Abstract
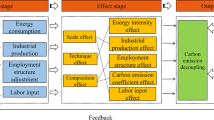
Urban carbon emissions are one of the most important areas contributing to the growth of carbon emissions, and resource-dependent cities with natural resource extraction and processing as their leading industries tend to have higher carbon emissions. Ordos is the city with the highest coal production in China, and its economic development is dominated by coal, oil and gas, and other resource extraction and processing industries, with industrial activities making a large contribution to carbon emissions. At the same time, Ordos has undergone rapid industrialization in recent years, but still faces the problem of environmental pollution, epitomizing a typical resource-dependent city in China. Therefore, this paper takes Ordos as an example and uses the Generalized Divisa Index Method (GDIM) to study the drivers of industrial carbon emissions in Ordos from 2005–2020, a typical resource-dependent city in China, and further analyzes are conducted in relation to the three phases of development. Based on the key drivers, the Monte Carlo method is used to forecast industrial carbon emissions from 2021 to 2030. The results show that the most important factors driving the growth of industrial carbon emissions are the scale of industrial output and industrial energy consumption, while the intensity of industrial energy investment is the most important factor mitigating industrial carbon emissions, and that energy efficiency and carbon intensity of energy consumption can also mitigate carbon emissions after economic transformation. At the same time, investment is the factor with the greatest potential for optimization on the path to emissions reduction.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Ang BW (2004) Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: which is the preferred method? Energy Policy 32:1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(03)00076-4
Ang BW (2005) The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: a practical guide. Energy Policy 33:867–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2003.10.010
Cai B, Cui C, Zhang D et al (2019) China city-level greenhouse gas emissions inventory in 2015 and uncertainty analysis. Appl Energy 253:113579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113579
Chen Q, Wang Q, Zhou D, Wang H (2023) Drivers and evolution of low-carbon development in China’s transportation industry: an integrated analytical approach. Energy (Oxf) 262:125614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.125614
Chen XM, Zhou B (2022) Time-varying effects of industrial structure upgrading on carbon emissions by sector. Technoeconomics Manag Res 123–128. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-292X.2022.06.022. (in Chinese)
Cui C, Li J, Lu Z, Yan Z (2022) Empirical analysis of the role of the environmental accountability system in energy conservation and emission reduction in China. Sci Rep 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-19604-8
Dhakal S (2009) Urban energy use and carbon emissions from cities in China and policy implications. Energy Policy 37:4208–4219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.05.020
Dong XS, Xiao X (2016) Does the change of demographic dividend affect China’s industrialization? China Popul Resources Environ 26:20–27. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.09.003. (in Chinese)
Ge QY, Zhang LY, Qiu RZ, Hu XS, Zhang YY (2022) Analysis on driving factors of transportation carbon emissions in Fujian Province based on GDIM. J Fujian Agric For Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 51 131–136. https://doi.org/10.13323/j.cnki.j.fafu(nat.sci.).2022.01.020 (in Chinese)
Ge X, Xu J, Xie Y, Guo X, Yang D (2021) Evaluation and dynamic evolution of eco-efficiency of resource-based cities—a case study of typical resource-based cities in China. Sustainability 13:6802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126802
Gu Q, Wu Z, Xie D (2022) Transformation and development of resource-based cities in China: a review and bibliometric analysis. Front Environ Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.975669
He SY, Lee J, Zhou T, Wu D (2017) Shrinking cities and resource-based economy: the economic restructuring in China’s mining cities. Cities 60:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2016.07.009
He YD, Lin BQ (2022) The impact of heterogeneous labor agglomeration on regional carbon emission. Popul J 44:39–56. https://doi.org/10.16405/j.cnki.1004-129X.2022.04.004. (in Chinese)
Howie P (2018) Policy transfer and diversification in resource-dependent economies: lessons for Kazakhstan from Alberta. Polit Policy 46:110–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/polp.12239
Huang Y, Matsumoto K (2021) Drivers of the change in carbon dioxide emissions under the progress of urbanization in 30 provinces in China: a decomposition analysis. J Clean Prod 322:129000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129000
Hui C, Shen F, Tong L, Zhang J, Liu B (2022) Fiscal pressure and air pollution in resource-dependent cities: evidence from China. Front Environ Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.908490
Jiang TY (2020) Study on carbon emission and reduction of China’s industry and energy systems: the perspective of input-output analysis, Chongqing University. https://doi.org/10.27670/d.cnki.gcqdu.2020.000383. (in Chinese)
