Abstract
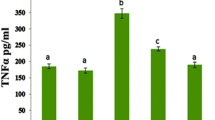
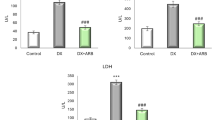
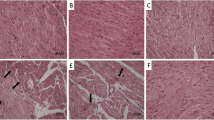
This study aimed to explore whether allicin (ALC) and lycopene (LP) could offer protection against the harmful effects of methotrexate (MTX), a type of chemotherapy drug known for its severe side effects, on the heart of rats. In this experiment, seven groups of rats (n = 7) were used. The first group was given saline as a control vehicle, the second group was given ALC at a dosage of 20 mg/kg orally, the third group was given LP at a dosage of 10 mg/kg orally, and the fourth group was given MTX at a dosage of 20 mg/kg intraperitoneally on the 15th day of the experiment. The remaining three groups received treatments, including ALC + MTX, LP + MTX, and ALC + LP + MTX. After the administration of MTX, the concentrations of serum cardiac biomarkers, such as Creatine kinase (CK), Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and creatine kinase-myoglobin binding (CK-MB) were found to increase. Also, MTX caused a notable rise in malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and significant declines in the levels of glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) in the heart tissues of rats. In addition, MTX caused alterations in the cardiac histopathology and enhanced the caspase-3 expression in the cardiac tissues, indicating the occurrence of apoptosis. The antioxidant properties of ALC and/or LP were effectively reduced cardiac toxicity and apoptosis induced by MTX. The administration of ALC and/or LP was found to alleviate these effects caused by MTX.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the first author.
References
Abdel-Daim MM, Khalifa HA, Abushouk AI, Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy SA (2017a) Diosmin attenuates methotrexate-induced hepatic, renal, and cardiac injury: a biochemical and histopathological study in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:3281670
Abdel-Daim MM, Kilany OE, Khalifa HA, Ahmed AA (2017b) Allicin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80:745–753
Abdel-Daim MM, Eltaysh R, Hassan A, Mousa SA (2018) Lycopene attenuates tulathromycin and diclofenac sodium-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. Int J Mol Sci 19:344
Abei H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Aboubakr M, Elshafae SM, Abdelhiee EY, Fadl SE, Soliman A, Abdelkader A, Abdel-Daim MM, Bayoumi KA, Baty RS, Elgendy E (2021) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of thymoquinone and lycopene mitigate the chlorpyrifos-induced toxic neuropathy. Pharmaceuticals 14:940
Aboubakr M, Elmahdy AM, Taima S, Emam MA, Farag A, Alkafafy M, Said AM, Soliman A (2023) Protective effects of N acetylcysteine and vitamin E against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Pak Vet J 43:262–268
Al-Abkal F, Abdel-Wahab BA, El-Kareem HFA, Moustafa YM, Khodeer DM (2022) Protective effect of pycnogenol against methotrexate-induced hepatic, renal, and cardiac toxicity: An in vivo study. Pharmaceuticals 15:674
Al-Taher AY, Morsy MA, Rifaai RA, Zenhom NM, Abdel-Gaber SA (2020) Paeonol attenuates methotrexate-induced cardiac toxicity in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and suppressing TLR4-induced NF-κB inflammatory pathway. Mediators Inflamm 2020:8641026
Amagase H (2020) Clarifying the real bioactive constituents of garlic. J Nutr 136:716S-725S
Asci H, Ozmen O, Ellidag HY, Aydin B, Bas E, Yilmaz N (2017) The impact of gallic acid on the methotrexate-induced kidney damage in rats. J Food Drug Anal 25:890–897
Aydin S, Ugur K, Aydin S, Sahin İ, Yardim M (2019) Biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction: current perspectives. Vasc Health Risk Manag 15:1–10
Bancroft JD, Layton C, Suvarna SK (2013) Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier
Bartyik K, Turi S, Orosz F, Karg E (2004) Methotrexate inhibits the glyoxalase system in vivo in children with acute lymphoid leukaemia. Eur J Cancer 40:2287–2292
