Abstract
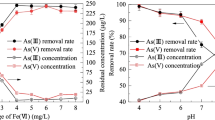
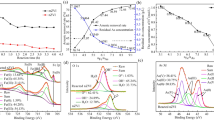
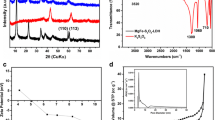
Arsenite is both more harmful and challenging to get out of water than arsenate. For enhanced As (III) removal, a ternary oxide nanoparticle (FCCTO) mainly composed of iron(Fe), with a small proportion of cerium(Ce) and copper(Cu) was created using a coprecipitation–calcination process. FCCTO was found to be effective in removing As (III) from water, with factors such as adsorbent dose, pH, temperature, and coexisting anions influencing its efficiency. The surface area of FCCTO reached 180.2 m2/g and the doping significantly increased its pore volume and diameter. The adsorption process on FCCTO was endothermic and spontaneous. Ce and Cu in FCCTO were able to efficiently oxidize 81.3% As (III) to As(V). Abundant sites were provided by surface hydroxyl groups for arsenic adsorption. The maximal As(III) adsorption capacity of this adsorbent under the synergistic impact of oxidation and adsorption was 101.5 mg/g. After five cycles, the FCCTO’s As(III) adsorption rate dropped to 60% as a result of tetravalent Ce consumption. Surface complexation, redox, and adsorption all had a significant impact on the adsorption process. Overall, FCCTO was an excellent adsorbent with benefits of being facile fabrication, environmentally, recyclable, and having a high As(III) adsorption capacity.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ayub A, Raza ZA, Majeed MI, Tariq MR, Irfan A (2020) Development of sustainable magnetic chitosan biosorbent beads for kinetic remediation of arsenic contaminated water. Int J Biol Macromol 163:603–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.287
Ayub A, Srithilat K, Fatima I, Panduro-Tenazoa NM, Ahmed I, Akhtar MU, Ahmad K, Muhammad A (2022) Arsenic in drinking water: overview of removal strategies and role of chitosan biosorbent for its remediation. Environ Sci Pollut R 29(43):64312–64344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21988-z
Basu T, Nandi D, Sen P, Ghosh UC (2013) Equilibrium modeling of As(III,V) sorption in the absence/presence of some groundwater occurring ions by iron(III)–cerium(IV) oxide nanoparticle agglomerates: a mechanistic approach of surface interaction. Chem Eng J 228:665–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.037
Çermikli E, Şen F, Altıok E, Wolska J, Cyganowski P, Kabay N, Bryjak M, Arda M, Yüksel M (2020) Performances of novel chelating ion exchange resins for boron and arsenic removal from saline geothermal water using adsorption-membrane filtration hybrid process. Desalination 491:114504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114504
Chen B, Zhu ZL, Ma J, Qiu YL, Chen JH (2013) Surfactant assisted Ce–Fe mixed oxide decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes and their arsenic adsorption performance. J Mater Chem A 1(37):11355–11367. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta11827d
Chen J, Wang JY, Zhang GS, Wu QY, Wang DT (2018) Facile fabrication of nanostructured cerium-manganese binary oxide for enhanced arsenite removal from water. Chem Eng J 334:1518–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.062
Chen L, Zhang KS, He JY, Cai XG, Xu WH, Liu JH (2016) Performance and mechanism of hierarchically porous Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres encapsulated calcium alginate beads for fluoride removal from water. RSC Adv 6(43):36296–36306. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra01337f
Dodd MC, Vu ND, Ammann A, Le VC, Kissner R, Pham HV, Cao TH, Berg M, Gunten AV (2006) Kinetics and mechanistic aspects of As(III) oxidation by aqueous chlorine, chloramines, and ozone: relevance to drinking water treatment. Environ Sci Technol 40(10):3285–3292. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0524999
Feng QZ, Zhang ZY, Ma YH, He X, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2012) Adsorption and desorption characteristics of arsenic onto ceria nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-84
Guo HC, Li WJ, Wang HY, Zhang JH, Liu Y, Zhou Y (2011) A study of phosphate adsorption by different temperature treated hydrous cerium oxides. Rare Metals 30(1):58–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0197-5
