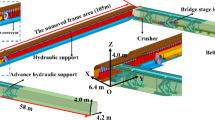
Abstract
Dust exposures during mining activity can result in lung diseases such as coal workers’ pneumoconiosis (CWP) and silicosis, and it is closely related to quartz dust. In the present study, coal-quartz dust mixture were investigated considering the particle size and the specific constituents. Multiple numerical techniques, including computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method (CFD-DEM), hard sphere model, and direct Monte Carlo simulation (DSMC), were presented, and the dust diffusion processes were investigated. According to the validation of the numerical method, the suspension characteristics of the polydisperse mixed dust were analyzed in detail. The results show that PM10 responds quickly, has a large diffusion range, and is easily affected by the reflux. The particle size increases gradually from top to bottom. When the air velocity is low, the percentage of coal dust in the breathing zone tends to be 50%. The results provide theoretical guidance for the comprehensive prevention of the mixed dust in underground coal mines.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- C d :
-
Drag coefficient
- d p :
-
Particle diameter (m)
- e :
-
Reversion coefficient.
- f d :
-
Drag force (N)
- f g :
-
Gravity force (N)
- f p :
-
The friction coefficient of Coulomb’s friction law
- G 0 :
-
Relative velocity between particles (m/s)
- \({{\varvec{G}}}_{ct}^{0}\) :
-
Tangential component of G0 (m/s)
- G ij :
-
Relative velocity between particle i and particle j (m/s)
- m p :
-
Mass of particle (kg)
- N :
-
Sample number of particles
- n :
-
Number density of particles
- p ij :
-
Probability of particle–particle collision
- R:
-
Random number \(0\le R\le 1\)
- Re p :
-
Particle Reynolds number
- t :
-
Time (s)
- u p :
-
Particle velocity (m/s)
- u a :
-
Velocity of the surrounding air (m/s)
- V i :
-
Translational velocity of particle after collision (m/s)
- \({{\varvec{V}}}_{i}^{0}\) :
-
Translational velocity of particle before collision (m/s)
- V j :
-
Translational velocity of particle after collision (m/s)
- \({{\varvec{V}}}_{j}^{0}\) :
-
Translational velocity of particle before collision (m/s)
- \({\overset{\rightharpoonup }{F}}_{q}\) :
-
External body force (N)
- \({\overset{\rightharpoonup }{F}}_{lift,q}\) :
-
A lift force (N)
- \({\overset{\rightharpoonup }{F}}_{Vm,q}\) :
-
A virtual mass force (N)
- \({\overset{\rightharpoonup }{v}}_{pq}\) :
-
Interphase velocity (m/s)
- \({\overset{\rightharpoonup }{R}}_{pq}\) :
-
Interaction force between phases (N)
- \({K}_{pq}\left(={K}_{qp}\right)\) :
-
Interphase momentum exchange coefficient
- F c :
-
Collision force (N)
- F d :
-
Drag force (N)
- M c :
-
Total torque
- I :
-
The moment of inertia of the particle
- r p :
-
Particle diameter
- \({\rho }_{q}\) :
-
The physical density of particle
- \({\rho }_{a}\) :
-
Air density (kg/m3)
- \({\omega }_{i}\) :
-
Rotational velocity of particle after collision (rad/s)
- \({\omega }_{i}^{0}\) :
-
Rotational velocity of particle before collision (rad/s)
- \({\omega }_{j}\) :
-
Rotational velocity of particle after collision (rad/s)
- \({\omega }_{j}^{0}\) :
-
Rotational velocity of particle before collision (rad/s)
- \({\alpha }_{q}\) :
-
The space occupied by each phase.
