Abstract
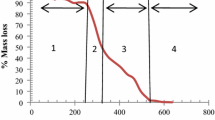
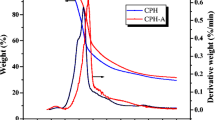
The objective of this research was to produce an activated carbon (AC) from exhausted coffee grounds (ECG) and chemically activate it with natural lye from eucalyptus ash to subsequently evaluate the fluoride adsorption process in an aqueous medium. The thermal analysis of ECG was determined as well as solubilized extraction, alkalinity and calcium content of eucalyptus ashes. AC was characterized by elemental analysis, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), analysis of textural properties, pH and point of zero charge (PZC). The AC presented macroporosity and XRD confirmed the amorphous characteristic of cellulose-containing materials. Carboxylic acid functional group was identified in the AC surface, which can contribute to the adsorption of fluoride. The specific surface area of ECG and AC were 189.01 and 21.74 m2/g. The adsorption kinetics of fluoride revealed that equilibrium is reached around 800 min and the data followed the pseudo-second order model. The Freundlich model fitted the experimental data with the best quality and Freundlich’s constant n allowed inferring that the adsorption is favorable and the isotherm appears to be L-type, with an initial downward curvature, which suggests less availability of active sites when increasing the adsorbent concentration.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Alves A, Antero R, Oliveira S, Ojala S, Scalize P (2019) Activated carbon produced from waste coffee grounds for an effective removal of bisphenol-A in aqueous medium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:24850–24862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05717-7
American Public Health Association (2017) Ion-Selective Electrode Method 4500-F. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation. https://www.standardmethods.org/doi/10.2105/SMWW.2882.081. Accessed 12 October 2022
Babu AN, Reddy DS, Kumar GS, Ravindhranath K, Mohan GVK (2018) Removal of lead and fluoride from contaminated water using exhausted coffee grounds based bio-sorbent. J Environ Manag 218:602–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.091
Ballesteros LF, Teixeira JA, Mussatto SI (2014) Chemical, Functional, and Structural Properties of Spent Coffee Grounds and Coffee Silverskin. Food Bioprocess Technol 7:3493–3503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1349-z
Barrett EP, Joyner LG, Halenda PP (1951) The Determination of Pore Volume and Area Distributions in Porous Substances I Computations from Nitrogen. I. sotherms. J Am Chem Soc 73(1):373–380. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01145a126
Bhatnagar A, Kumar E, Sillanpää M (2011) Fluoride removal from water by adsorption - A review. Chem Eng J 171:811–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.028
Block I, Günter C, Rodrigues AD, Paasch S, Hesemann P, Taubert A (2021) Carbon Adsorbents from Spent Coffee for Removal of Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange from Water. Materials 14:3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143996
Bok JP, Choi HS, Choi YS, Park HC, Kim SJ (2012) Fast pyrolysis of coffee grounds: Characteristics of product yields and biocrude oil quality. Energy 47:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.06.003
Boudrahem F, Aissani-Benissad F, Aït-Amar H (2009) Batch sorption dynamics and equilibrium for the removal of lead ions from aqueous phase using activated carbon developed from coffee residue activated with zinc chloride. J Environ Manag 90:3031–3039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.04.005
Brazil (2017) Portaria de Consolidação n. 5, de 28 de setembro de 2017. Consolidação das normas sobre as ações e os serviços de saúde do Sistema Único de Saúde. Diário Oficial da União. https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/composicao/sectics/farmacia-popular%20old/legislacao/prc-5-portaria-de-consolida-o-n-5-de-28-de-setembro-de-2017.pdf/view. Accessed 28 March 2022
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorpotion of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J Am Chem Soc 60(2):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a023
Cao H, Wu X, Syed-Hassan SSA, Zhang S, Mood SH, Milan YJ, Garcia-Perez M (2020) Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphorous adsorption by rape straw-derived biochar functionalized with calcium from eggshell. Bioresour Technol 318:124063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124063
Cetesb (2014) Valores orientadores para solo e água subterrânea no estado de São Paulo. Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo. https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/aguas-subterraneas/valores-orientadores-para-solo-e-agua-subterranea/. Accessed 28 March 2022
