Abstract
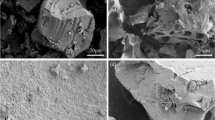
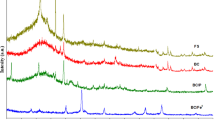
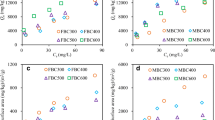
In this study, the tetracycline (TC) removal performance of iron-loaded biochar (BPFSB) derived from sugarcane bagasse and polymerized iron sulfate was investigated, and the mechanism of TC removal was also explored by study of isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics and characterization of fresh and used BPFSB (XRD, FTIR, SEM and XPS). The results showed that under optimized conditions (initial pH 2; BPFSB dosage 0.8 g·L−1; TC initial concentration 100 mg·L−1; Contact time 24 h; temperature 298 K), the removal efficiency of TC was as high as 99.03%. The isothermal removal of TC followed well the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models, indicating that multilayer surface chemisorption dominated the TC removal. The maximum removal capacity of TC by BPFSB at different temperatures was 185.5 mg·g−1 (298 K), 192.7 mg·g−1 (308 K), and 230.9 mg·g−1 (318 K), respectively. The pseudo-second-kinetic model described the TC removal better, while its rate-controlling step was a combination of liquid film diffusion, intraparticle diffusion, and chemical reaction. Meanwhile, TC removal was also a spontaneous and endothermic process, during which the randomness and disorder between the solid–liquid interface was increased. According to the characterization of BPFSBs before and after TC removal, H-bonding and complexation were the major interactions for TC surface adsorption. Furthermore, BPFSB was efficiently regenerated by NaOH. In summary, BPFSB had the potential for practical application in TC removal.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data-set used and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alchouron J, Navarathna C, Chludil HD, Dewage NB, Perez F, Hassan EB, Pittman CU Jr, Vega AS, Mlsna TE (2020) Assessing South American Guadua chacoensis bamboo biochar and Fe3O4 nanoparticle dispersed analogues for aqueous arsenic(V) remediation. Sci Total Environ 706:135943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135943
Amaly N, El-Moghazy AY, Sun G, Pandey PK (2021) Effective tetracycline removal from liquid streams of dairy manure via hierarchical poly (vinyl alcohol-co-ethylene)/polyaniline metal complex nanofibrous membranes. J Colloid Interface Sci 597:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.03.165
Chen W, Zhao B, Guo Y, Guo Y, Zheng Z, Pak T, Li G (2021) Effect of hydrothermal pretreatment on pyrolyzed sludge biochars for tetracycline adsorption. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106557
Gan Q, Hou H, Liang S, Qiu J, Tao S, Yang L, Yu W, Xiao K, Liu B, Hu J, Wang Y, Yang J (2020) Sludge-derived biochar with multivalent iron as an efficient Fenton catalyst for degradation of 4-Chlorophenol. Sci Total Environ 725:138299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138299
Gómez E, Cestaro R, Philippe L, Serrà A (2022) Electrodeposition of nanostructured Bi2MoO6@Bi2MoO6–x homojunction films for the enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics. Appl Catal B-Environ 317:121703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121703
Güleç F, Williams O, Kostas ET, Samson A, Stevens LA, Lester E (2022) A comprehensive comparative study on methylene blue removal from aqueous solution using biochars produced from rapeseed, whitewood, and seaweed via different thermal conversion technologies. Fuel 330:125428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125428
Guo X, Mu Q, Zhong H, Li P, Zhang C, Wei D, Zhao T (2019) Rapid removal of tetracycline by Myriophyllum aquaticum: Evaluation of the role and mechanisms of adsorption. Environ Pollut 254:113101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113101
Hao D, Chen Y, Zhang Y, You N (2021) Nanocomposites of zero-valent iron@biochar derived from agricultural wastes for adsorptive removal of tetracyclines. Chemosphere 284:131342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131342
Hassan M, Liu Y, Naidu R, Parikh SJ, Du J, Qi F, Willett IR (2020) Influences of feedstock sources and pyrolysis temperature on the properties of biochar and functionality as adsorbents: A meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 744:140714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140714