- \({\overline{\overline{\tau }}}_{q}\) :
-
Phase stress–strain tensor
- \({\mu }_{q}\) :
-
Shear viscosity
- \({\lambda }_{q}\) :
-
Bulk viscosity
- o :
-
Before the collision
- a :
-
Air phase
- i :
-
Particle i
- j :
-
Particle j
- p :
-
Particle phase
- q :
-
Particle phase
References
Azam S, Mishra DP (2019) Effects of particle size, dust concentration and dust-dispersion-air pressure on rock dust inertant requirement for coal dust explosion suppression in underground coal mines. Process Saf Environ Prot 126:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.03.030
Azam S, Kurashov V, Golbeck JH, Bhattacharyya S, Zheng SY, Liu SM (2023a) Comparative 6+studies of environmentally persistent free radicals on nano-sized coal dusts. Sci Total Environ 878:163163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163163
Azam S, Liu SM, Ang Liu SB (2023b) Measurement and modeling of water vapor sorption on nano-sized coal particulates and its implication on its transport and deposition in the environment. Sci Total Environ 889:164095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164095
Brodny J, Tutak M (2018) Exposure to harmful dusts on fully powered longwall coal mines in Poland. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091846
Cai P, Nie W, Chen DW, Yang SB, Liu ZQ (2019) Effect of air flowrate on pollutant dispersion pattern of coal dust particles at fully mechanized mining face based on numerical simulation. Fuel 239:623–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.11.030
Chang P, Xu G, Zhou FB, Mullins B, Abishek S, Chalmers D (2019) Minimizing DPM pollution in an underground mine by optimizing auxiliary ventilation systems using CFD. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 87:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2019.02.014
Chang M, Fan YP, Lu CX (2022) Intrusive sampling of dust deposition in a granular bed filter-cyclone coupled separator. Chem Eng Sci 260:117824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2022.117824
Cohen RA, Petsonk EL, Rose C, Young B, Regier M, Najmuddin A, Abraham JL, Churg A, Green FHY (2016) Lung pathology in U.S. coal workers with rapidly progressive pneumoconiosis implicates silica and silicates. Am J Respir Crit Care 193:673–680. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201505-1014OC
Ding TX, Deng ZQ, Hou XY, Liu YM, Liu YF, Li M, Li M (2020) Investigation on the simulation approach for Martian rarefied aeolian activities based on discrete element method. Powder Technol 369:202–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.05.055
Eades R, Perry K, Johnson C, Miller J (2018) Evaluation of the 20 L dust explosibility testing chamber and comparison to a modified 38 L vessel for underground coal. Int J Min Sci Tech 28:885–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.05.016
Fan FX, Parteli EJR, Poschel T (2017) Origin of granular capillarity revealed by particle-based simulations. Phys Rev Lett 118 218001 https://journals.aps.org/prl/issues/118/21
Fan L, Liu SM (2021) Respirable nano-particulate generations and their pathogenesis in mining workplaces: a review. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8:179–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-021-00412-w
Geng F, Luo G, Wang YC, Peng ZB, Hu SY, Zhang TT, Chai HL (2018) Dust dispersion in a coal roadway driven by a hybrid ventilation system: a numerical study. Process Saf Environ Prot 113:388–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.11.010
Geng F, Gui CG, Teng HX, Tang JH, Niu HW, Zhou FB, Liu C, Hu SD, Li SH (2020) Dispersion characteristics of dust pollutant in a typical coal roadway under an auxiliary ventilation system. J Clean Prod 275:122889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122889
Gui CG, Geng F, Tang JH, Niu HW, Zhou FB, Liu C, Hu SD, Teng HX (2020) Gas-solid two-phase flow in an underground mine with an optimized air-curtain system: a numerical study. Process Saf Environ Prot 140:137–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.04.028
Guo KJ, Liu J (2017) Experimental study on the minimalist ignition temperature of the mixed coal and rock dust cloud. J Saf Environ 17:1331–1333. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2017.04.024
Guo XW, Fan FX, Hu XH, Su MX (2016) Influence of characteristic parameters in the simulation of acoustic particle collision using DSMC method. J Univ Shanghai Sci Tech 38:419–426. https://doi.org/10.13255/j.cnki.jusst.2016.05.003
He XY, He BJ, Cai GB (2012) Simulation of rocket plume and lunar dust using DSMC method. Acta Astronaut 70:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2011.07.014
Hu SY, Liao Q, Feng GR, Huang YS, Shao H, Gao Y, Hu F (2020) Influences of ventilation velocity on dust dispersion in coal roadways. Powder Technol 360:683–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.09.080
Jiang HP, Bi MS, Gao W (2022) In situ analysis of suppression mechanism of DMMP water mist in coal dust explosions using pyrolysis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Chem Eng Sci 260:117836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2022.117836
Johann-Essex V, Keles C, Rezaee M, Scaggs-Witte M, Sarver E (2017) Respirable coal mine dust characteristics in samples collected in central and northern Appalachia. Int J Coal Geol 182:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2017.09.010
Laney AS, Petsonk EL, Hale JM, Wolfe AL, Attfield MD (2012) Potential determinants of coal workers’ pneumoconiosis, advanced pneumoconiosis, and progressive massive fibrosis among underground coal miners in the United States, 2005–2009. Am. J Public Health 102:S279–S283. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2011.300427
Li Y, Yang JH, Pan ZJ, Meng SZ, Wang K, Niu XL (2019) Unconventional natural gas accumulations in stacked deposits: a discussion of Upper Paleozoic coal-bearing strata in the East Margin of the Ordos Basin. China Bull Geol Soc Chin 93:111–129. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.13767