Chae G, Yun S, Kwon M, Kim Y, Mayer B (2006) Batch dissolution of granite and biotite in water: Implication for fluorine geochemistry in groundwater. Geochem J 40:95–102. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.40.95
Chen N, Zhang Z, Feng C, Sugiura N, Li M, Chen R (2010) Fluoride removal from water by granular ceramic adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 348(2):579–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.04.048
Delle Site A (2001) Factors Affecting Sorption of Organic Compounds in Natural Sorbent/Water Systems and Sorption Coefficients for Selected Pollutants: a review. J Phys Chem Ref Data 30(1):187–439. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1347984
Dhillon A, Prasad S, Kumar D (2016) Recent advances and spectroscopic perspectives in fluoride removal. Appl Spectrosc Rev 52(3):175–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2016.1213737
Dong Z-B, Liang Y-R, Fan F-Y, Ye J-H, Zheng X-Q, Lu J-L (2011) Adsorption Behavior of the Catechins and Caffeine onto Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone. J Agric Food Chem 59(8):4238–4247. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf200089m
Gao Y, Li L, Jin Y, Wang Y, Yuan C, Wei Y, Chen G, Ge J, Lu H (2015) Porous carbon made from rice husk as electrode material for electrochemical double layer capacitor. Appl Energy 153:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.070
Giles CH, Macewan TH, Nakhwa SN, Smith D (1960) Studies in adsorption. Part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J Chem Soc 846:3973–3993. https://doi.org/10.1039/JR9600003973
Guijarro-Aldaco A, Hernández-Montoya V, Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Montes-Morán MA, Mendoza-Castillo D (2011) I. Improving the adsorption of heavy metals from water using commercial carbons modified with egg shell wastes. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(15):9354–9362. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie2006627
Habuda-Stanić M, Ravančić M, Flanagan A (2014) A Review on Adsorption of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution. Materials 7(9):6317–6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7096317
Ho YS, Mckay G (1998) A Comparison of Chemisorption Kinetic Models Applied to Pollutant Removal on Various Sorbents. Process Saf Environ Prot 76(4):332–340. https://doi.org/10.1205/095758298529696
IUPAC (1985) Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure Appl Chem 57(4):603–619. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603
IUPAC (1994) Recommendations for the Characterization of Porous Solids. Pure Appl Chem 66(8):1739–1758. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199466081739
Júnior RB (2017) Coffee ground pyrolysis: chemical kinetics and fixed bed operation. Dissertation, Federal University of Triângulo Mineiro. http://bdtd.uftm.edu.br/handle/tede/627. Accessed 12 Mar 2023
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven Vetenskapsakad Handingarl 24(4):1–39
Li J, Tian T, Jia Y, Xu N, Yang S, Zhang C, Gao S, Shen W, Wang Z (2023) Adsorption performance and optimization by response surface methodology on tetracycline using Fe-doped ZIF-8-loaded multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:4123–4136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22524-9
Lima ACA, Santos BA, França AMM, Vidal CB, Melo DQ, Raulino GSC, Rocha JS, Sasaki JM, Nascimento RF (2020) Caracterização de Materiais Adsorventes. In: Nascimento RF, Lima ACA, Vidal CB, Melo DQ, Raulino GSC (eds) Adsorção: aspectos teóricos e aplicações ambientais, 2nd edn. Imprensa Universitária, Fortaleza, pp 258–303
Lima SB (2013) Preparation of activated carbon from coconut mesocarp, using different activating agents. Dissertation, Bahia Federal University
Melo DQ, França AMM, Barros AL, Lima ACA, Vidal CB, Raulino GSC, Nascimento RF, Neto VCS (2020) Equilíbrio de Adsorção. In: Nascimento RF, Lima ACA, Vidal CB, Melo DQ, Raulino GSC (eds) Adsorção: aspectos teóricos e aplicações ambientais, 2nd edn. Imprensa Universitária, Fortaleza, pp 25–63
Miretzky P, Cirelli AF (2011) Fluoride removal from water by chitosan derivatives and composites: A review. J Fluorine Chem 132:231–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2011.02.001
Nowicki P (2016) Effect of heat treatment on the physicochemical properties of nitrogen-enriched activated carbons. J Therm Anal Calorim 125:1017–1024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5254-8
Ogata F, Tominaga H, Yabutani H, Kawasaki N (2011) Removal of Fluoride Ions from Water by Adsorption onto Carbonaceous Materials Produced from Coffee Grounds. J Oleo Sci 60(12):619–625. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.60.619
Oliveira YR (2018) Study of Cu (II) adsorption using Conilon coffee straw carbon. Dissertation, Federal University of Espírito Santo. http://repositorio.ufes.br/handle/10/10203. Accessed 20 Mar 2023
