Abstract
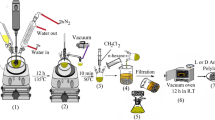
Dye-contaminated water has caused a worldwide pollution, which is threatening aquatic organisms and human health. In this work, a pressure-driven foam adsorbent (PFA) was bioinspired from the tapestry turban for purifying the dye-contaminated water. The PFA was prepared using an one-step method from nanocellulose (NC), amino-functionalized ZIF-8 (ZIF-8-NH2), and high resilience polyurethane foam (PUF). It was applied to efficiently remove methyl orange (MO) and crystal violet (CV) dyes from dye-contaminated waste solutions. The maximum adsorption capacity of PFA for MO and CV was 225.9 mg/g (25 °C, pH = 2) and 41.6 mg/g (25 °C, pH = 10), respectively, which were acceptable as compared with the reported works. The dyes could be efficiently removed from various river water samples. After 5 cycles, the removal efficiencies of MO and CV decreased from 92.0% and 85.7% to 84.7% and 76.1%, respectively. Moreover, the PFA relied on pressure-driven force to release the purified water under a low pressure.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Abd Rashid R, Jawad AH, MohdIshak MA, Kasim NN (2018) FeCl3-Activated Carbon Developed from Coconut Leaves: Characterization and Application for Methylene Blue Removal. Sains Malays 47:603–610. https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2018-4703-22
Akdemir M, Isik B, Cakar F, Cankurtaran O (2022) Comparison of the adsorption efficiency of cationic (Crystal Violet) and anionic (Congo Red) dyes on Valeriana officinalis roots: Isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamic studies, and error functions. Mater Chem Phys 291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126763
Arica TA, Balci FM, Balci S, Arica MY (2022) Highly porous poly(o-Phenylenediamine) loaded magnetic carboxymethyl cellulose hybrid beads for removal of two model textile dyes. Fibers and Polymers 23:2838–2854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-0221-4
Bayramoglu G, Arica MY (2020) Modification of epoxy groups of poly(hydroxylmethyl methacrylate-co-glycidyl methacrylate) cryogel with H(3)PO(4) as adsorbent for removal of hazardous pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:43340–43358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10170-y
Bayramoglu G, Arica MY (2021) Grafting of regenerated cellulose films with fibrous polymer and modified into phosphate and sulfate groups: application for removal of a model azo-dye. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126173
Bayramoglu G, Kunduzcu G, Arica MY (2019) Preparation and characterization of strong cation exchange terpolymer resin as effective adsorbent for removal of disperse dyes. Polym Eng Sci 60:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25272
Chang CW, Kao YH, Shen PH, Kang PC, Wang CY (2020) Nanoconfinement of metal oxide MgO and ZnO in zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-8 for CO(2) adsorption and regeneration. J Hazard Mater 400:122974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122974
Chen X, Huang Z, Luo S-Y, Zong M-H, Lou W-Y (2021) Multi-functional magnetic hydrogels based on Millettia speciosa Champ residue cellulose and Chitosan: Highly efficient and reusable adsorbent for Congo red and Cu2+ removal. Chem Eng J 423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130198
Cuong DV, Hou C-H (2022) Engineered biochar prepared using a self-template coupled with physicochemical activation for highly efficient adsorption of crystal violet. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2022.104533
Gonder ZB, Vergili I, Kaya Y, Barlas H (2010) Adsorption of cationic and anionic surfactants onto organic polymer resin Lewatit VPOC 1064 MD PH. Environ Geochem Health 32:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-010-9297-7
Gopi S, Pius A, Thomas S (2016) Enhanced adsorption of crystal violet by synthesized and characterized chitin nano whiskers from shrimp shell. J Water Process Eng 14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.07.010
Han Y, Xu Z, Gao C (2013) Ultrathin Graphene Nanofiltration Membrane for Water Purification. Adv Funct Mater 23:3693–3700. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201202601
Hong HJ, Lim JS, Hwang JY, Kim M, Jeong HS, Park MS (2018) Carboxymethlyated cellulose nanofibrils(CMCNFs) embedded in polyurethane foam as a modular adsorbent of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 195:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.081
Hong YL, Sun J, Fang XQ, Liu QW, Wang C, Liu CM (2023) beta-Cyclodextrin network crosslinked by novel phosphonium-based tetrakiscarboxylic acid derived from PH(3) tail gas: Synthesis and application for rapid removal of organic dyes from wastewater. Carbohydr Polym 316:121059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121059