Gupta AD, Rene ER, Giri BS, Pandey A, Singh H (2021) Adsorptive and photocatalytic properties of metal oxides towards arsenic remediation from water: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 9(6):106376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106376
Han YS, Kim SH, Jang JY, Ji S (2022) Arsenic removal characteristics of natural Mn-Fe binary coating on waste filter sand from a water treatment facility. Environ Sci Pollut R 29(2):2136–2145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15580-0
Hoang VA, Yoshizuka K, Nishihama S (2022) Oxidative adsorption of arsenic from water environment by activated carbon modified with cerium oxide/hydroxide. Chem Eng Res Des 186:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2022.08.006
Hu QL, Zhang ZY (2019) Application of Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherm model at the solid/solution interface: a theoretical analysis. J Mol Liq 277:646–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.01.005
Huang YL, Tian XK, Nie YL, Yang C, Wang YX (2018) Enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation for phenol degradation over MnO2 at pH 3.5-9.0 via Cu(II) substitution. J Hazard Mater 360:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.028
Jin LF, Chai LY, Song TT, Yang WC, Wang HY (2020) Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4@Cu/Ce microspheres for efficient catalytic oxidation co-adsorption of arsenic(III). J Cent South Univ 27(04):1176–1185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4358-2
Kim MJ, Nriagu J (2000) Oxidation of arsenite in groundwater using ozone and oxygen. Sci Total Environ 247(1):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00470-2
Koseoglu P, Yoshizuka K, Nishihama S, Yuksel U, Kabay N (2011) Removal of boron and arsenic from geothermal water in Kyushu Island, Japan, by using selective ion exchange resins. Solvent Extr Ion Exc 29(3):440–457. https://doi.org/10.1080/07366299.2011.573448
Lashanizadegan M, Esfandiari Z, Mirzazadeh H (2019) Evaluation performance of Fe–Mn–Ce–O mixed metal oxides and Fe–Mn–Ce–O/Montmorillonite for adsorption of azo dyes in aqueous solution and oxidation reaction. Mater Res Express 6(12):125028. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab5550
Li GL, Gao S, Zhang GS, Zhang XW (2014) Enhanced adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution by nanostructured iron(III)-copper(II) binary oxides. Chem Eng J 235:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.021
Li RH, Yang WY, Gao S, Shang JK, Li Q (2021) Hydrous cerium oxides coated glass fiber for efficient and long-lasting arsenic removal from drinking water. J Adv Ceramics 10(2):247–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-020-0435-0
Li X, He K, Pan BC, Zhang SJ, Lu L, Zhang WM (2012) Efficient As(III) removal by macroporous anion exchanger-supported Fe–Mn binary oxide: bbehavior and mechanism. Chem Eng J 193-194(15):131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.04.036
Lin L, Qiu WW, Wang D, Huang Q, Song ZG, Chaud HW (2017) Arsenic removal in aqueous solution by a novel Fe-Mn modified biochar composite: characterization and mechanism. Ecotox Environ Safe 144:514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.06.063
Lin PF, Zhang XJ, Yang HW, Li Y, Chen C (2015) Applying chemical sedimentation process in drinking water treatment plant to address the emergent arsenic spills in water sources. Front Env Sci Eng 9(1):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0733-2
Liu J, Ren SX, Cao JL, Tsang DCW, Beiyuan JZ, Peng YT, Fang F, She JY, Yin ML, Shen NP, Wang J (2021) Highly efficient removal of thallium in wastewater by MnFe2O4-biochar composite. J Hazard Mater 401:123311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123311
Luo XB, Wang CC, Luo SL, Dong RZ, Tu XM, Zeng GS (2012) Adsorption of As (III) and As (V) from water using magnetite Fe3O4-reduced graphite oxide–MnO2 nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 187:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.073
Luo XB, Wang CC, Wang LC, Deng F, Luo SL, Tu XM, Au C (2013) Nanocomposites of graphene oxide-hydrated zirconium oxide for simultaneous removal of As(III) and As(V) from water. Chem Eng J 220:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.017