Bedoui Y, Guillot X, Sélambarom J, Guiraud P, Giry C, Jaffar-Bandjee MC, Ralandison S, Gasque P (2019) Methotrexate an old drug with new tricks. Int J Mol Sci 20:5023
Buhl S, Jackson K (1978) Optimal conditions and comparison of lactate dehydrogenase catalysis of the lactate-to-pyruvate and pyruvate-to-lactate reactions in human serum at 25, 30, and 37 degrees C. Clin Chem 24:828–831
Çakır T, Özkan E, Dulundu E, Topaloğlu Ü, Şehirli AÖ, Ercan F, Şener E, Şener G (2011) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) prevents methotrexate-induced hepatorenal oxidative injury in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 63:1566–1571
Castrogiovanni P, Trovato FM, Szychlinska MA, Loreto C, Giunta S, Scuderi S, Passanisi R, Fidone F, Fagone P, Imbesi R (2016) Effects of synthetic anti-inflammatory sterol in CB3V-induced myocarditis: a morphological study on heart muscle tissue. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol 1:69–89
Cui L, Xu F, Wu K, Li L, Qiao T, Li Z, Chen T, Sun C (2020) Anticancer effects and possible mechanisms of lycopene intervention on N-methylbenzylnitrosamine induced esophageal cancer in F344 rats based on PPARγ1. Eur J Pharmacol 881:173230
Duzen I, Oguz E, Yilmaz R, Taskin A, Vuruskan E, Cekici Y, Bilgel Z, Goksuluk H, Candemir B, Sucu M (2019) Lycopene has a protective effect on septic shock-induced cardiac injury in rats. Bratisl Lek Listy 120:919–923
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Elsayed A, Elkomy A, Elkammar R, Youssef G, Abdelhiee EY, Abdo W, Fadl SE, Soliman A, Aboubakr M (2021) Synergistic protective effects of lycopene and N-acetylcysteine against cisplatin-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats. Sci Rep 11:1–10
Elsayed A, Elkomy A, Alkafafy M, Elkammar R, El-Shafey A, Soliman A, Aboubakr M (2022a) Testicular toxicity of cisplatin in rats: ameliorative effect of lycopene and N-acetylcysteine. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:24077–24084
Elsayed A, Elkomy A, Alkafafy M, Elkammar R, Fadl SE, Abdelhiee EY, Abdeen A, Youssef G, Shaheen H, Soliman A (2022b) Ameliorating effect of lycopene and N-acetylcysteine against cisplatin-induced cardiac injury in rats. Pak Vet J 42:107–111
Erdogan E, Ilgaz Y, Gurgor PN, Oztas Y, Topal T, Oztas E (2015) Rutin ameliorates methotrexate induced hepatic injury in rats. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira 30:778–784
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hosseini A, Hosseinzadeh H (2015) A review on the effects of Allium sativum (Garlic) in metabolic syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest 38:1147–1157
Imran M, Ghorat F, Ul-Haq I, Ur-Rehman H, Aslam F, Heydari M, Shariati MA, Okuskhanova E, Yessimbekov Z, Thiruvengadam M, Hashempur MH, Rebezov M (2020) Lycopene as a Natural Antioxidant Used to Prevent Human Health Disorders. Antioxidants (basel) 9:706
Lawson LD, Hunsaker SM (2018) Allicin bioavailability and bioequivalence from garlic supplements and garlic foods. Nutrients 10:812
Liu S, He Y, Shi J, Liu L, Ma H, He L, Guo Y (2019) Allicin attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats by inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress, Transplantation proceedings. Elsevier, pp 2060–2065
Ma L-N, Li L-D, Li S-C, Hao X-M, Zhang J-Y, He P, Li Y-K (2017) Allicin improves cardiac function by protecting against apoptosis in rat model of myocardial infarction. Chin J Integr Med 23:589–597
Mahmoud RH, Mohammed MA, Said ES, Morsi EM, Abdelaleem OO, All MA, Elsayed RM, Abdelmeguid EA, Eldosoki DE (2021) Assessment of the cardioprotective effect of liraglutide on methotrexate induced cardiac dysfunction through suppression of inflammation and enhancement of angiogenesis in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 25:6013–6024