Huang R, Liu Q, Huo J, Yang B (2017) Adsorption of methyl orange onto protonated cross-linked chitosan. Arab J Chem 10:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.05.017
Huang X, De Hoop CF, Xie J, Wu Q, Boldor D, Qi J (2018) High bio-content polyurethane (PU) foam made from bio-polyol and cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) via microwave liquefaction. Mater Des 138:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.10.058
Huang H, Guo T, Wang K, Li Y, Zhang G (2021) Efficient activation of persulfate by a magnetic recyclable rape straw biochar catalyst for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in water. Sci Total Environ 758:143957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143957
Kim D, Kim J, Lee K-W, Lee TS (2019) Removal of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate using surface-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mat 275:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.09.007
Kumari S, Chauhan GS, Ahn JH (2016) Novel cellulose nanowhiskers-based polyurethane foam for rapid and persistent removal of methylene blue from its aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 304:728–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.008
Li K, Li X, Li B (2022) Investigation the adsorption behavior of functional carbon-based composites for efficient removing anions / cations in single and multicomponent systems. Sep Purif Technol 289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120737
Liu L, Gao ZY, Su XP, Chen X, Jiang L, Yao JM (2015) Adsorption Removal of Dyes from Single and Binary Solutions Using a Cellulose-based Bioadsorbent. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:432–442. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500848m
Liu L, Wu Y, Zhu Z (2017a) Internal structure and crystallinity investigation of segmented thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer degradation in supercritical methanol. Polym Degrad Stabil 140:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.03.003
Liu Y, Luo F, Liu S, Liu S, Lai X, Li X, Lu Y, Li Y, Hu C, Shi Z, Zheng Z (2017b) Aminated graphene oxide impregnated with photocatalytic polyoxometalate for efficient adsorption of dye pollutants and its facile and complete photoregeneration. Small 13. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201603174
Liu H, Chen M, Wei D, Ma Y, Wang F, Zhang Q, Shi J, Zhang H, Peng J, Liu G, Zhang S (2020) Smart Removal of Dye Pollutants via Dark Adsorption and Light Desorption at Recyclable Bi(2)O(2)CO(3) Nanosheets Interface. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:20490–20499. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c02848
Lu Y, Li S, Chen F, Ma H, Gao C, Xue L (2022) Development of coin-shaped ZIF-7 functionalized superhydrophobic polysulfone composite foams for continuous removal of oily contaminants from water. J Hazard Mater 421:126788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126788
Ma X, Lou Y, Chen X-B, Shi Z, Xu Y (2019) Multifunctional flexible composite aerogels constructed through in-situ growth of metal-organic framework nanoparticles on bacterial cellulose. Chem Eng J 356:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.034
Ma H, Wang Z, Zhang XF, Ding M, Yao J (2021) In situ growth of amino-functionalized ZIF-8 on bacterial cellulose foams for enhanced CO(2) adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 270:118376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118376
Mohammed N, Lian H, Islam MS, Strong M, Shi Z, Berry RM, Yu H-Y, Tam KC (2021) Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes using functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chem Eng J. 417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129237
Momina, Ahmad K (2022) Remediation of anionic dye from aqueous solution through adsorption on polyaniline/FO nanocomposite-modelling by artificial neural network (ANN). J Mol Liq 360 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119497
Ncibi MC, Gaspard S, Sillanpaa M (2015) As-synthesized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the removal of ionic and non-ionic surfactants. J Hazard Mater 286:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.039
Ni W, Xiao X, Geng W, Zhang L, Li Y, Li N (2021) Controllable preparation of amino-functionalized ZIF-8: a functionalized MOF material for adsorbing Congo Red and Eriochrome Black T in aqueous solution. JCIS Open 3 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jciso.2021.100018
Nie J, Xie H, Zhang M, Liang J, Nie S, Han W (2020) Effective and facile fabrication of MOFs/cellulose composite paper for air hazards removal by virtue of in situ synthesis of MOFs/chitosan hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym 250:116955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116955