Li GZ, Li ZZ (2010) Carbon emissions decomposition analysis on agricultural energy consumption, ——based LMDI model. J Agrotech Econ 66–72. https://doi.org/10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2010.10.011. (in Chinese)
Li H, Zhang RN, Ai XN (2022) The current situation, problems, and countermeasures for high quality development of the Chinese coal industry. Coal Econ Res 42:48–54. https://doi.org/10.13202/j.cnki.cer.2022.07.012. (in Chinese)
Li ZG, Zhu YM, Wu Q (2019) GDIM-based research on driving factors of carbon emissions from manufacturing industry in Shandong Province. East China Econ Manag 33:30–36 (in Chinese)
Liao Q, Li P, Roosli RB et al (2022) Carbon emission characteristics of resource-based cities in China. Iran J Sci Technol, Trans Civil Eng 46:4579–4591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-022-00876-z
Lin B, Ouyang X (2014) Analysis of energy-related co2 (carbon dioxide) emissions and reduction potential in the Chinese non-metallic mineral products industry. Energy (oxf) 68:688–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.01.069
Lin BQ, Liu XY (2010) China’s carbon dioxide emissions under the urbanization process: influence factors and abatement policies. Econ Res J 45:66–78 (in Chinese)
Liu BS, Yang ZQ, Xue F, Sun XZ (2023) Policy effects assessment of urban sustainable development in China – quasi experimental evidence based on the National Sustainable Development Experimental Zones. J Public Manag 20:69–83. https://doi.org/10.16149/j.cnki.23-1523.20221128.003. (in Chinese)
Liu E, Wang Y, Chen W, Chen W, Ning S (2021) Evaluating the transformation of China’s resource-based cities: an integrated sequential weight and topsis approach. Socioecon Plann Sci 77:101022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2021.101022
Liu M, Yang X, Wen J et al (2023) Drivers of China’s carbon dioxide emissions: based on the combination model of structural decomposition analysis and input-output subsystem method. Environ Impact Assess Rev 100:107043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2023.107043
Liu YH, Li Y (2022) Calculation and decomposition of transport carbon emissions in Hubei Province. Statistics and Decision 38:88–92. https://doi.org/10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2022.15.016. (in Chinese)
Liu YX, Deng XR (2021) An empirical study on the influencing factors of carbon emissions in China: based on fixed effect panel quantile regression model. Journal of Shanxi University (Philosophy and Social Science Edition) 44:86–96. https://doi.org/10.13451/j.cnki.shanxi.univ(phil.soc.).2021.06.010. (in Chinese)
Liu Z, Guan D, Wei W et al (2015) Reduced carbon emission estimates from fossil fuel combustion and cement production in China. Nature 524:335–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14677
Lu C, Wang D, Meng P, Yang J, Pang M, Wang L (2019) Research on resource curse effect of resource-dependent cities: case study of Qing yang, Jin chang and Bai yin in China. Sustainability 11:91. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11010091
Ma XJ, Wang CX, Dong BY et al (2019) Carbon emissions from energy consumption in china: its measurement and driving factors. Sci Total Environ 648:1411–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.183
Martinez-Fernandez C, Audirac I, Fol S, Cunningham-Sabot E (2012) Shrinking cities: urban challenges of globalization. Int J Urban Reg Res 36:213–225. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2427.2011.01092.x
Masson-Delmotte V, Zhai P, Pirani A et al (2021) Climate change 2021: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group i to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. IPCC. https://iupac.org/climate-change-2021-the-physical-science-basis/
Meng Z, Wang H, Wang B (2018) Empirical analysis of carbon emission accounting and influencing factors of energy consumption in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112467
Nahrin R, Rahman MH, Majumder SC, Esquivias MA (2023) Economic growth and pollution nexus in Mexico, Colombia, and Venezuela (g-3 countries): the role of renewable energy in carbon dioxide emissions. Energies (Basel) 16:1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031076
Nie S, Zhou J, Yang F et al (2022) Analysis of theoretical carbon dioxide emissions from cement production: methodology and application. J Clean Prod 334:130270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130270
Pan XH, Chou W (2012) Empirical analysis of influence of fixed assets Investment on carbon dioxide emission in China. Soc Sci Guangxi 56–59. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-6917.2012.12.013. (in Chinese)
Peng D, Liu H (2023) Measurement and driving factors of carbon emissions from coal consumption in China based on the kaya-LMDI model. Energies (Basel) 16:439. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010439
Qian X, Wang D, Wang J, Chen S (2021) Resource curse, environmental regulation and transformation of coal-mining cities in China. Resour Policy 74:101447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101447
Ramírez A, de Keizer C, Van der Sluijs JP, Olivier J, Brandes L (2008) Monte Carlo analysis of uncertainties in the Netherlands greenhouse gas emission inventory for 1990–2004. Atmos Environ (1994) 42:8263–8272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.07.059