Martinson CA, Reddy KJ (2009) Adsorption of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) by cupric oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interf Sci 336(2):406–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.04.075
Masuda H (2018) Arsenic cycling in the Earth’s crust and hydrosphere: interaction between naturally occurring arsenic and human activities. Prog Earth Planet Sc 5(1):68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40645-018-0224-3
Mohan D, Pittman CU, Bricka M, Smith F, Yancey B, Mohammad J, Steele PH, Alexandre-Franco MF, Gómez-Serrano V, Gong H (2007) Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J Colloid Interf Sci 310:57–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.01.020
Moretti E, Storaro L, Talon A, Riello P, Molina AI, Castellón ER (2015) 3-D flower like Ce–Zr–Cu mixed oxide systems in the CO preferential oxidation (CO-PROX): effect of catalyst composition. Appl Catal B-Environ 168−169:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.12.032
Nanseu-Njiki C, Alonzo V, Bartak D, Ngameni E, Darchen A (2007) Electrolytic arsenic removal for recycling of washing solutions in a remediation process of CCA-treated wood. Sci Total Environ 384(1-3):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.04.043
Peng XJ, Luan ZK, Ding J, Di ZC, Li YH, Tian BH (2005) Ceria nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes for the removal of arsenate from water. Mater Lett 59(4):399–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2004.05.090
Shan SJ, Chen ZH, Koh KY, Wang W, Wu JY, Chen JP, Cui FY (2022) Decontamination of arsenite by a nano-sized lanthanum peroxide composite through a simultaneous treatment process combined with spontaneously catalytic oxidation and adsorption reactions. Chem Eng J 435(3):135082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135082
Sherlala AIA, Raman AAA, Bello MM, Buthiyappan A (2019) Adsorption of arsenic using chitosan magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite. J Environ Manage 246:547–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.117
Siddiqui SI, Chaudhry SA (2017) Iron oxide and its modified forms as an adsorbent for arsenic removal: a comprehensive recent advancement. Process Saf Environ 111:592–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.08.009
Sigdel A, Park J, Kwak H, Park PK (2016) Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto hydrous iron oxide-impregnated alginate beads. J Ind Eng Chem 35:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.01.005
Song WY, Yamaki T, Yamaji N, Ko D, Jung KH, Fujii-Kashino M, An G, Martinoia E, Lee Y, Ma JF (2014) A rice ABC transporter, OsABCC1, reduces arsenic accumulation in the grain. P Nati A Sci 111(44):15699–15704. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1414968111
Sorlini S, Gialdini F (2010) Conventional oxidation treatments for the removal of arsenic with chlorine dioxide, hypochlorite, potassium permanganate and monochloramine. Water Res 44(19):5653–5659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.032
Sun WZ, Li Q, Gao SA, Shang JK (2012) Exceptional arsenic adsorption performance of hydrous cerium oxide nanoparticles: Part B. Integration with silica monoliths and dynamic treatment. Chem Eng J 185-186:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.060
Wang T, Yang WC, Song TT, Li CF, Zhang LY, Wang HY, Chai LY (2015) Cu doped Fe3O4 magnetic adsorbent for arsenic: synthesis, property, and sorption application. RSC Adv 5(62):50011–50018. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra03951g
Wang TN, Jiao YH, He MC, Ouyang W, Lin CY, Liu XT (2022) Facile co-removal of As(V) and Sb(V) from aqueous solution using Fe-Cu binary oxides: structural modification and self-driven force field of copper oxides. Sci Total Environ 803:150084–150084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150084
Wei DH, Sun YW, Xu D, Li WZ, Zhao XC, Tao XQ, Zeng SY (2017) Mesoporous Fe2O3 nanomaterials from natural rust for lithium storage. J Mater Sci-Mater El 28(24):19098–19104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7864-8
Wen ZP, Ke J, Xu JL, Guo S, Zhang YL, Chen R (2018) One-step facile hydrothermal synthesis of flowerlike Ce/Fe bimetallic oxides for efficient As(V) and Cr(VI) remediation: performance and mechanism. Chem Eng J 343:416–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.034
