID-19 and non-human and animal health, COVID-19 pandemic and environment and pollution, COVID-19 and healthcare and treatment, and COVID-19 and food nutrition from dairy and meat products. The thematic map analysis identifies potential research areas such as mental health, anxiety, and depression in the agricultural system, which may help in setting future research agenda and help devising policy supports for managing the agriculture sector better during crisis. The paper also highlights the theoretical and practical implications.


Source: analyzed from Scopus database using VOSviewer

Source: analyzed from Scopus database using R-Studio

Source: analyzed from Scopus database using R-Studio

Source: analyzed from Scopus database using VOSviewer

Source: analyzed from Scopus database using VOSviewer

Source: analyzed from Scopus database using R-Studio
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
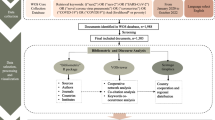
Data has been extracted from the Scopus database.
References
Abdallah MB, Fekete-Farkas M, Lakner Z (2021) Exploring the link between food security and food price dynamics: a bibliometric analysis. Agriculture (switzerland) 11(3):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11030263
Abid A, & Jie S (2021). Impact of COVID‐19 on agricultural food: a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) analysis. Food Frontiers. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/fft2.93
Abugabbara M, Javed S, Bagge H, Johansson D (2020) Bibliographic analysis of the recent advancements in modeling and co-simulating the fifth-generation district heating and cooling systems. Energy and Buildings 224:110260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2020.110260
Ali J, Khan W (2020). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on agricultural wholesale prices in India: a comparative analysis across the phases of the lockdown. J Public Affairs. 20(4). https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2402
Altieri MA, Nicholls CI (2020). Agroecology and the reconstruction of a post-COVID-19 agriculture. J Peasant Studies, 881–898. https://doi.org/10.1080/03066150.2020.1782891
Alvi M, Barooah P, Gupta S, Saini S (2021) Women’s access to agriculture extension amidst COVID-19: insights from Gujarat, India and Dang Nepal. Agric Syst 188(January):103035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.103035
Amjath-Babu TS, Krupnik TJ, Thilsted SH, McDonald AJ (2020) Key indicators for monitoring food system disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic: insights from Bangladesh towards effective response. Food Security 12(4):761–768
Ancog RC, Gregorio GB (2020). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on agriculture production in Southeast Asia: reinforcing transformative change in agricultural food systems (No. 2020–1). Southeast Asian Regional Center for Graduate Study and Research in Agriculture (SEARCA)
Andrieu N, Hossard L, Graveline N, Dugue P, Guerra P, Chirinda N (2021) Covid-19 management by farmers and policymakers in Burkina Faso, Colombia and France: lessons for climate action. Agric Syst 190(January):103092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103092
Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informet 11(4):959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Aristovnik A, Ravšelj D, Umek L (2020) A bibliometric analysis of COVID-19 across science and social science research landscape. Sustainability 12(21):9132. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219132
Arndt C, Davies R, Gabriel S, Harris L, Makrelov K, Robinson S, Levy S, Simbanegavi W, van Seventer D, Anderson L (2020) Covid-19 lockdowns, income distribution, and food security: An analysis for South Africa. Global Food Security 26(July):100410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100410
Arouna A, Soullier G, Mendez del Villar P, Demont M (2020) Policy options for mitigating impacts of COVID-19 on domestic rice value chains and food security in West Africa. Global Food Security 26(July):100405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100405
Azra MN, Kasan NA, Othman R, Noor GAGR, Mazelan S, Jamari Z Bin, Sarà G, Ikhwanuddin M (2021). Impact of COVID-19 on aquaculture sector in Malaysia: findings from the first national survey. Aquaculture Reports19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100568
