Abstract
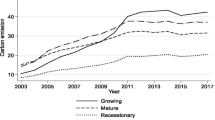
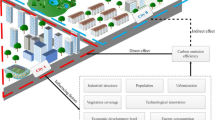
As an important part of regional coordinated development, the high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin has become a national strategy. It is imminent for resource-based cities to perform a high-quality transformation. The analysis of carbon emission efficiency in the Yellow River Basin includes the examination of spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and the main driving factors. This is done by utilizing the super-efficiency SBM-DEA and panel Tobit regression models, with the assistance of night light data. Our findings are as follows: (1) Carbon emissions continue to grow. The “Jiziwan” basin is an area where plenty of high-emitting cities agglomerate. The carbon emission of resource-based cities presents a W-shaped pattern in time. (2) In time, the carbon emission efficiency follows a U-shaped curve. Spatially, the carbon emission efficiency in the middle reaches is comparatively low, whereas it is relatively high in both the upper and lower reaches. And that in high carbon-emitting resource-based cities are in the low to medium range. (3) Carbon emission efficiency has a significant negative relationship with energy intensity, urbanization rate, and population density and a significant positive relationship with industrial proportion. Energy intensity is the most direct driving force. That is to say, we can increase carbon emission efficiency effectively by reducing energy intensity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, Liyan Zhang, upon reasonable request.
References
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2:429–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8
Chen L, Li X, Yang Y, Wang M (2021a) Analyzing the features of energy consumption and carbon emissions in the upper Yangtze River Economic Zone. Greenh Gases Sci Technol 11:573–589. https://doi.org/10.1002/ghg.2067
Chen Y, Wong CWY, Yang R, Miao X (2021b) Optimal structure adjustment strategy, emission reduction potential and utilization efficiency of fossil energies in China. Energy 237:121623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121623
Du KR, Lin BQ, Xie CP (2017) Exploring change in China’s carbon intensity: a decomposition approach. Sustainability 9(2):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9020296
Elvidge CD, Baugh KE, Kihn EA et al (1997) Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int J Remote Sens 18:1373–1379. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311697218485
Elvidge CD, Ziskin D, Baugh KE et al (2009) A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2(3):595–663. https://doi.org/10.3390/en20300595
Gao H, Zhang H (2021) Study on coordination and quantification of ecological protection and high quality development in the Yellow River Basin. IOP Conf. Ser: Earth Environ Sci 647:12168. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/647/1/012168
Gao P, Yue S, Chen H (2021) Carbon emission efficiency of China’s industry sectors: from the perspective of embodied carbon emissions. J Clean Prod 283:124655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124655
Hu K, Qi KL, Guan QF et al (2017) A scientometric visualization analysis for night-time light remote sensing research from 1991 to 2016. Remote Sens 9(8):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080802
Li QY, Zeng FE, Liu SH et al (2021) The effects of China’s sustainable development policy for resource-based cities on local industrial transformation. Resour Policy 71:101940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101940
Li XC, Zhou YY (2017) A stepwise calibration of global DMSP/OLS stable nighttime light data (1992–2013). Remote Sens 9(6):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060637
Liu S, Xia XH, Tao F et al (2018) Assessing urban carbon emission efficiency in China: based on the global data envelopment analysis. Clean Energy Clean Cities 152:762–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.09.242
Liu Y, Lin BQ, Xu B (2021) Modeling the impact of energy abundance on economic growth and CO2 emissions by quantile regression: evidence from China. Energy 227:120416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120416
Man DC, Tsubasa H, Fukui H (2021) Normalization of VIIRS DNB images for improved estimation of socioeconomic indicators. Int J Digit Earth 14:540–554. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2020.1849438
Mellander C, Lobo J, Stolarick K, Matheson Z (2015) Night-time light data: a good proxy measure for economic activity? PLoS One 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139779
Meng X, Han J, Huang C (2017) An improved vegetation adjusted nighttime light urban index and its application in quantifying spatiotemporal dynamics of carbon emissions in China. Remote Sens 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080829
Perez K, Gonzalez-Araya MC, Iriarte A (2017) Energy and GHG emission efficiency in the Chilean manufacturing industry: sectoral and regional analysis by DEA and Malmquist indexes. Energ Econ 66:290–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.05.022
Shen L, Du X, Cheng G et al (2021) Capability maturity model (CMM) method for assessing the performance of low-carbon city practice. Environ Impact Assess 87:106549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2020.106549
Sheng PF, Li J, Zhai MX et al (2020) Coupling of economic growth and reduction in carbon emissions at the efficiency level: evidence from China. Energy 213:118747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118747
Shi KF, Chen Y, Yu BL et al (2016) Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl Energy 168:523–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.11.055
Song M, Hao XG, Li DD et al (2021a) Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and driving forces of mining industry agglomeration in the Yellow River Basin. Coal Eng 53(9):165–172
Song M, Hao XG, Liu JB (2021b) Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of carbon balance and decoupling effect of economic growth in the Yellow River Basin. Urban Probl 7:91–103. https://doi.org/10.13239/j.bjsshkxy.cswt.210710
Su ZX, Zhang GX, Xu L et al (2021) Carbon emission performance in logistics in the Yellow River Basin. Desalin Water Treat 220:14–21. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27072
Sun JW (2005) The decrease of CO2 emission intensity is decarbonization at national and global levels. Energy Policy 33:975–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2003.10.023