Liu T, Liu SM (2020) The impacts of coal dust on miners’ health: a review. Environ Res 190:109849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109849
Liu C, Luo Nie W, Luo C, Hua Y, Yu F, Niu W, Zhang X, Zhang S (2022) Numerical study on temporal and spatial distribution of particulate matter under multi-vehicle working conditions. Sci Total Environ 862:160710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160710
Mischler SE, Cauda EG, DiGiuseppe M, McWilliams LJ, Croix CS, Sun M, Franks J, Ortiz LA (2016) Differential activation of RAW 264.7 macrophages by size-segregated crystalline silica. J Occup Med Toxicol 11:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12995-016-0145-2
Moreno T, Techera P, Querol X, Lah R, Johnson D, Wrana A, Williamson B (2019) Trace element fractionation between PM10 and PM2.5 in coal mine dust: implications for occupational respiratory health. Int J Coal Geol 203:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2019.01.006
Nie W, Liu F, Xu C, Peng H, Zhang H, Mwabaima F (2022) Study on the optimal parameter range of droplet-wrapped respirable dust in spray dustfall by mesoscopic method. Environ Res 214:114035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114035
Peng ZB, Gai SL, Barma M, Rahman MM, Moghtaderi B, Doroodchi E (2021) Experimental study of gas-liquid-solid flow characteristics in slurry Taylor flow-based multiphase microreactors. Chem Eng J 405:126646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126646
Peng ZB, Wang GC, Moghtaderi B, Doroodchi E (2022) A review of microreactors based on slurry Taylor (segmented) flow. Chem Eng Sci 247:117040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2021.117040
Ren T, Wang ZW, Zhang J (2018) Improved dust management at a longwall top coal caving (LTCC) face — a CFD modelling approach. Adv Powder Technol 29:2368–2379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2018.06.016
Schatzel SJ (2009) Identifying sources of respirable quartz and silica dust in underground coal mines in southern west Virginia, western Virginia, and eastern Kentucky. J Coal Geol 78:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2009.01.003
Shekarian Y, Rahimi E, Shekarian N, Razaee M, Roghanchi P (2021) An analysis of contributing mining factors in coal workers’ pneumoconiosis prevalence in the United States coal mines, 1986–2018. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8:1227–12377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-021-00464-y
Sun SS, Yuan ZL, Peng ZB, Moghtaderi B, Doroodchi E (2018) Computational investigation of particle flow characteristics in pressurised dense phase pneumatic conveying systems. Powder Technol 329:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.01.078
Trechera P, Moreno T, Córdoba P, Moreno N, Zhuang XG, Li BQ, Li J, Shangguan YF, Kandler K, Dominguez AO, Kelly F, Querol X (2020) Mineralogy, geochemistry and toxicity of size-segregated respirable deposited dust in underground coal mines. J. Hazard. Mater 399:122935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122935
Trechera P, Querol X, Lah R, Johnson D, Wrana A, Williamson B, Moreno T (2022) Chemistry and particle size distribution of respirable coal dust in underground mines in Central Eastern Europe. Int J Coal Sci Technol 9:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-022-00468-2
Tsuji Y (2007) Multi-scale modeling of dense phase gas–particle flow. Chem Eng Sci 62:3410–3418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2006.12.090
Wang PP, Ji DP, Yang YC, Zhao LL (2016) Mineralogical compositions of Late Permian coals from the Yueliangtian Mine, Western Guizhou, China: comparison to coals from Eastern Yunnan, with an emphasis on the origin of the minerals. Fuel 181:859–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.05.043
Wang YC, Geng F, Yang SQ, Jing HW, Meng B (2019) Numerical simulation of particle migration from crushed sandstones during groundwater inrush. J Hazard Mater 362:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.011
Wu ZH, Fan FX, Hu XH (2021) Development and verification of DSMC method for solving particle agglomeration and rebound. Chin Pow Sci Tech 27:38–46. https://doi.org/10.13732/j.issn.1008-5548.2021.05.005
Zazouli MA, Dehbandi R, Mohammadyan M, Aarabi M, Dominguez AO, Kelly FJ, Khodabakhshloo N, Rahman MM, Naidu R (2020) Physico-chemical properties and reactive oxygen species generation by respirable coal dust: implication for human health risk assessment. J Hazar Mater 405:124185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124185
Zhang R, Liu SM, Zheng SY (2021) Characterization of nano-to-micron sized respirable coal dust: particle surface alteration and the health impact. J Hazar Mater 413:125447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125447
Funding
This study received financial supports from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC3003304), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42272313), and the scientific research project of China Railway Shanghai Group Co., Ltd. (2022178).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fan Geng and Yingchao Wang: conceptualization and methodology; Jiajun An and Fan Geng: software, formal analysis and visualization, writing — review and editing; Jiajun An and Changgeng Gui: investigation, validation, data curation and writing — original draft; Changgeng Gui, Heng Guo, Tianliang Wen: resources and writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Shimin Liu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, F., An, J., Wang, Y. et al. Suspension characteristics of the coal-quartz dust mixture in the working environment during the fully mechanized mining process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 102244–102259 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28911-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28911-0