Balwinder-Singh, Shirsath PB, Jat ML, Mcdonald AJ, Srivastava AK, Craufurd P, Rana DS, Singh AK, Chaudhari SK, Sharma PC, Singh R, Jat HS, Sidhu HS, Gerard B, Braun H (2020) Agricultural labor, COVID-19, and potential implications for food security and air quality in the breadbasket of India. Agri Syst 185(2020):102954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.102954
Barman A, Das R, De PK (2021). Impact of COVID-19 in food supply chain: disruptions and recovery strategy. Curr Res Behav Sci 2(November 2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crbeha.2021.100017
Beckman J, Countryman AM (2021) The importance of agriculture in the economy: impacts from COVID-19. Am J Agr Econ 00(00):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajae.12212
Béné C (2020) Resilience of local food systems and links to food security – a review of some important concepts in the context of COVID-19 and other shocks. Food Security 12(4):805–822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-020-01076-1
Bilan Y, Pimonenko T, Starchenko L (2020) Sustainable business models for innovation and success: Bibliometric analysis. E3S Web of Conferences 159:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202015904037
Block J, Fisch C, Rehan F (2020) Religion and entrepreneurship: a map of the field and a bibliometric analysis. Manag Rev Q 70(4):591–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-019-00177-2
Boughton D, Goeb J, Lambrecht I, Headey D, Takeshima H, Mahrt K, Masias I, Goudet S, Ragasa C, Maredia MK, Minten B, Diao X (2021) Impacts of COVID-19 on agricultural production and food systems in late transforming Southeast Asia the case of Myanmar. Agricultural Systems 188(December 2020):103026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.103026
Campi M, Dueñas M, Fagiolo G (2021) Specialization in food production affects global food security and food systems sustainability. World Development 141:105411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2021.105411
Cariappa AA, Acharya KK, Adhav CA, Sendhil R, Ramasundaram P (2021) Impact of COVID-19 on the Indian agricultural system: a 10-point strategy for post-pandemic recovery. Outlook on Agriculture 50(1):26–33. https://doi.org/10.1177/0030727021989060
Cash R, Patel V (2020) Has COVID-19 subverted global health? The Lancet 395(10238):1687–1688
Castillo-Vergara M, Alvarez-Marin A, Placencio-Hidalgo D (2018) A bibliometric analysis of creativity in the field of business economics. J Bus Res 85(December 2017):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.12.011
Ceballos F, Kannan S, Kramer B (2020a) Impacts of a national lockdown on smallholder farmers’ income and food security: empirical evidence from two states in India. World Development 136:105069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105069
Ceballos F, Kannan S, Kramer B, Ritchie H, Reay D, Higgins P, Chiwona-Karltun L, Amuakwa-Mensah F, Wamala-Larsson C, Amuakwa-Mensah S, Abu Hatab A, Made N, Taremwa NK, Melyoki L, Rutashobya LK, Madonsela T, Lourens M, Stone W, Bizoza AR, Vaziralli S (2020b) COVID-19: From health crises to food security anxiety and policy implications. Agri Syst 12(4):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.103027
Ceballos F, Kannan S, Kramer B (2021) Crop prices, farm incomes, and food security during the COVID-19 pandemic in India: phone-based producer survey evidence from Haryana State. Agric Econ (united Kingdom) 52(3):525–542. https://doi.org/10.1111/agec.12633
Chiwona-Karltun L, Amuakwa-Mensah F, Wamala-Larsson C, Amuakwa-Mensah S, Abu Hatab A, Made N, Taremwa NK, Melyoki L, Rutashobya LK, Madonsela T, Lourens M, Stone W, Bizoza AR (2021) COVID-19: from health crises to food security anxiety and policy implications. Ambio 50(4):794–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-020-01481-y
Das NK, Roy A (2021) COVID-19 and agri-food value chain: a systematic review and bibliometric mapping. Journal of Agribusiness in Developing and Emerging Economies. https://doi.org/10.1108/JADEE-07-2021-0188
de Boef WS, Borman GD, Gupta A, Subedi A, Thijssen MH, Aga AA, Oyee P (2021) Rapid assessments of the impact of COVID-19 on the availability of quality seed to farmers: advocating immediate practical, remedial and preventative action. Agricultural Systems 188:103037