Oliveira JMS, de Lima ESMR, Issa CG, Corbi JJ, Damianovic M, Foresti E (2020) Intermittent aeration strategy for azo dye biodegradation: a suitable alternative to conventional biological treatments? J Hazard Mater 385:121558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121558
Parale VG, Lee K-Y, Jung H-N-R, Nah H-Y, Choi H, Kim T-H, Phadtare VD, Park H-H (2018) Facile synthesis of hydrophobic, thermally stable, and insulative organically modified silica aerogels using co-precursor method. Ceram Int 44:3966–3972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.189
Putri KNA, Keereerak A, Chinpa W (2020) Novel cellulose-based biosorbent from lemongrass leaf combined with cellulose acetate for adsorption of crystal violet. Int J Biol Macromol 156:762–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.100
Qiu C, Tang Q, Zhang X, Li M-C, Zhang X, Xie J, Zhang S, Su Z, Qi J, Xiao H, Chen Y, Jiang Y, de Hoop CF, Huang X (2022) High-efficient double-cross-linked biohybrid aerogel biosorbent prepared from waste bamboo paper and chitosan for wastewater purification. J Clean Prod 338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130550
Rafieian F, Jonoobi M, Yu Q (2019) A novel nanocomposite membrane containing modified cellulose nanocrystals for copper ion removal and dye adsorption from water. Cellulose 26:3359–3373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02320-4
Ran J, Chen H, Bi S, Guo Q, Yan C, Tang X, Cheng D, Cai G, Wang X (2021) Polydopamine-induced in-situ growth of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/TiO2 nanoparticles on cotton fabrics for photocatalytic performance. Prog Org Coat 152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.106123
Ren L, Tang Z, Du J, Chen L, Qiang T (2021) Recyclable polyurethane foam loaded with carboxymethyl chitosan for adsorption of methylene blue. J Hazard Mater 417:126130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126130
Schejn A, Balan L, Falk V, Aranda L, Medjahdi G, Schneider R (2014) Controlling ZIF-8 nano- and microcrystal formation and reactivity through zinc salt variations. CrystEngComm 16:4493–4500. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ce42485e
Sun E, Jiang Y, Wang B, Wang X, Zhao F (2022) Synthesis of catechol-polyethyleneimine nano/submicro-particles via mussel-inspired chemistry for highly efficient removal of methyl orange. Powder Technol 403 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117396
Tang Q, Qiu C, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Yuan Z, Tan H, Wang L, de Hoop CF, Qi J, Huang X (2022) Effective Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium from Wastewater by Nanocellulose/Alum/Chitosan/Polyethyleneimine Biohybrid Aerogel Beads Adsorbent. J Polym Environ 31:1129–1143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02664-2
Tian F, Cerro AM, Mosier AM, Wayment-Steele HK, Shine RS, Park A, Webster ER, Johnson LE, Johal MS, Benz L (2014) Surface and Stability Characterization of a Nanoporous ZIF-8 Thin Film. J Phys Chem C 118:14449–14456. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp5041053
Tkaczyk A, Mitrowska K, Posyniak A (2020) Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review. Sci Total Environ 717:137222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137222
Vinothkumar K, Shivanna Jyothi M, Lavanya C, Sakar M, Valiyaveettil S, Balakrishna RG (2022) Strongly co-ordinated MOF-PSF matrix for selective adsorption, separation and photodegradation of dyes. Chem Eng J 428 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132561
Wang J, Wu L, Li J, Tang D, Zhang G (2018) Simultaneous and efficient removal of fluoride and phosphate by Fe-La composite: Adsorption kinetics and mechanism. J Alloy Compd 753:422–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.177
Wang Y, Wang K, Lin J, Xiao L, Wang X (2020) The preparation of nano-MIL-101(Fe)@chitosan hybrid sponge and its rapid and efficient adsorption to anionic dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 165:2684–2692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.073
Wei X, Chen D, Wang L, Ma Y, Yang W (2022) Carboxylate-functionalized hollow polymer particles modified polyurethane foam for facile and selective removal of cationic dye. Appl Surf Sci 579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.152153
Wjihi S, Peres EC, Dotto GL, Lamine AB (2019) Physicochemical assessment of crystal violet adsorption on nanosilica through the infinity multilayer model and sites energy distribution. J Mol Liq 280:58–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.064