Panchal M, Raghavendra G, Ojha S, Omprakash M, Acharya SK (2019) A single step process to synthesize ordered porous carbon from coconut shells-eggshells biowaste. Mater Res Express 6(11):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab4cb3
Park J, Regalbuto J (1995) A Simple, Accurate Determination of Oxide PZC and the Strong Buffering Effect of Oxide Surfaces at Incipient Wetness. J Colloid Interface Sci 175(1):239–252. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1995.1452
Pujol D, Liu C, Gominho J, Olivella MÀ, Fiol N, Villaescusa I, Pereira H (2013) The chemical composition of exhausted coffee waste. Ind Crops Prod 50:423–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.07.056
Qiu J, Hou H, Liang S, Yang L, Gan Q, Tao S, Yu W, Ruibin LV, Ding L, Xiao K, Hu J, Liu B, Yang J (2022) Hierarchically porous biochar preparation and simultaneous nutrient recovery from sewage sludge via three steps of alkali-activated pyrolysis, water leaching and acid leaching. Resour Conserv Recycl 176:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105953
Rahmani-Sani A, Singh P, Raizada P, Lima EC, Anastopoulos I, Giannakoudakis DA, Sivamani S, Dontsova TA, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A (2020) Use of chicken feather and eggshell to synthesize a novel magnetized activated carbon for sorption of heavy metal ions. Bioresour Technol 297:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122452
Salifu A (2017) Fluoride Removal from Groundwater by Adsorption Technology: the occurrence, adsorbent synthesis, regeneration and disposal. CRC Press, London. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781351199995
Santos HVR (2022) Removal of fluoride from aqueous media using biochar produced from coffee grounds and functionalized with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Dissertation, Goiás Federal University
Shi Y, Liu G, Li M, Wang L (2020) Egg shell waste as an activation agent for the manufacture of porous carbon. Chin J Chem Eng 28(3):896–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.09.014
Singh YD, Mahanta P, Bora U (2017) Comprehensive characterization of lignocellulosic biomass through proximate, ultimate and compositional analysis for bioenergy production. Renew Energy 103:490–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.11.039
Swain SK, Dey RK, Islam M, Patel RK, Jha U, Patnaik T, Airoldi C (2009) Removal of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution Using Aluminum-Impregnated Chitosan Biopolymer. Sep Sci Technol 44(9):2096–2116. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390902881212
Vardon D, Moser B, Zheng W, Witkin K, Evangelista R, Strathmann T, Rajagopalan K, Sharma B (2013) Complete utilization of spent coffee grounds to produce biodiesel, bio-oil, and biochar. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1(10):1286–1294. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc400145w
Vidal CB, Lima ACA, Melo DQ, Raulino GSC, Nascimento RF (2020) Cinética de Adsorção. In: Nascimento RF, Lima ACA, Vidal CB, Melo DQ, Raulino GSC (eds) Adsorção: aspectos teóricos e aplicações ambientais, 2nd edn. Imprensa Universitária, Fortaleza, pp 64–87
World Health Organization (2017) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Yang H, Yan R, Chen H, Lee DH, Zheng C (2007) Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 86(12–13):1781–1788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.12.013
Funding
This work was supported by Fundação Nacional de Saúde (FUNASA) through TED 03/2018, Universidade Federal de Goiás (UFG) and Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia de Goiás (IFG) for the master’s scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Mário Henrique Lobo Bergamini, Sérgio Botelho de Oliveira and Paulo Sérgio Scalize. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mário Henrique Lobo Bergamini and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No individual information was included in our study, so our study was exempted from approval by the Ethics Committee of Universidade Federal de Goiás, Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil.
Consent to participate
All the authors participated in this article.
Consent to Publish
All of the authors approved the manuscript for publication.
Financial interests
All authors declare they have no financial interests.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bergamini, M.H.L., de Oliveira, S.B. & Scalize, P.S. Production of activated carbon from exhausted coffee grounds chemically modified with natural eucalyptus ash lye and its use in the fluoride adsorption process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 91276–91291 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28825-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28825-x