de Rooij MMT, Smit LAM, Erbrink HJ, Hagenaars TJ, Hoek G, Ogink NWM, Winkel A, Heederik DJJ, Wouters IM (2019) Endotoxin and particulate matter emitted by livestock farms and respiratory health effects in neighboring residents. Environ Int 132(August):105009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105009
Deaton BJ, Deaton BJ (2020) Food security and Canada’s agricultural system challenged by COVID-19. Can J Agric Econ 68(2):143–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/cjag.12227
Di Renzo L, Gualtieri P, Pivari F, Soldati L, Attinà A, Cinelli G, Cinelli G, Leggeri C, Caparello G, Barrea L, Scerbo F, Esposito E, De Lorenzo A (2020) Eating habits and lifestyle changes during COVID-19 lockdown: An Italian survey. J Transl Med 18(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-020-02399-5
Di Vaio A, Hasan S, Palladino R, Hassan R (2023) The transition towards circular economy and waste within accounting and accountability models: a systematic literature review and conceptual framework. Environ Dev Sustain 25(1):734–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02078-5
Ding X, Yang Z (2020) Knowledge mapping of platform research: a visual analysis using VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Electron Commerce Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-020-09410-7
Donthu N, Kumar S, Pattnaik D (2020) Forty-five years of Journal of Business Research: a bibliometric analysis. J Bus Res 109(November 2019):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.10.039
ElHawary H, Salimi A, Diab N, Smith L (2020) Bibliometric analysis of early COVID-19 research: the top 50 cited papers. Infect Dis: Res Treatment 13:117863372096293. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178633720962935
Elleby C, Domínguez IP, Adenauer M, Genovese G (2020) Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global agricultural markets. Environ Resource Econ 76(4):1067–1079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-020-00473-6
Fahimnia B, Sarkis J, Davarzani H (2015) Green supply chain management: a review and bibliometric analysis. Int J Prod Econ 162:101–114
Falagas ME, Pitsouni EI, Malietzis GA, Pappas G (2008) Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of science, and google scholar: strengths and weaknesses. FASEB Journal 22(2):338–342
FAO (2020) COVID-19 and rural poverty: Supporting and protecting the rural poor in times of pandemic. Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations, April, 10. http://www.fao.org/3/ca8824en/CA8824EN.pdf
Farrukh M, Javed S, Raza A, Lee JWC (2020) Twenty years of green innovation research: trends and way forward. World J Entrep Manag Sustain Dev 17(3):488–501. https://doi.org/10.1108/WJEMSD-06-2020-0068
Fellnhofer K (2019) Toward a taxonomy of entrepreneurship education research literature: a bibliometric mapping and visualization. Ed Res Rev 27(July 2018):28–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2018.10.002
Ferreira C, Robertson J (2020) Examining the boundaries of entrepreneurial marketing: a bibliographic analysis. J Res Mark Entrep 22(2):161–180. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRME-05-2020-0046
Gong Y, Ma T, Can X, Yang Y, Yang R, Gao LJ, Wu SH, Li J, Yue ML, Liang HG, He X, Yun T (2020) Early research on COVID-19: a bibliometric analysis. The Innovation 1(2):100027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100027
Gray RS (2020) Agriculture, transportation, and the COVID-19 crisis. Can J Agric Econ 68(2):239–243. https://doi.org/10.1111/cjag.12235
Guo J, Mao K, Yuan Z, Qin Z, Xu T, Bateni SM, Zhao Y, Ye C (2021) Global Food Security Assessment during 1961–2019. Sustainability 13(24):14005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132414005
Gupta D, Fischer H, Shrestha S, Ali SS, Chhatre A, Devkota K, Rana P (2021) Dark and bright spots in the shadow of the pandemic: rural livelihoods, social vulnerability, and local governance in India and Nepal. World Development 141:105370
Habanyati EJ, Paramasivam S, Seethapathy P, Jayaraman A, Kedanhoth R, Viswanathan PK, Manalil S (2022) Impact of COVID-19 on the agriculture sector: survey analysis of farmer responses from Kerala and Tamil Nadu States in India. Agronomy 12(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020503
