Abstract
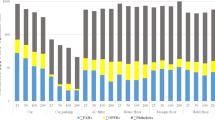
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released along with soil disturbance during the remediation of abandoned industrial sites have attracted great attention due to their possible toxicity and odour. However, the real-time emission characteristics of these VOCs and their subsequent effects on health and olfaction are less understood. In this study, the gaseous VOCs released from soil disturbance by excavators and drilling rigs at an abandoned chemical pesticide plant were monitored online with a laboratory-built single photoionization time-of-flight mass spectrometer (SPI-TOFMS). Twelve main VOCs with total mean concentrations ranging from 2350 to 3410 μg m−3 were observed, with dichloromethane (DCM) having a significant contribution. The total concentrations of the remaining 11 VOCs increased substantially during soil disturbance, with the total mean concentrations increasing from 18.65–39.05 to 37.95–297.94 μg m−3 and those of peak concentrations increasing from 28.46–58.97 to 88.38–839.13 μg m−3. This increase in VOC concentrations during soil disturbance leads to an enhanced heath risk for on-site workers. The distinctive difference between the mean and peak concentrations of VOCs indicates the importance of using mean and peak concentrations, respectively, for risk and olfactory evaluation due to the rapid response of the human nose to odours. As a result, the cumulative noncarcinogenic risk at the relatively high pollutant plot was higher than the occupational safety limit, while the total carcinogenic risks at all monitored scenarios exceeded the acceptable limit. Among the VOCs investigated, DCM and trichloroethylene (TCE) were determined to be crucial pollutants for both noncarcinogenic and carcinogenic risks of VOCs. With regard to olfactory effects, organic sulphides, including dimethyl disulphide (DMDS), dimethyl sulphide (DMS), and dimethyl trisulphide (DMTS) were identified as dominant odour contributors (78.28–92.11%) during soil disturbance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
An J, Zhu B, Wang H, Li Y, Lin X, Yang H (2014) Characteristics and source apportionment of VOCs measured in an industrial area of Nanjing, Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos Environ 97:206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.08.021
Civan MY, Elbir T, Seyfioglu R, Kuntasal ÖO, Bayram A, Doğan G, Yurdakul S, Andiç Ö, Müezzinoğlu A, Sofuoglu SC, Pekey H, Pekey B, Bozlaker A, Odabasi M, Tuncel G (2015) Spatial and temporal variations in atmospheric VOCs, NO2, SO2, and O3 concentrations at a heavily industrialized region in Western Turkey, and assessment of the carcinogenic risk levels of benzene. Atmos Environ 103:102–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.12.031
Dai H, Jing S, Wang H, Ma Y, Li L, Song W, Kan H (2017) VOC characteristics and inhalation health risks in newly renovated residences in Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 577:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.071
Duan Z, Lu W, Mustafa MF, Du J, Wen Y (2022) Odorous gas emissions from sewage sludge composting windrows affected by the turning operation and associated health risks. Sci Total Environ 839:155996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155996
Dumanoglu Y, Kara M, Altiok H, Odabasi M, Elbir T, Bayram A (2014) Spatial and seasonal variation and source apportionment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in a heavily industrialized region. Atmos Environ 98:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.08.048
Fisher RM, Le-Minh N, Alvarez-Gaitan JP, Moore SJ, Stuetz RM (2018) Emissions of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) throughout wastewater biosolids processing. Sci Total Environ 616–617:622–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.282
Han Z, Qi F, Wang H, Liu B, Shen X, Song C, Bao Z, Zhao X, Xu Y, Sun D (2018) Emission characteristics of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) from a municipal sewage sludge aerobic composting plant. Waste Manage 77:593–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.05.049
Hayes JE, Stevenson RJ, Stuetz RM (2014) The impact of malodour on communities: a review of assessment techniques. Sci Total Environ 500–501:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.09.003
Hu G, Liu H, Chen C, Li J, Hou H, Hewage K, Sadiq R (2021) An integrated geospatial correlation analysis and human health risk assessment approach for investigating abandoned industrial sites. J Environ Manage 293:112891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112891
Huang B, Lei C, Wei C, Zeng G (2014) Chlorinated volatile organic compounds (Cl-VOCs) in environment - sources, potential human health impacts, and current remediation technologies. Environ Int 71:118–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.06.013
Jia H, Gao S, Duan Y, Fu Q, Che X, Xu H, Wang Z, Cheng J (2021) Investigation of health risk assessment and odor pollution of volatile organic compounds from industrial activities in the Yangtze River Delta region. China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111474