Sun XM, Zhang HT, Ahmad M et al (2022) Analysis of influencing factors of carbon emissions in resource-based cities in the Yellow River basin under carbon neutrality target. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(16):23847–23860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17386-6
Teng XY, Liu FP, Chiu YH (2021) The change in energy and carbon emissions efficiency after afforestation in China by applying a modified dynamic SBM model. Energy 216:119301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119301
Tobin J (1958) Estimation of Relationships for Limited Dependent Variables. Econometrica 26(1):24–36. https://doi.org/10.2307/1907382
Vujovic T, Petkovic Z, Pavlovic M et al (2018) Economic growth based in carbon dioxide emission intensity. Physicaa 506:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2018.04.074
Wang Y, Xu Z, Zhang Y (2019) Influencing factors and combined scenario prediction of carbon emission peaks in megacities in China: based on Threshold-STIRPAT Model. Acta Sci Circumst 39(12):4284–4292. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0290
Wang Q, Chiu YH, Chiu CR (2015) Driving factors behind carbon dioxide emissions in China: a modified production-theoretical decomposition analysis. Energ Econ 51:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2015.07.009
Wang RZ, Hao JX, Wang CA et al (2020) Embodied CO2 emissions and efficiency of the service sector: Evidence from China. J Clean Prod 247:119116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119116
Wang S, Li Q, Fang C et al (2016) The relationship between economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from China. Sci Total Environ 542:360–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.027
Wang SJ, Liu XP (2017) China’s city-level energy-related CO2 emissions: spatiotemporal patterns and driving forces. Appl Energy 200:204–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.05.085
Wang YD (2021) Analysis on the changes and differences of carbon emissions in different industries based on the research of various provinces in China. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 804(4):42007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/804/4/042007
Wen L, Li ZK (2019) Exploring the driving forces for emission reduction strategies in Henan by combining spectral clustering with two-layer LMDI decomposition. Environ Sci Pollut R 26(28):29246–29256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06093-y
Xie SD, Mo XG, Hu S et al (2020) Contributions of climate change, elevated atmospheric CO2 and human activities to ET and GPP trends in the Three-North Region of China. Agric For Meteorol 295(10):108183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2020.108183
Xu GY, Dong HY, Xu ZC et al (2022) China can reach carbon neutrality before 2050 by improving economic development quality. Energy 243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.123087
Yuan XL, Sheng XR, Chen LP et al (2022) Carbon footprint and embodied carbon transfer at the provincial level of the Yellow River Basin. Sci Total Environ 803:149993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149993
Zhang CQ, Chen PY (2021) Industrialization, urbanization, and carbon emission efficiency of Yangtze River Economic Belt—empirical analysis based on stochastic frontier model. Environ Sci Pollut R 28(47):66914–66929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15309-z
Zhang GX, Zhang PD, Zhang ZG et al (2019) Impact of environmental regulations on industrial structure upgrading: an empirical study on Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. J Clean Prod 238:117848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117848
Zhang LL, Xiong LC, Cheng BD et al (2018) How does foreign trade influence China’s carbon productivity? Based on panel spatial lag model analysis. Struct Chang Econ D 47:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2018.08.008
Zhang ML, Liu Y (2022) Influence of digital finance and green technology innovation on China’s carbon emission efficiency: empirical analysis based on spatial metrology. Sci Total Environ 838:156463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156463
Zhang N, Yu K, Chen ZF (2017) How does urbanization affect carbon dioxide emissions? a cross-country panel data analysis. Energ Policy 107:678–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.03.072
Zhang X, Li M, Li Q et al (2021) Spatial threshold effect of industrial land use efficiency on industrial carbon emissions: a case study in China. Int J Env Res Pub He 18(17):9368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179368
Zhou YJ, Ji P (2019) Research on the impact of industrial upgrade and financial resource allocation efficiency on carbon emissions—based on provincial spatial panel data analysis. East China Econo Manag 33(12):59–68. https://doi.org/10.19629/j.cnki.34-1014/f.190415018
Zhou G, Jia B, Tao X et al (2020) Estimation of karst carbon sink and its contribution to CO2 emissions over a decade using remote sensing imagery. Appl Geochem 121(12):104689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104689
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the editors and the reviewers for their helpful suggestions and comments.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Laboratory of Carrying Capacity Assessment for Resource and Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources (Grant No. CCA2019.16), China Academy of Engineering (Grant No. 2017-ZD-03), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (Grant No. NCET-11-0731), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2022YJSGL08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mei Song: conceptualization, writing-review and editing, supervision, and project administration; Yujin Gao: writing-original draft and validation; Liyan Zhang: methodology, writing-original draft, software, and visualization; Furong Dong: writing-original draft and validation; Xinxin Zhao: visualization and formal analysis; Jin Wu: data curation, resources, and investigation
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors are in agreement with the publishment.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, ., Gao, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of carbon emission efficiency of resource-based cities in the Yellow River Basin of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 96795–96807 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29113-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29113-4