Harris J, Depenbusch L, Pal AA, Nair RM, Ramasamy S (2020) Food system disruption: initial livelihood and dietary effects of COVID-19 on vegetable producers in India. Food Security 12(4):841–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-020-01064-5
Hogerwerf L, Post PM, Bom B, van der Hoek W, van de Kassteele J, Stemerding AM, de Vries W, Houthuijs D (2022) Proximity to livestock farms and COVID-19 in the Netherlands, 2020–2021. Int J Hygiene Environ Health 245(May):114022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2022.114022
Hossain ST (2020) Impacts of COVID-19 on the agri-food sector: Food security policies of Asian productivity organization members. J Agri Sci - Sri Lanka 15(2):116–132. https://doi.org/10.4038/jas.v15i2.8794
Huss M, Brander M, Kassie M, Ehlert U, Bernauer T (2021) Improved storage mitigates vulnerability to food-supply shocks in smallholder agriculture during the COVID-19 pandemic. Global Food Security 28(November 2020):100468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100468
Jaacks LM, Veluguri D, Serupally R, Roy A, Prabhakaran P, Ramanjaneyulu G (2021) Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on agricultural production, livelihoods, and food security in India: baseline results of a phone survey. Food Security. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-021-01164-w
Jha PK, Araya A, Stewart ZP, Faye A, Traore H, Middendorf BJ, Prasad PVV (2021) Projecting potential impact of COVID-19 on major cereal crops in Senegal and Burkina Faso using crop simulation models. Agric Syst 190:103107
Jhajhria A, Kandpal A, Balaji SJ, Jumrani J, Kingsly IT, Kumar K, Singh NP, Birthal PS, Sharma P, Saxena R, Srivastava S, Subash SP, Pal S, Nikam V (2020). COVID-19 lockdown and Indian agriculture: options to reduce the impact, National Institute of Agricultural Economics and Policy Research, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, Government of India. Working Paper, October 2020
Kamath S, Kamath R, Salins P (2020) COVID-19 pandemic in India: Challenges and silver linings. Postgrad Med J 96(1137):422–423. https://doi.org/10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-137780
Kansiime MK, Tambo JA, Mugambi I, Bundi M, Kara A, Owuor C (2021) COVID-19 implications on household income and food security in Kenya and Uganda: findings from a rapid assessment. World Dev 137:105199
Kaya M, Erbay E (2020) Global trends of the researches on COVID-19: a bibliometric analysis via VOSviewer COVID-19 Araştırmalarının Küresel Eğilimleri: VOSviewer ile Bibliyometrik Analiz. ASBD) J Ankara Health Sci 5989:201–216
Kerr WA (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic and agriculture: Short- and long-run implications for international trade relations. Can J Agric Econ 68(2):225–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/cjag.12230
Kumar P, Kumar Singh R (2022) Strategic framework for developing resilience in agri-food supply chains during COVID 19 pandemic. Int J Log Res Appl 25(11):1401–1424. https://doi.org/10.1080/13675567.2021.1908524
Kumar A, Padhee AK, Kumar S (2020) How Indian agriculture should change after COVID-19. Food Security 12(4):837–840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-020-01063-6
Kumar P, Singh SS, Pandey AK, Singh RK, Srivastava PK, Kumar M, Dubey SK, Sah U, Nandan R, Singh SK, Agrawal P, Kushwaha A, Rani M, Biswas JK, Drews M (2021) Multi-level impacts of the COVID-19 lockdown on agricultural systems in India: the case of Uttar Pradesh. Agricultural Systems 187(December 2020):103027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.103027
Leung XY, Sun J, Bai B (2017) Bibliometrics of social media research: a co-citation and co-word analysis. Int J Hosp Manag 66:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2017.06.012
Lioutas ED, Charatsari C (2021) Enhancing the ability of agriculture to cope with major crises or disasters: What the experience of COVID-19 teaches us. Agricultural Systems 187(August 2020):103023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.103023
Loayza N, Pennings SM (2020). Macroeconomic policy in the time of COVID-19: a primer for developing countries. World Bank Res Policy Briefs (147291)