Kan H, Wang T, Yu J, Qu G, Zhang P, Jia H, Sun H (2021) Remediation of organophosphorus pesticide polluted soil using persulfate oxidation activated by microwave. J Hazard Mater 401:123361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123361
Lee HD, Jeon SB, Choi WJ, Lee SS, Lee MH, Oh KJ (2013) A novel assessment of odor sources using instrumental analysis combined with resident monitoring records for an industrial area in Korea. Atmos Environ 74:277–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.04.001
Lewkowska P, Cieslik B, Dymerski T, Konieczka P, Namiesnik J (2016) Characteristics of odors emitted from municipal wastewater treatment plant and methods for their identification and deodorization techniques. Environ Res 151:573–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.08.030
Li Y, Yan B (2022) Human health risk assessment and distribution of VOCs in a chemical site, Weinan, China. Open Chem 20:192–203. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2022-0132
Ma Y, Du X, Shi Y, Hou D, Dong B, Xu Z, Li H, Xie Y, Fang J, Li Z, Cao Y, Gu Q, Li F (2016) Engineering practice of mechanical soil aeration for the remediation of volatile organic compound-contaminated sites in China: advantages and challenges. Front Environ Sci Eng 10:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-016-0870-x
Mishra H, Singh J, Karmakar S, Kumar R (2021) An integrated approach for modeling uncertainty in human health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:56053–56068. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14531-z
Moran M, Zogorski J, Squillace P (2007) Chlorinated solvents in groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 41:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061553y
Mustafa MF, Liu Y, Duan Z, Guo H, Xu S, Wang H, Lu W (2017) Volatile compounds emission and health risk assessment during composting of organic fraction of municipal solid waste. J Hazard Mater 327:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.046
Nie E, Zheng G, Shao Z, Yang J, Chen T (2018) Emission characteristics and health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds produced during municipal solid waste composting. Waste Manage 79:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.07.024
Nie E, Zheng G, Gao D, Chen T, Yang J, Wang Y, Wang X (2019) Emission characteristics of VOCs and potential ozone formation from a full-scale sewage sludge composting plant. Sci Total Environ 659:664–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.404
Olvera-Bello AE, Estrada-Muniz E, Elizondo G, Vega L (2010) Susceptibility to the cytogenetic effects of dichloromethane is related to the glutathione S-transferase theta phenotype. Toxicol Lett 199:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.09.002
Palmiotto M, Fattore E, Paiano V, Celeste G, Colombo A, Davoli E (2014) Influence of a municipal solid waste landfill in the surrounding environment: toxicological risk and odor nuisance effects. Environ Int 68:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.03.004
Panagos P, Van Liedekerke M, Yigini Y, Montanarella L (2013) Contaminated sites in Europe: review of the current situation based on data collected through a European network. J Environ Public Health 2013:158764. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/158764
Pranjic A, Oprckal P, Mladenovic A, Zapusek P, Urleb M, Turk J (2018) Comparative life cycle assessment of possible methods for the treatment of contaminated soil at an environmentally degraded site. J Environ Manage 218:497–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.051
Sazakli E, Leotsinidis M (2020) Odor nuisance and health risk assessment of VOC emissions from a rendering plant. Air Qual Atmos Health 14:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00935-2
Sivret EC, Wang B, Parcsi G, Stuetz RM (2016) Prioritisation of odorants emitted from sewers using odour activity values. Water Res 88:308–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.020
Song Y, Kirkwood N, Maksimovic C, Zheng X, O’Connor D, Jin Y, Hou D (2019) Nature based solutions for contaminated land remediation and brownfield redevelopment in cities: a review. Sci Total Environ 663:568–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.347
Starr TB, Matanoski G, Anders MW, Andersen ME (2006) Workshop overview: reassessment of the cancer risk of dichloromethane in humans. Toxicol Sci 91:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfj145
Tansel B, Inanloo B (2019) Odor impact zones around landfills: delineation based on atmospheric conditions and land use characteristics. Waste Manage 88:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.03.028
Tong R, Cheng M, Zhang L, Liu M, Yang X, Li X, Yin W (2018) The construction dust-induced occupational health risk using Monte-Carlo simulation. J Clean Prod 184:598–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.286
Wang Y, Li L, Qiu Z, Yang K, Han Y, Chai F, Li P, Wang Y (2021) Trace volatile compounds in the air of domestic waste landfill site: identification, olfactory effect and cancer risk. Chemosphere 272:129582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129582