Xiao J, Lv W, Xie Z, Tan Y, Song Y, Zheng Q (2016) Environmentally friendly reduced graphene oxide as a broad-spectrum adsorbent for anionic and cationic dyes via π–π interactions. J Mater Chem A 4:12126–12135. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta04119a
Xin X, Jing Y, Li P, Zhang X, Li J, Li L, Zhang L (2023) Imidazole-Based Metal-Organic Framework for the “On1–Off–On2” Fluorescence-Based Detection of Picric Acid and the Adsorption of Congo Red. Cryst Growth Des. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.2c01186
Xiong Y, Deng N, Wu X, Zhang Q, Liu S, Sun G (2022) De novo synthesis of amino-functionalized ZIF-8 nanoparticles: Enhanced interfacial compatibility and pervaporation performance in mixed matrix membranes applying for ethanol dehydration. Sep Purif Technol 285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120321
Yagub MT, Sen TK, Afroze S, Ang HM (2014) Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 209:172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002
Yan J, Ma M, Liu K, Bao Y, Li F (2023) Anchoring NH2-MIL-101(Fe/Ce) within Melamine Sponge Boosts Rapid Adsorption and Recovery of Phosphate from Water. ACS EST Engg. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestengg.2c00324
Yin Z, Cui C, Chen H, Duoni YuX, Qian W (2020) The Application of Carbon Nanotube/Graphene-Based Nanomaterials in Wastewater Treatment. Small 16:e1902301. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201902301
Zaki M, Atiqah MSN, Khalil HPSA, Ikram H, Alfatah T, Mistar EM, Adisalamun A, Yahya EB (2022) Microbial enhancement of nanocellulose isolation from sawn timber industrial wastes and fabrication of biocomposite membranes. Bioresour Technol Rep 20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2022.101242
Zhang J, Li Y, Dai Y, Lin T, Shao H, Liu Y, Liu X (2023a) Three-dimensional porous hydrogel based on hyperbranched polyethyleneimine functionalized apple pomace derived cellulose for efficient removal of methyl orange. Chem Eng J 456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140995
Zhang Z, He YC, Liu Y (2023b) Efficient antibacterial and dye adsorption by novel fish scale silver biochar composite gel. Int J Biol Macromol 125804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125804
Zhao D, Song Q, Li Y, Li L, Yuan F, Yang Y, Xiang S, Zhang Z (2023) Isoelectric substitution strategy to construct a partially charged MOF for C2H2 capture and selective dye adsorption. ACS Appl Nano Mater. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.3c01191
Zheng B, Lin X, Zhang X, Wu D, Matyjaszewski K (2019) Emerging functional porous polymeric and carbonaceous materials for environmental treatment and energy storage. Adv Funct Mater 30. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201907006
Zheng X, Zheng H, Xiong Z, Zhao R, Liu Y, Zhao C, Zheng C (2020) Novel anionic polyacrylamide-modify-chitosan magnetic composite nanoparticles with excellent adsorption capacity for cationic dyes and pH-independent adsorption capability for metal ions. Chem Eng J 392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123706
Zhou G, Wang KP, Liu HW, Wang L, Xiao XF, Dou DD, Fan YB (2018) Three-dimensional polylactic acid@graphene oxide/chitosan sponge bionic filter: Highly efficient adsorption of crystal violet dye. Int J Biol Macromol 113:792–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.017
Zhu T, Yu X, Yi M, Wang Y (2020) Facile Covalent Crosslinking of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework/Polydimethylsiloxane Mixed Matrix Membrane for Enhanced Ethanol/Water Separation Performance. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:12664–12676. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04584
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (32101598).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaobo Huang: Data curation, Writing-original draft. Chongpeng Qiu: Writing—original draft, Conceptualization. Yuanlong Chen: Investigation, Methodology. Xuefeng Zhang: Software, Data curation. Yongze Jiang: Validation, Investigation. Cornelis F. de Hoop: Software, Visualization. Jinqiu Qi: Writing—review & editing, Conceptualization, Supervision. Xingyan Huang: Writing—review & editing, Conceptualization, Supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
All authors agreed with the content and gave explicit consent to publish this article.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xiaobo Huang and Chongpeng Qiu are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Qiu, C., Chen, Y. et al. Nanocellulose-based polyurethane foam adsorbent for pressure-driven dye-contaminated water purification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 93817–93829 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29098-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29098-0