Lopez-Ridaura S, Sanders A, Barba-Escoto L, Wiegel J, Mayorga-Cortes M, Gonzalez-Esquivel C, García-Barcena TS (2021) Immediate impact of COVID-19 pandemic on farming systems in Central America and Mexico. Agricultural Systems 192:103178
Mahajan K, Tomar S (2021) COVID-19 and supply chain disruption: evidence from food markets in India†. Am J Agr Econ 103(1):35–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajae.12158
Mahmud M, Riley E (2021) Household response to an extreme shock: evidence on the immediate impact of the Covid-19 lockdown on economic outcomes and well-being in rural Uganda. World Development 140(March 2020):105318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105318
Malahayati M, Masui T, Anggraeni L (2021) An assessment of the short-term impact of COVID-19 on economics and the environment: a case study of Indonesia. Economia 22(3):291–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econ.2021.12.003
Mao X, Guo L, Fu P, Xiang C (2020) The status and trends of coronavirus research: A global bibliometric and visualized analysis. Medicine 99(22):e20137. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000020137
Merigó JM, Pedrycz W, Weber R, de la Sotta C (2018) Fifty years of information sciences: a bibliometric overview. Inf Sci 432:245–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.11.054
Meuwissen MPM, Feindt PH, Slijper T, Spiegel A, Finger R, de Mey Y, Reidsma P (2021) Impact of Covid-19 on farming systems in Europe through the lens of resilience thinking. Agricultural Systems 191:103152
Mikhael EM, Al-Jumaili AA (2020) Can developing countries face novel coronavirus outbreak alone? The Iraqi situation. Public Health in Practice 1(March):100004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhip.2020.100004
Modak TS, Baksi S, Johnson D (2020) Impact of Covid-19 on Indian Villages. Rev Agr Stud 10(1):181–203
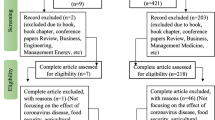
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Altman D, Antes G, Atkins D, Barbour V, Barrowman N, Berlin JA, Clark J, Clarke M, Cook D, D’Amico R, Deeks JJ, Devereaux PJ, Dickersin K, Egger M, Ernst E, … Tugwell P (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Most F, Conejo FJ, Cunningham LF (2018) Bridging past and present entrepreneurial marketing research: a co-citation and bibliographic coupling analysis. J Res Mark Entrep 20(2):229–251. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRME-11-2017-0049
Mukhra R, Krishan K, Kanchan T (2020) COVID-19 sets off mass migration in India. Arch Med Res 51(7):736–738
Nicola M, Alsafi Z, Sohrabi C, Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A, Iosifidis C, Agha M, Agha R (2020) The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): a review. Int J Surg 78(March):185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.018
Niebla-Zatarain JC, Pinedo-De-Anda FJ, Leyva-Duarte E (2020) Entrepreneurship on family business: bibliometric overview (2005–2018). J Intell Fuzzy Syst 38(5):5589–5604. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-179649
Niknejad N, Ismail W, Bahari M, Hendradi R, Salleh AZ (2021) Mapping the research trends on blockchain technology in food and agriculture industry: a bibliometric analysis. Environ Technol Innov 21:101272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101272
Niles MT, Bertmann F, Belarmino EH, Wentworth T, Biehl E, Neff R (2020) The early food insecurity impacts of COVID-19. Nutrients 12(7):2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072096
O’Hara S, Toussaint EC (2021) Food access in crisis: Food security and COVID-19. Ecological Economics 180(June 2020):106859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2020.106859
Okolie CC, Ogundeji AA (2022) Effect of COVID-19 on agricultural production and food security: a scientometric analysis. Humanit Social Sci Commun 9(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01080-0
Park Y, Shin Y-W (2022) Trend analysis of balcony vegetable gardens in Korea, before and after COVID-19 pandemic using big data. J Human Plant Environ 25(5):447–456
Popescu GC, Popescu M (2022) COVID-19 pandemic and agriculture in Romania: effects on agricultural systems, compliance with restrictions and relations with authorities. Food Security 14(2):557–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-021-01239-8