He L, Lv L, Pillai SC, Wang H, Xue J, Ma Y, Liu Y, Chen Y, Wu L, Zhang Z, Yang L (2021) Efficient degradation of diclofenac sodium by periodate activation using Fe/Cu bimetallic modified sewage sludge biochar/UV system. Sci Total Environ 783:146974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146974
He X, Kai T, Ding P (2021b) Heterojunction photocatalysts for degradation of the tetracycline antibiotic: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:4563–4601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01295-8
Hu Y, Chen D, Zhang R, Ding Y, Ren Z, Fu M, Cao X, Zeng G (2021) Singlet oxygen-dominated activation of peroxymonosulfate by passion fruit shell derived biochar for catalytic degradation of tetracycline through a non-radical oxidation pathway. J Hazard Mater 419:126495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126495
Jiang YC, Luo MF, Niu ZN, Xu SY, Gao Y, Gao Y, Gao WJ, Luo JJ, Liu RL (2023) In-situ growth of bimetallic FeCo-MOF on magnetic biochar for enhanced clearance of tetracycline and fruit preservation. Chem Eng J 451:138804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138804
Jin J, Yang Z, Xiong W, Zhou Y, Xu R, Zhang Y, Cao J, Li X, Zhou C (2019) Cu and Co nanoparticles co-doped MIL-101 as a novel adsorbent for efficient removal of tetracycline from aqueous solutions. Sci Total Environ 650:408–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.434
Kulandaivelu J, Choi PM, Shrestha S, Li X, Song Y, Li J, Sharma K, Yuan Z, Mueller JF, Wang C, Jiang G (2020) Assessing the removal of organic micropollutants from wastewater by discharging drinking water sludge to sewers. Water Res 181:115945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115945
Li A, Ge W, Liu L, Qiu G (2022) Preparation, adsorption performance and mechanism of MgO-loaded biochar in wastewater treatment: A review. Environ Res 212:113341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113341
Li S, Huang W, Yang P, Li Z, Xia B, Li M, Xue C, Liu D (2021) One-pot synthesis of N-doped carbon intercalated molybdenum disulfide nanohybrid for enhanced adsorption of tetracycline from aqueous solutions. Sci Total Environ 754:141925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141925
Li X, Wang C, Zhang J, Liu J, Liu B, Chen G (2020) Preparation and application of magnetic biochar in water treatment: A critical review. Sci Total Environ 711:134847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134847
Li Y, Cao H, Liu W, Liu P (2022) Effective degradation of tetracycline via recyclable cellulose nanofibrils/polyvinyl alcohol/Fe3O4 hybrid hydrogel as a photo-Fenton catalyst. Chemosphere 307:135665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135665
Li Z, Wang Y, Zheng S, Qian P, Zhang X, Han P, Tu Y, Ye S (2022c) Nanosheets-MnxOy anchored biochar for efficient removal of methyl blue and tetracycline from water. Chem Eng Res Des 182:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2022.03.032
Lian J, Zhou F, Chen B, Yang M, Wang S, Liu Z, Niu S (2020) Enhanced adsorption of molybdenum(VI) onto drinking water treatment residues modified by thermal treatment and acid activation. J Clean Prod 244:118719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118719
Liang J, Li X, Yu Z, Zeng G, Luo Y, Jiang L, Yang Z, Qian Y, Wu H (2017) Amorphous MnO2 Modified Biochar Derived from Aerobically Composted Swine Manure for Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II). ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 5:5049–5058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00434
Liao Q, Rong H, Zhao M, Luo H, Chu Z, Wang R (2022) Strong adsorption properties and mechanism of action with regard to tetracycline adsorption of double-network polyvinyl alcohol-copper alginate gel beads. J Hazard Mater 422:126863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126863
Liu H, Xu G, Li G (2020) The characteristics of pharmaceutical sludge-derived biochar and its application for the adsorption of tetracycline. Sci Total Environ 747:141492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141492
Liu X, Guo X, Liu Y, Lu S, Xi B, Zhang J, Wang Z, Bi B (2019) A review on removing antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater by constructed wetlands: Performance and microbial response. Environ Pollut 254:112996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.112996
Ma Y, Lu T, Tang J, Li P, Mašek O, Yang L, Wu L, He L, Ding Y, Gao F, Qi X, Zhang Z (2022) One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic N-doped sludge biochar for efficient removal of tetracycline from various environmental waters. Sep Purif Technol 297:121426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121426