Wen ZP, Lu J, Zhang YL, Cheng G, Huang SN, Chen J, Xu R, Ming YA, Wang YR, Chen R (2020) Facile inverse micelle fabrication of magnetic ordered mesoporous iron cerium bimetal oxides with excellent performance for arsenic removal from water. J Hazard Mater 383:121172.1–121172.12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121172
World Health Organization (2010) Preventing disease through healthy environments-exposure to lead: a major public health concern. WHO, Geneva
Wu K, Wang M, Li AZ, Zhao ZX, Liu T, Hao XD, Yang SJ, Jin PK (2021) The enhanced As(III) removal by Fe-Mn-Cu ternary oxide via synergistic oxidation: performances and mechanisms. Chem Eng J 406:126739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126739
Xu WH, Wang J, Wang L, Sheng GP, Liu JH, Yu HQ, Huang XJ (2013) Enhanced arsenic removal from water by hierarchically porous CeO2–ZrO2 nanospheres: role of surface- and structure-dependent properties. J Hazard Mater 260:498–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.010
Yin GC, Song XW, Tao L, Sarkar B, Sarmah AK, Zhang WX, Lin QT, Xiao RB, Liu QJ, Wang HL (2020) Novel Fe-Mn binary oxide-biochar as an adsorbent for removing Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 389:124465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124465
Yoon Y, Park WK, Hwang TM, Yoon DH, Yang WS, Kang JW (2016) Comparative evaluation of magnetite–graphene oxide and magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composite for As(III) and As(V) removal. J Hazard Mater 304:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.053
Zhang GS, Qu JH, Liu HJ, Liu RP, Wu RC (2007) Preparation and evaluation of a novel Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent for effective arsenite removal. Water Res 41:1921–1928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.009
Zhang GS, Ren ZM, Zhang XW, Chen J (2013) Nanostructured iron(III)-copper(II) binary oxide: a novel adsorbent for enhanced arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. Water Res 47(12):4022–4031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.059
Zhang LF, Zhu TY, Liu X, Zhang WQ (2016) Simultaneous oxidation and adsorption of As(III) from water by cerium modified chitosan ultrafine nanobiosorbent. J Hazard Mater 308:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.015
Zhang W, Zhang GS, Liu CH, Li J, Zheng T, Ma J, Wang L, Jiang J, Zhai XD (2018) Enhanced removal of arsenite and arsenate by a multifunctional Fe-Ti-Mn composite oxide: photooxidation, oxidation and adsorption. Water Res 147(15):264–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.001
Zhang Y, Dou XM, Zhao B, Yang M, Takayama T, Kato S (2010) Removal of arsenic by a granular Fe–Ce oxide adsorbent: fabrication conditions and performance. Chem Eng J 162(1):164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.05.021
Zhang Y, Yang M, Huang X (2003) Arsenic(V) removal with a Ce(IV)-doped iron oxide adsorbent. Chemosphere 51(9):945–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00850-0
Zhao YG, Li JX, Zhao LP, Zhang SW, Huang YS, Wu XL, Wang XK (2014) Synthesis of amidoxime-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic microspheres for highly efficient sorption of U(VI). Chem Eng J 235:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.034
Zheng Q, Hou JT, Hartley W, Ren L, Wang MX, Tu SX, Tan WF (2020) As(III) adsorption on Fe-Mn binary oxides: are Fe and Mn oxides synergistic or antagonistic for arsenic removal? Chem Eng J 389:124470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124470
Funding
We acknowledge the key Research and Development Projects of Hunan Province (No. 2019WK2031) for financial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ying Liu: conceptualization, methodology, data analysis, writing—review and editing, visualization, and validation. Leyi Li: methodology, data collection, review and editing. Xuemei Huang: review and editing. Yaochi Liu: supervision, review and editing, visualization, and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, L., Huang, X. et al. Enhanced arsenite removal in aqueous with Fe-Ce-Cu ternary oxide nanoparticle. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 95493–95506 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29082-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29082-8