Sarpong KA, Xu W, Gyamfi BA, Ofori EK (2023) A step towards carbon neutrality in e7: the role of environmental taxes, structural change, and green energy. J Environ Manage 337:117556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117556
Shan Y, Guan D, Liu J et al (2017) Methodology and applications of city level co2 emission accounts in China. J Clean Prod 161:1215–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.075
Shao S, Liu J, Geng Y, Miao Z, Yang Y (2016) Uncovering driving factors of carbon emissions from China’ s mining sector. Appl Energy 166:220–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.01.047
Shao S, Zhang X, Zhao XR (2017) Empirical decomposition and peaking pathway of carbon dioxide emissions of China’s manufacturing sector: generalized divisia index method and dynamic scenario analysis. China Ind Econ 44–63. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2017.03.003. (in Chinese)
Shen L, Wu Y, Lou Y, Zeng D, Shuai C, Song X (2018) What drives the carbon emission in the Chinese cities? — a case of pilot low carbon city of Beijing. J Clean Prod 174:343–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.333
Shen W, Cao L, Li Q, Zhang W, Wang G, Li C (2015) Quantifying co2 emissions from China’s cement industry. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 50:1004–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.05.031
Sun Q, Lin D, Khayatnezhad M, Taghavi M (2021) Investigation of phosphoric acid fuel cell, linear fresnel solar reflector and organic rankine cycle polygeneration energy system in different climatic conditions. Process Saf Environ Prot 147:993–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.01.035
Tong X (2020) The spatiotemporal evolution pattern and influential factor of regional carbon emission convergence in China. Adv Meteorol 2020:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4361570
Trotta G (2020) Assessing drivers of energy consumption and progress toward energy targets in italy. Energy sources. Part B, Econ, Plan Policy 15:137–156. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567249.2020.1778817
Vaninsky A (2014) Factorial decomposition of co2 emissions: a generalized divisia index approach. Energy Econ 45:389–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2014.07.008
Wang C, Wang F, Zhang X et al (2017) Examining the driving factors of energy related carbon emissions using the extended STIRPAT model based on IPAT identity in Xinjiang. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 67:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.006
Wang Y (2022) Scenario prediction of China’s carbon emissions under the targets of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, Shandong University of Finance and Economics. https://doi.org/10.27274/d.cnki.gsdjc.2022.000612. (in Chinese)
Yi RG (2020) Research on Ordos’ industrial diversification development path avoiding “resource curse”, Inner Mongolia Normal University. https://doi.org/10.27230/d.cnki.gnmsu.2020.000402. (in Chinese)
Yu JH, Li JM, Zhang WZ (2018) Identification and classification of resource-based cities in China. Acta Geograph Sin 73:677–687. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb201804007. (in Chinese)
Yu Y, Jiang T, Li S, Li X, Gao D (2020) Energy-related co2 emissions and structural emissions’ reduction in China’s agriculture: an input–output perspective. J Clean Prod 276:124169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124169
Zhang C, Su B, Zhou K, Yang S (2019) Decomposition analysis of China’s co2 emissions (2000–2016) and scenario analysis of its carbon intensity targets in 2020 and 2030. Sci Total Environ 668:432–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.406
Zhang N, Lv L, Zhao M, Xiang M, Bai Z, Luo H (2022) A comparative study of stage characteristics and factorial decomposition of co2 emissions between China and the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:48769–48783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18811-0
Zhong MC, Wang YS (2022) Research on the transformation direction of fixed asset investment under the “dual carbon” goals: based on the perspective of “steady growth”. Shanghai J Econ 75–92. https://doi.org/10.19626/j.cnki.cn31-1163/f.2022.12.004. (in Chinese)
Zhou J, Zhang Z, Xu X, Chang D (2022) Does the transformation of resource-dependent cities promote the realization of the carbon-peaking goal? An analysis based on typical resource-dependent city clusters in China. J Clean Prod 365:132731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132731
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express gratitude to the editor and anonymous referees for their insightful and constructive comments.
Funding
This study is supported by Expert Advisory and Argumentation Committee of Ordos City (ZXW2000-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jing Li: conceptualization, methodology, date curation, software, writing—original draft, formal analysis, visualization. Zhuoya Ma: methodology, date curation, validation, writing—review and editing. Haowei Sun: software, visualization. Wenhui Chen: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Ma, Z., Sun, H. et al. Driving factor analysis and dynamic forecast of industrial carbon emissions in resource-dependent cities: a case study of Ordos, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 92146–92161 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28872-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28872-4