Ma Y, Qi Y, Yang L, Wu L, Li P, Gao F, Qi X, Zhang Z (2021) Adsorptive removal of imidacloprid by potassium hydroxide activated magnetic sugarcane bagasse biochar: Adsorption efficiency, mechanism and regeneration. J Clean Prod 292:126005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126005
Mei Y, Xu J, Zhang Y, Li B, Fan S, Xu H (2021) Effect of Fe-N modification on the properties of biochars and their adsorption behavior on tetracycline removal from aqueous solution. Bioresource Technol 325:124732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124732
Ndagijimana P, Liu X, Xu Q, Li Z, Pan B, Liao X, Wang Y (2022) Nanoscale zero-valent iron/silver@activated carbon-reduced graphene oxide: Efficient removal of trihalomethanes from drinking water. Sci Total Environ 839:156228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156228
Oladipo AA, Ifebajo AO (2018) Highly efficient magnetic chicken bone biochar for removal of tetracycline and fluorescent dye from wastewater: Two-stage adsorber analysis. J Environ Manage 209:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.12.030
Omidi MH, Azqhandi MHA, Ghalami-Choobar B (2022) Synthesis, characterization, and application of graphene oxide/layered double hydroxide /poly acrylic acid nanocomposite (LDH-rGO-PAA NC) for tetracycline removal: A comprehensive chemometric study. Chemosphere 308:136007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136007
Pi Z, Li X, Wang D, Xu Q, Tao Z, Huang X, Yao F, Wu Y, He L, Yang Q (2019) Persulfate activation by oxidation biochar supported magnetite particles for tetracycline removal: Performance and degradation pathway. J Clean Prod 235:1103–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.037
Raj V, Chauhan MS, Pal SL (2022) Potential of sugarcane bagasse in remediation of heavy metals: A review. Chemosphere 307:135825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135825
Shaheen SM, Mosa A, Natasha Abdelrahman H, Niazi NK, Antoniadis V, Shahid M, Song H, Kwon EE, Rinklebe J (2022) Removal of toxic elements from aqueous environments using nano zero-valent iron- and iron oxide-modified biochar: a review. Biochar 4:24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-022-00149-y
Shi W, Ren H, Li M, Shu K, Xu Y, Yan C, Tang Y (2020) Tetracycline removal from aqueous solution by visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation with low cost red mud wastes. Chem Eng J 382:122876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122876
Singh M, Ahsan M, Pandey V, Singh A, Mishra D, Tiwari N, Singh P, Karak T, Khare P (2022) Comparative assessment for removal of anionic dye from water by different waste-derived biochar vis a vis reusability of generated sludge. Biochar 4:13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-022-00140-7
Song W, Wu Z, Xu X, Wu H, Yao Y (2022) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets with Fe-based nanoparticles for highly efficient degradation of antibiotics and sulfate ion enhancement effect. Chemosphere 294:133704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133704
Song X, Shui B, Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang S, Wu N (2022b) Adsorption performance of GO-doped activated ATP composites towards tetracycline. RSC Adv 12:19917–19928. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra03023c
Song YX, Chen S, You N, Fan HT, Sun LN (2020) Nanocomposites of zero-valent Iron@Activated carbon derived from corn stalk for adsorptive removal of tetracycline antibiotics. Chemosphere 255:126917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126917
Sun L, Li J, Li X, Liu C, Wang H, Huo P, Yan YS (2019) Molecularly imprinted Ag/Ag(3)VO(4)/g-C(3)N(4) Z-scheme photocatalysts for enhanced preferential removal of tetracycline. J Colloid Interf Sci 552:271–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.05.060
Sun S, Jiang Q, Zhang W, Tian L, Li T, Zheng L, Gao Y, Zeng X, Zhou L (2022) Efficient adsorption of tetracycline in aquatic system by thermally-treated sediment. Environ Res 214:113779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113779
Tang J, Ma Y, Cui S, Ding Y, Zhu J, Chen X, Zhang Z (2022) Insights on ball milling enhanced iron magnesium layered double oxides bagasse biochar composite for ciprofloxacin adsorptive removal from water. Bioresource Technol 359:127468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127468