Marón FJM, Camargo AB, Manucha W (2020) Allicin pharmacology: Common molecular mechanisms against neuroinflammation and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci 249:117513
Neumeier D, Prellwitz W, Würzburg U, Brundobler M, Olbermann M, Just H-J, Knedel M, Lang H (1976) Determination of creatine kinase isoenzyme MB activity in serum using immunological inhibition of creatine kinase M subunit activity activity kinetics and diagnostic significance in myocardial infarction. Clin Chim Acta 73:445–451
Nishikimi M, Rao NA, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Rose P, Moore PK, Zhu Y-Z (2018) Garlic and gaseous mediators. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39:624–634
Sánchez-Gloria JL, Arellano-Buendía AS, Juárez-Rojas JG, García-Arroyo FE, Argüello-García R, Sánchez-Muñoz F, Sánchez-Lozada LG, Osorio-Alonso H (2022) Cellular Mechanisms Underlying the Cardioprotective Role of Allicin on Cardiovascular Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 23(16):9082
Solomon DH, Glynn RJ, Karlson EW, Lu F, Corrigan C, Colls J, Xu C, MacFadyen J, Barbhaiya M, Berliner N (2020) Adverse effects of low-dose methotrexate: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 172:369–380
Szasz G, Waldenström J, Gruber W (1979) Creatine kinase in serum: 6. Inhibition by endogenous polyvalent cations, and effect of chelators on the activity and stability of some assay components. Clin Chem 25:446–452
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278
Ugwor EI, Ugbaja RN, James AS, Dosumu OA, Thomas FC, Ezenandu EO, Graham RE (2022) Inhibition of fat accumulation, lipid dysmetabolism, cardiac inflammation, and improved nitric oxide signalling mediate the protective effects of lycopene against cardio-metabolic disorder in obese female rats. Nutr Res 104:140–153
Wang J, Geng T, Zou Q, Yang N, Zhao W, Li Y, Tan X, Yuan T, Liu X, Liu Z (2020) Lycopene prevents lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by stimulating PPARα and improving mitochondrial function. J Funct Foods 67:103857
Xu W, Li X-p, Li E-z, Liu Y-f, Zhao J, Wei L-n, Ma L (2020) Protective Effects of Allicin on ISO-Induced Rat Model of Myocardial Infarction via JNK Signaling Pathway. Pharmacology 105:505–513
Yiang G-T, Chou P-L, Hung Y-T, Chen J-N, Chang W-J, Yu Y-L, Wei C-W (2014) Vitamin C enhances anticancer activity in methotrexate-treated Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 32:1057–1063
Yilmaz S, Kaya E, Karaca A, Karatas O (2018) Aflatoxin B1 induced renal and cardiac damage in rats: protective effect of lycopene. Res Vet Sci 119:268–275
Zhu R, Wei J, Liu H, Liu C, Wang L, Chen B, Li L, Jia Q, Tian Y, Li R (2020) Lycopene attenuates body weight gain through induction of browning via regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J Nutr Biochem 78:108335
Acknowledgements
The researchers would like to acknowledge Deanship of Scientific Research, Taif University for funding this work.
Funding
Deanship of Scientific Research, Taif University, Saudi Arabia (For Mohamed Alkafafy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experiment design: MA. Data collection, and statistical analysis: AS and ME. Writing and drafting: AF, AF, and MA. All authors reviewed and edited the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine's Research Ethical Committee, Cairo University, Egypt (Vet CU 01122022619) approved the study.
Consent to participate
All authors approved the final version.
Consent for publication
• The manuscript is not previously published in the same or very similar form in other
Journal.
• The manuscript is not currently under consideration in other journals
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aboubakr, M., Farag, A., Elfadadny, A. et al. Antioxidant and anti-apoptotic potency of allicin and lycopene against methotrexate-induced cardiac injury in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 88724–88733 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28686-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28686-4