Wenjing L, Zhenhan D, Dong L, Jimenez LM, Yanjun L, Hanwen G, Hongtao W (2015) Characterization of odor emission on the working face of landfill and establishing of odorous compounds index. Waste Manage 42:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.04.030
Wu C, Liu J, Zhao P, Li W, Yan L, Piringer M, Schauberger G (2017) Evaluation of the chemical composition and correlation between the calculated and measured odour concentration of odorous gases from a landfill in Beijing, China. Atmos Environ 164:337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.06.010
Wu C, Liu J, Liu S, Li W, Yan L, Shu M, Zhao P, Zhou P, Cao W (2018) Assessment of the health risks and odor concentration of volatile compounds from a municipal solid waste landfill in China. Chemosphere 202:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.068
Wu X, Li Z, Shu J, Lu Z, Gao J, Yang B, Jiang K, Guo Y, Huang J (2022) Exploring breath biomarkers in BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice with associative ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Talanta 239:123120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123120
Xiong Y, Bari MA, Xing Z, Du K (2020) Ambient volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in two coastal cities in western Canada: spatiotemporal variation, source apportionment, and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 706:135970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135970
Yang K, Wang C, Xue S, Li W, Liu J, Li L (2019) The identification, health risks and olfactory effects assessment of VOCs released from the wastewater storage tank in a pesticide plant. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184:109665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109665
Zhang K, Liu S, Wang S, Zhao M, Jia J (2018a) Health risk assessment and distribution of VOCs during excavation processes for the remediation of contaminated sites. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25:2073–2088. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1488578
Zhang Z, Yan X, Gao F, Thai P, Wang H, Chen D, Zhou L, Gong D, Li Q, Morawska L, Wang B (2018b) Emission and health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in various processes of a petroleum refinery in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Pollut 238:452–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.054
Zhang K, Chang S, Fu Q, Sun X, Fan Y, Zhang M, Tu X, Qadeer A (2021) Occurrence and risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in multiple drinking water sources in the Yangtze River Delta region China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 225:112741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112741
Zhang Y, Ning X, Li Y, Wang J, Cui H, Meng J, Teng C, Wang G, Shang X (2021b) Impact assessment of odor nuisance, health risk and variation originating from the landfill surface. Waste Manage 126:771–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.03.055
Zhang L, Sun P, Sun D, Zhou Y, Han L, Zhang H, Zhu B, Wang B (2022) Occupational health risk assessment of the benzene exposure industries: a comprehensive scoring method through 4 health risk assessment models. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:84300–84311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21275-x
Zhao X, Ma H, Lu J, Yin T, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Dong X, Shuai Q, Wei T, Gong X (2020) Characteristics and source apportionment of volatile organic compounds during the remediation of contaminated sites in Zhenjiang, China. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18:2271–2282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02947-y
Zhou J, You Y, Bai Z, Hu Y, Zhang J, Zhang N (2011) Health risk assessment of personal inhalation exposure to volatile organic compounds in Tianjin, China. Sci Total Environ 409:452–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.10.022
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFC1806101), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22076184), and the Research Equipment Development Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (YJKYYQ20180072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Methodology, data collection and analysis, and writing–review and editing were performed by Haijie Wang and Bo Yang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Bo Yang. Methodology, material preparation, and investigation were performed by Zitao Yan, Zuojian Zhang, Kui Jiang, Jin Yu, Yong Yang, Bo Yang, Jinian Shu, Zhangqi Yu, and Zhiyang Wei and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Constantini Samara
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Yan, Z., Zhang, Z. et al. Real-time emission characteristics, health risks, and olfactory effects of VOCs released from soil disturbance during the remediation of an abandoned chemical pesticide industrial site. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 93617–93628 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28942-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28942-7