Wang W, Gao M, Cao M, Dan J, Yang H (2021) Self-propagating synthesis of Zn-loaded biochar for tetracycline elimination. Sci Total Environ 759:143542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143542
Wang W, Gao M, Cao M, Liu X, Yang H, Li Y (2021) A series of novel carbohydrate-based carbon adsorbents were synthesized by self-propagating combustion for tetracycline removal. Bioresource Technol 332:125059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125059
Wang W, Kang R, Yin Y, Tu S, Ye L (2022) Two-step pyrolysis biochar derived from agro-waste for antibiotics removal: Mechanisms and stability. Chemosphere 292:133454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133454
Wei J, Liu Y, Li J, Zhu Y, Yu H, Peng Y (2019) Adsorption and co-adsorption of tetracycline and doxycycline by one-step synthesized iron loaded sludge biochar. Chemosphere 236:124254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.224
Wei M, Marrakchi F, Yuan C, Cheng X, Jiang D, Zafar FF, Fu Y, Wang S (2022) Adsorption modeling, thermodynamics, and DFT simulation of tetracycline onto mesoporous and high-surface-area NaOH-activated macroalgae carbon. J Hazard Mater 425:127887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127887
Wen J, Fu W, Ding S, Zhang Y, Wang W (2022) Pyrogallic acid modified nanoscale zero-valent iron efficiently removed Cr(VI) by improving adsorption and electron selectivity. Chem Eng J 443:136510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136510
Wu J, Hou B, Wang X, Liu Z, Wang Z, Liu B, Li S, Gao H, Zhu X, Mao Y (2022) Preparation of N, S-codoped magnetic bagasse biochar and adsorption characteristics for tetracycline. RSC Adv 12:11786–11795. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra08404f
Wu T, Xue Q, Liu F, Zhang J, Zhou C, Cao J, Chen H (2019) Mechanistic insight into interactions between tetracycline and two iron oxide minerals with different crystal structures. Chem Eng J 366:577–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.128
Xia Y, Luo H, Li D, Chen Z, Yang S, Liu Z, Yang T, Gai C (2020) Efficient immobilization of toxic heavy metals in multi-contaminated agricultural soils by amino-functionalized hydrochar: Performance, plant responses and immobilization mechanisms. Environ Pollut 261:114217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114217
Xiang W, Zhang X, Luo J, Li Y, Guo T, Gao B (2022) Performance of lignin impregnated biochar on tetracycline hydrochloride adsorption: Governing factors and mechanisms. Environ Res 215:114339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114339
Xu D, Gao Y, Lin Z, Gao W, Zhang H, Karnowo K, Hu X, Sun H, Syed-Hassan SSA, Zhang S (2019) Application of Biochar Derived From Pyrolysis of Waste Fiberboard on Tetracycline Adsorption in Aqueous Solution. Front Chem 7:943. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00943
Xu J, Zhang Y, Li B, Fan S, Xu H, Guan DX (2022) Improved adsorption properties of tetracycline on KOH/KMnO4 modified biochar derived from wheat straw. Chemosphere 296:133981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133981
Xue Y, Guo Y, Zhang X, Kamali MM, Aminabhavi T, Appels L, Dewil R (2022) Efficient adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin and carbamazepine using modified pinewood biochar – A kinetic, mechanistic study. Chem Eng J 450:137896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137896
Yang Q, Wu P, Liu J, Rehman S, Ahmed Z, Ruan B, Zhu N (2020) Batch interaction of emerging tetracycline contaminant with novel phosphoric acid activated corn straw porous carbon: Adsorption rate and nature of mechanism. Environ Res 181:108899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108899
Yang S, Liu Y, Shen C, Li F, Yang B, Huang M, Yang M, Wang Z, Sand W (2020) Rapid decontamination of tetracycline hydrolysis product using electrochemical CNT filter: Mechanism, impacting factors and pathways. Chemosphere 244:125525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125525
Yu H, Gu L, Chen L, Wen H, Zhang D, Tao H (2020) Activation of grapefruit derived biochar by its peel extracts and its performance for tetracycline removal. Bioresource Technol 316:123971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123971