Poudel K, Subedi P (2020) Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on socioeconomic and mental health aspects in Nepal. Int J Soc Psychiatry 66(8):748–755. https://doi.org/10.1177/0020764020942247
Pu M, Zhong Y (2020) Rising concerns over agricultural production as COVID-19 spreads: lessons from China. Global Food Security 26(May):100409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100409
Rad AK, Shamshiri RR, Azarm H, Balasundram SK, Sultan M (2021) Effects of the covid-19 pandemic on food security and agriculture in Iran: A survey. Sustainability (Switzerland) 13(18). https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810103
Radhakrishnan S, Erbis E, Isaacs J, Kamarthi S (2017) Novel keyword co-occurrence network- based methods to foster systematic reviews of scientific literature. PLoS ONE 12(3):172778
Rasul G (2021) Twin challenges of COVID-19 pandemic and climate change for agriculture and food security in South Asia. Environ Challenges 2(January):100027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100027
Rawal V, Kumar M, Verma A, Pais J (2020) COVID-19 Lockdown: Impact on agriculture and rural economy. Social scientist, March–June 2020 Vol. 48, No. 3/6 (562–565) (March–June 2020), pp 67–82
Reardon T, Mishra A, Nuthalapati CSR, Bellemare MF, Zilberman D (2020) Covid-19’s disruption of India’s transformed food supply chains. Econ Pol Wkly 55(18):18–22
Ronaghi M (2022) Effects of COVID-19 on Iran’s livestock and meat market. J Agric Sci Technol 24(5):1017–1028
Rukasha T, Nyagadza B, Pashapa R, Muposhi A (2021) Covid-19 impact on Zimbabwean agricultural supply chains and markets: a sustainable livelihoods perspective. Cogent Social Sci 7(1):1928980
Sapbamrer R, Sittitoon N, La-up A, Pakvilai N, Chittrakul J, Sirikul W, Kitro A, Hongsibsong S (2022) Changes in agricultural context and mental health of farmers in different regions of Thailand during the fifth wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Public Health 22(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14464-3
Selim T, Eltarabily MG (2022) Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on small-scale farming in Northeastern Nile Delta of Egypt and learned lessons for water conservation potentials. Ain Shams Eng J 13(4):101649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2021.11.018
Shah SHH, Lei S, Ali M, Doronin D, Hussain ST (2020) Prosumption: bibliometric analysis using HistCite and VOSviewer. Kybernetes 49(3):1020–1045. https://doi.org/10.1108/K-12-2018-0696
Sharma R, Shishodia A, Kamble S, Gunasekaran A, Belhadi A (2020) Agriculture supply chain risks and COVID-19: mitigation strategies and implications for the practitioners. Int J Logist Res App 0(0):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/13675567.2020.1830049
Siche R (2020) What is the impact of COVID-19 disease on agriculture? Scientia Agropecuaria 11(1):3–9. https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2020.01.00
Štreimikienė D, Baležentis T, Volkov A, Ribašauskienė E, Morkūnas M, Žičkienė A (2022) Negative effects of covid-19 pandemic on agriculture: systematic literature review in the frameworks of vulnerability, resilience and risks involved. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istrazivanja 35(1):529–545. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2021.1919542
Subramanian M, Shanmuga Vadivel K, Hatamleh WA, Alnuaim AA, Abdelhady M, Sathishkumar VE (2022) The role of contemporary digital tools and technologies in COVID-19 crisis: an exploratory analysis. Expert Syst 39(6):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12834
Temesgen F, Wakjira M, Abirham A (2022) Assessing the economic impact of the coronavirus pandemic on the production and distribution of livestock across value chain approach: the case of Kellem Wollega Zone, Oromia National Regional State. Ethiopia Int J Rural Manag 18(1):39–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/0973005221993369
Thanh PT, The Duy D, Bao Duong P (2022) Disruptions to agricultural activities, income loss and food insecurity during the COVID-19 pandemic: evidence from farm households in a developing country. J Agribus Dev Emerging Econ 12(3):531–547. https://doi.org/10.1108/JADEE-09-2021-0243