Yuan M, Li C, Zhang B, Wang J, Zhu J, Ji J, Ma Y (2021) A mild and one-pot method to activate lignin-derived biomass by using boric acid for aqueous tetracycline antibiotics removal in water. Chemosphere 280:130877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130877
Zeng S, Choi YK, Kan E (2021) Iron-activated bermudagrass-derived biochar for adsorption of aqueous sulfamethoxazole: Effects of iron impregnation ratio on biochar properties, adsorption, and regeneration. Sci Total Environ 750:141691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141691
Zeng S, Kan E (2022) Sustainable use of Ca(OH)2 modified biochar for phosphorus recovery and tetracycline removal from water. Sci Total Environ 839:156159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156159
Zhang B, Liu J, Zhao RS, Xian Q (2021) NDMA adsorption and degradation by a new-type of Ag-MONT material carrying nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 268:129271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129271
Zhang G, Li L, Zhou G, Lin Z, Wang J, Wang G, Ling F, Liu T (2022) Recyclable aminophenylboronic acid modified bacterial cellulose microspheres for tetracycline removal: Kinetic, equilibrium and adsorption performance studies for hoggery sewer. Environ Pollut 307:119544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119544
Zhang H, Song X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhao H, Hu J, Zhao J (2022) Performance and mechanism of sycamore flock based biochar in removing oxytetracycline hydrochloride. Bioresource Technol 350:126884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126884
Zhang L, Dong Y, Liu J, Liu W, Lu Y, Lin H (2022) Promotion of higher synthesis temperature for higher-efficient removal of antimonite and antimonate in aqueous solution by iron-loaded porous biochar. Bioresource Technol 363:127889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127889
Zhao Z, Nie T, Zhou W (2019) Enhanced biochar stabilities and adsorption properties for tetracycline by synthesizing silica-composited biochar. Environ Pollut 254:113015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113015
Zheng Z, Zhao B, Guo Y, Guo Y, Pak T, Li G (2021) Preparation of mesoporous batatas biochar via soft-template method for high efficiency removal of tetracycline. Sci Total Environ 787:147397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147397
Zhou Y, Liu X, Xiang Y, Wang P, Zhang J, Zhang F, Wei J, Luo L, Lei M, Tang L (2017) Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: Adsorption mechanism and modelling. Bioresource Technol 245:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.178
Zhu J, Ma Y, Chen X, Tang J, Yang L, Zhang Z (2022) One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of MoS2 modified sludge biochar for efficient removal of tetracycline from water. J Water Process Eng 49:103089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103089
Funding
This work was supported by Guangxi Key R&D Program Project (Guike AB21220006), National Natural Science Foundation of China (52160016), Guangxi Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Control Theory and Technology Fund Project (Guikeneng1801Z009), the project of high level innovation team and outstanding scholar in Guangxi colleges and universities (002401013001), and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Control Theory and Technology for Science and Education Combined with Science and Technology Innovation Base.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiaojing Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft. Xinfeng Cao: Validation, Visualization. Tiantian Yue: Validation, Visualization. Fengzhi Zhang: Validation, Visualization. Shaoyuan Bai: Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration. Liheng Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
None of the authors has any objection to participating in the study.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed with the content all gave explicit consent to submit and they obtained consent from the responsible authorities at the institute/organization where the work has been carried out before the work is submitted.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Cao, X., Yue, T. et al. Removal of tetracycline in aqueous solution by iron-loaded biochar derived from polymeric ferric sulfate and bagasse. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 87185–87198 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28685-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28685-5