Thapa Magar DB, Pun S, Pandit R, Rola-Rubzen MF (2021) Pathways for building resilience to COVID-19 pandemic and revitalizing the Nepalese agriculture sector. Agricultural Systems 187(December 2020):103022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.103022
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2017) Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 111(2):1053–1070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2300-7
Varshney D, Joshi PK, Roy D, Kumar A (2020) PMKISAN and the adoption of modern agricultural technologies. Econ Pol Wkly 55(23):49
Varshney D, Kumar A, Mishra AK, Rashid S, Joshi PK (2021) India’s COVID-19 social assistance package and its impact on the agriculture sector. Agric Syst 189:103049
Verma S, Gustafsson A (2020) Investigating the emerging COVID-19 research trends in the field of business and management: a bibliometric analysis approach. J Bus Res 118(July):253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.06.057
Wang P, Tian D (2021) Bibliometric analysis of global scientific research on COVID-19. J Biosafety and Biosecurity 3(1):4–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobb.2020.12.002
Wannaprasert P, Choenkwan S (2021). Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on ginger production: supply chains, labor, and food security in Northeast Thailand. Forest and Society, 120–135
Wassler P, Talarico C (2021) Sociocultural impacts of COVID-19: a social representations perspective. Tourism Manag Perspectives 38(April):100813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100813
Yadav S, Luthra S, Garg D (2022) Internet of things (IoT) based coordination system in agri-food supply chain: development of an efficient framework using DEMATEL-ISM. Oper Manag Res 15(1–2):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-020-00164-x
Yang F, Zhang S, Wang Q, Zhang Q, Han J, Wang L, Wu X, Xue F (2020) Analysis of the global situation of COVID-19 research based on bibliometrics. Health Inf Sci Syst 8(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-020-00120-w
Yang H, Liu L, Yang W, Liu H, Ahmad W, Ahmad A, Aslam F, Joyklad P (2022) A comprehensive overview of geopolymer composites: a bibliometric analysis and literature review. Case Studies Constr Mater 16(August 2021):e00830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00830
Yao H, Zuo X, Zuo D, Lin H, Huang X, Zang C (2020) Study on soybean potential productivity and food security in China under the influence of COVID-19 outbreak. Geogr Sustain 1(2):163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geosus.2020.06.002
Yu Y, Li Y, Zhang Z, Gu Z, Zhong H, Zha Q, Yang L, Zhu C, Chen E (2020). A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer of publications on COVID-19. Annals of
Zahraee SM, Shiwakoti N, Stasinopoulos P (2022) Agricultural biomass supply chain resilience: COVID-19 outbreak vs. sustainability compliance, technological change, uncertainties, and policies. Cleaner Logist Supply Chain 4(April):100049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clscn.2022.100049
Zaręba A, Krzemińska A, Kozik R (2021) Urban Vertical Farming as an Example of Nature-Based Solutions Supporting a Healthy Society Living in the Urban Environment. Resources 10(11):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources10110109
Zhan Y, Chen KZ (2021). Building resilient food system amidst COVID-19: responses and lessons from China. Agric Syst 190(January 2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103102
Zhao G, Liu S, Lopez C, Chen H, Lu H, Kumar S, Mangla, Elgueta S (2020) Risk analysis of the agri-food supply chain: a multi-method approach. Int J Prod Res 58(16):4851–4876. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1725684
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jabir Ali: conceptualization, methodology, accessing the Scopus database, formal analysis and investigation, writing—original draft preparation, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, J. Mapping scientific knowledge discovery on COVID-19 pandemic and agriculture: a bibliometric analysis and future research directions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 95155–95171 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29238-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29238-6